Xenon Flasher

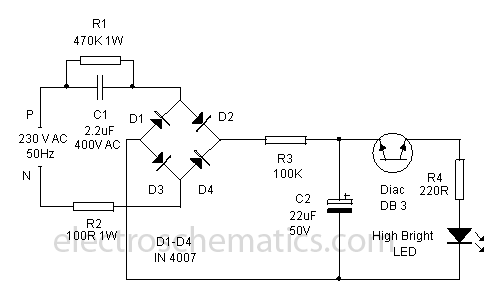
This circuit utilizes a voltage-doubler power supply to charge a 60 µF capacitor, which is subsequently discharged through a Xenon lamp. The SIDAC device, manufactured by Motorola, is a two-terminal component that triggers at a predetermined voltage level. The components R4, R5, and C4 are responsible for setting the flash rate of the circuit.
The voltage doubler circuit is designed to convert an AC input voltage into a higher DC output voltage, effectively doubling the voltage available for charging the capacitor. The 60 µF capacitor serves as the energy storage element, accumulating charge until it reaches a voltage sufficient to trigger the SIDAC device. The SIDAC, once activated, allows current to flow through the Xenon lamp, producing a brief and intense flash of light.
The flash rate of the circuit is controlled by the resistors R4 and R5, along with the capacitor C4. These components form an RC timing circuit that dictates how long the capacitor takes to charge and subsequently discharge. Adjusting the values of R4 and R5 will alter the time constant of the circuit, thereby changing the frequency of the flashes emitted by the Xenon lamp.
In practical applications, this circuit can be employed in photographic flash units, strobe lights, or other lighting systems requiring high-intensity bursts of light. The choice of a Xenon lamp is crucial due to its ability to produce a bright flash with a very short duration, making it ideal for applications where quick illumination is necessary. The SIDAC device ensures reliable triggering at a specified voltage, contributing to the overall efficiency and performance of the circuit. Using a voltage-doubler supply, this circuit charges a 60-/aF capacitor and discharges it through a Xenon lamp. The SIDAC dev ice is manufactured by Motorola. It is a two-terminal device that breaks over at a specified voltage. R4, R5, and C4 determine the flash rate. 🔗 External reference
The voltage doubler circuit is designed to convert an AC input voltage into a higher DC output voltage, effectively doubling the voltage available for charging the capacitor. The 60 µF capacitor serves as the energy storage element, accumulating charge until it reaches a voltage sufficient to trigger the SIDAC device. The SIDAC, once activated, allows current to flow through the Xenon lamp, producing a brief and intense flash of light.
The flash rate of the circuit is controlled by the resistors R4 and R5, along with the capacitor C4. These components form an RC timing circuit that dictates how long the capacitor takes to charge and subsequently discharge. Adjusting the values of R4 and R5 will alter the time constant of the circuit, thereby changing the frequency of the flashes emitted by the Xenon lamp.
In practical applications, this circuit can be employed in photographic flash units, strobe lights, or other lighting systems requiring high-intensity bursts of light. The choice of a Xenon lamp is crucial due to its ability to produce a bright flash with a very short duration, making it ideal for applications where quick illumination is necessary. The SIDAC device ensures reliable triggering at a specified voltage, contributing to the overall efficiency and performance of the circuit. Using a voltage-doubler supply, this circuit charges a 60-/aF capacitor and discharges it through a Xenon lamp. The SIDAC dev ice is manufactured by Motorola. It is a two-terminal device that breaks over at a specified voltage. R4, R5, and C4 determine the flash rate. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713