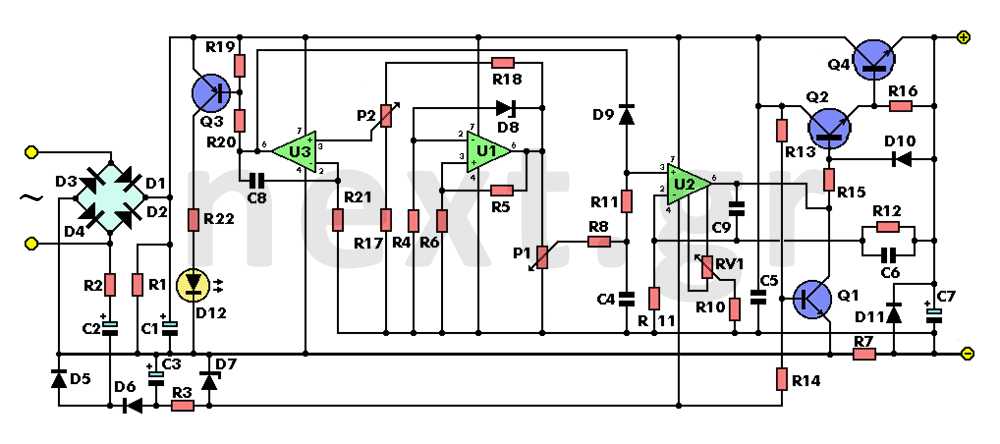
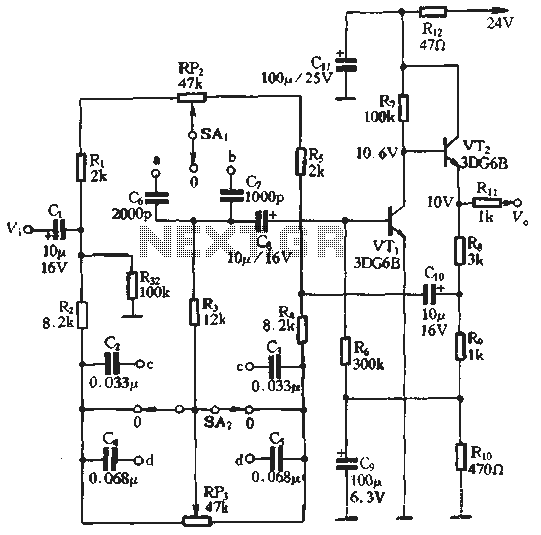
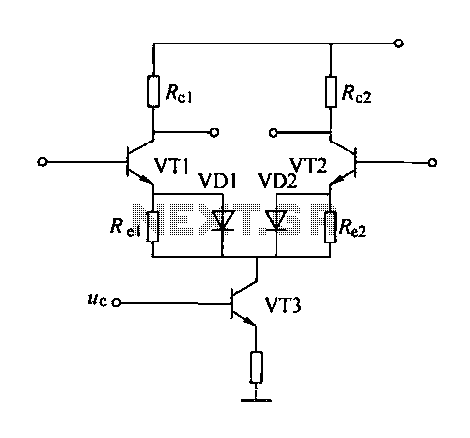
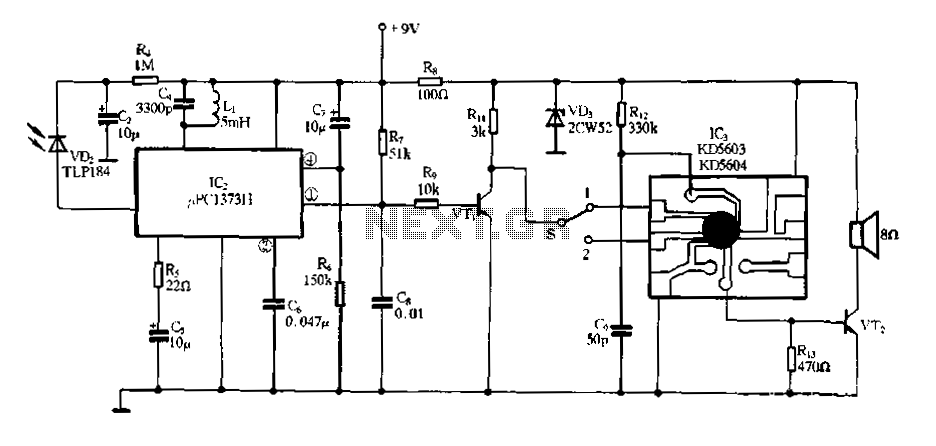
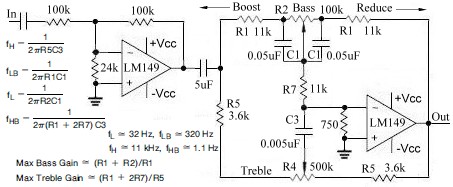
877 ~ 924MHz RF2152 power amplifier the circuit diagram
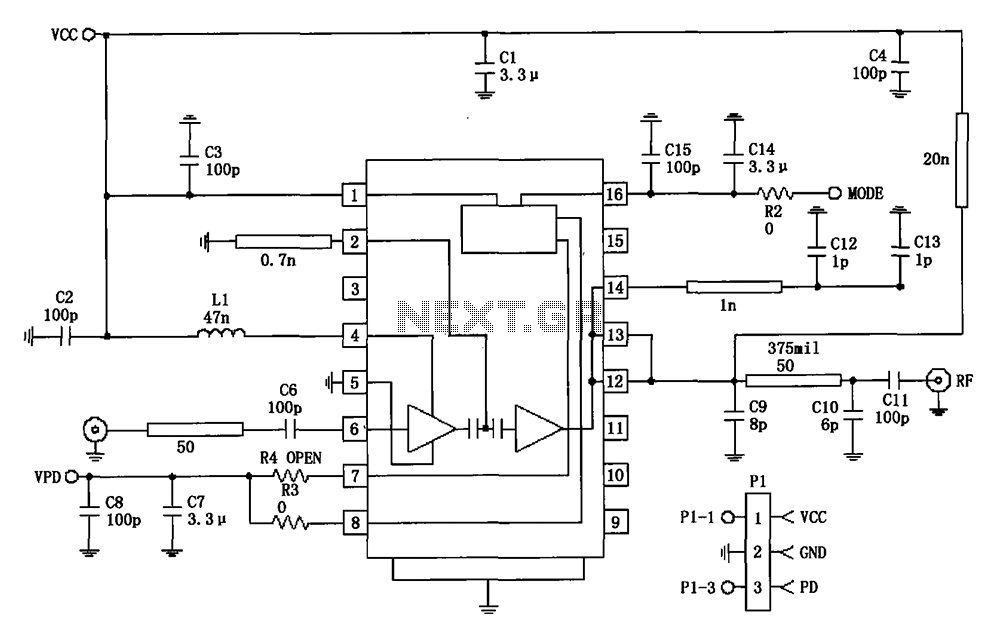
877 ~ 924MHz RF2152 power amplifier circuit diagram.
The RF2152 is a high-performance power amplifier designed for applications in the 877 to 924 MHz frequency range. This amplifier is typically used in various RF communication systems, including wireless networks and mobile communication devices.
The circuit diagram of the RF2152 power amplifier includes several key components to ensure efficient operation and signal integrity. The amplifier is typically powered by a suitable DC voltage source, which is connected to the Vcc pin. The device is designed to provide a significant gain while maintaining linearity, which is crucial for minimizing distortion in the transmitted signal.
Input matching networks are often employed at the input stage to optimize the impedance seen by the RF signal source, enhancing the power transfer to the amplifier. These matching networks may consist of inductors and capacitors configured to resonate at the desired frequency.
The output stage of the RF2152 includes a load matching network to ensure that the output impedance is compatible with the subsequent stage or antenna. This network is designed to maximize power transfer and minimize reflections, which can degrade performance.
Thermal management is also a critical aspect of the design, as power amplifiers generate heat during operation. Heat sinks or thermal pads may be utilized to dissipate heat effectively, ensuring the device operates within its specified temperature range.
Overall, the RF2152 power amplifier circuit is designed to provide robust performance in the specified frequency range, with careful consideration given to input and output matching, thermal management, and linearity to ensure high-quality signal amplification.877 ~ 924MHz RF2152 power amplifier constituting the circuit diagram:
The RF2152 is a high-performance power amplifier designed for applications in the 877 to 924 MHz frequency range. This amplifier is typically used in various RF communication systems, including wireless networks and mobile communication devices.
The circuit diagram of the RF2152 power amplifier includes several key components to ensure efficient operation and signal integrity. The amplifier is typically powered by a suitable DC voltage source, which is connected to the Vcc pin. The device is designed to provide a significant gain while maintaining linearity, which is crucial for minimizing distortion in the transmitted signal.
Input matching networks are often employed at the input stage to optimize the impedance seen by the RF signal source, enhancing the power transfer to the amplifier. These matching networks may consist of inductors and capacitors configured to resonate at the desired frequency.
The output stage of the RF2152 includes a load matching network to ensure that the output impedance is compatible with the subsequent stage or antenna. This network is designed to maximize power transfer and minimize reflections, which can degrade performance.
Thermal management is also a critical aspect of the design, as power amplifiers generate heat during operation. Heat sinks or thermal pads may be utilized to dissipate heat effectively, ensuring the device operates within its specified temperature range.
Overall, the RF2152 power amplifier circuit is designed to provide robust performance in the specified frequency range, with careful consideration given to input and output matching, thermal management, and linearity to ensure high-quality signal amplification.877 ~ 924MHz RF2152 power amplifier constituting the circuit diagram: