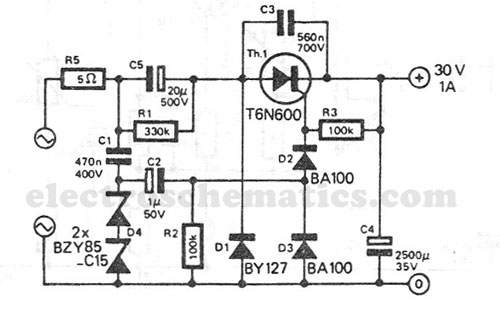
12V Relay on 6V power supply
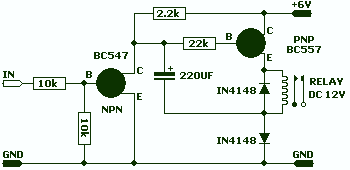
This circuit allows a 12v relay to operate on a 6v or 9v supply. Most 12v relays need about 12v to "pull-in" but will "hold" on about 6v. The 220u charges via the 2k2 and bottom diode. When an input above 1.5v is applied to the input of the circuit, both transistors are turned ON and the 5v across the electrolytic causes the negative end of the electro to go below the 0v rail by about 4.5v and this puts about 10v across the relay.
The circuit in question is designed to enable a 12V relay to function effectively with lower voltage supplies, specifically 6V or 9V. This is particularly advantageous in applications where the available power supply is less than the nominal voltage required by the relay for its operation.
The core components include a 220µF electrolytic capacitor, a 2.2kΩ resistor, and two transistors configured as a switching mechanism. The operation begins when a control voltage exceeding 1.5V is applied to the input. This voltage triggers both transistors to enter the ON state, allowing current to flow through the circuit.
The 220µF capacitor charges through the 2.2kΩ resistor and the lower diode, which is likely a standard rectifier diode. The charging process ensures that the capacitor accumulates sufficient charge, producing a voltage across its terminals. When the transistors are activated, the voltage across the capacitor is approximately 5V. This voltage is significant as it causes the negative terminal of the electrolytic capacitor to dip below the ground reference (0V) by about 4.5V.
As a result, the relay receives an effective voltage of around 10V across its coil. This voltage is adequate for the relay to pull in and maintain its state, even though it was initially powered by a lower voltage supply. The ability of the relay to hold its position at a lower voltage (6V) is leveraged here, ensuring reliable operation without the need for a higher voltage power source.
This circuit can be utilized in various applications, including automotive systems, low-voltage control systems, and other scenarios where efficient relay operation at reduced voltages is necessary. The design emphasizes simplicity and effectiveness, making it an ideal solution for specific control tasks.This circuit allows a 12v relay to operate on a 6v or 9v supply. Most 12v relays need about 12v to "pull-in" but will "hold" on about 6v. The 220u charges via the 2k2 and bottom diode. When an input above 1.5v is applied to the input of the circuit, both transistors are turned ON and the 5v across the electrolytic causes the negative end of the electro to go below the 0v rail by about 4.5v and this puts about 10v across the relay. 🔗 External reference
The circuit in question is designed to enable a 12V relay to function effectively with lower voltage supplies, specifically 6V or 9V. This is particularly advantageous in applications where the available power supply is less than the nominal voltage required by the relay for its operation.
The core components include a 220µF electrolytic capacitor, a 2.2kΩ resistor, and two transistors configured as a switching mechanism. The operation begins when a control voltage exceeding 1.5V is applied to the input. This voltage triggers both transistors to enter the ON state, allowing current to flow through the circuit.
The 220µF capacitor charges through the 2.2kΩ resistor and the lower diode, which is likely a standard rectifier diode. The charging process ensures that the capacitor accumulates sufficient charge, producing a voltage across its terminals. When the transistors are activated, the voltage across the capacitor is approximately 5V. This voltage is significant as it causes the negative terminal of the electrolytic capacitor to dip below the ground reference (0V) by about 4.5V.
As a result, the relay receives an effective voltage of around 10V across its coil. This voltage is adequate for the relay to pull in and maintain its state, even though it was initially powered by a lower voltage supply. The ability of the relay to hold its position at a lower voltage (6V) is leveraged here, ensuring reliable operation without the need for a higher voltage power source.
This circuit can be utilized in various applications, including automotive systems, low-voltage control systems, and other scenarios where efficient relay operation at reduced voltages is necessary. The design emphasizes simplicity and effectiveness, making it an ideal solution for specific control tasks.This circuit allows a 12v relay to operate on a 6v or 9v supply. Most 12v relays need about 12v to "pull-in" but will "hold" on about 6v. The 220u charges via the 2k2 and bottom diode. When an input above 1.5v is applied to the input of the circuit, both transistors are turned ON and the 5v across the electrolytic causes the negative end of the electro to go below the 0v rail by about 4.5v and this puts about 10v across the relay. 🔗 External reference