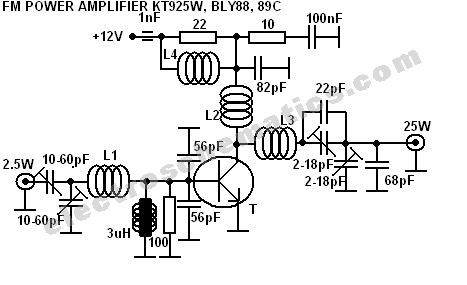
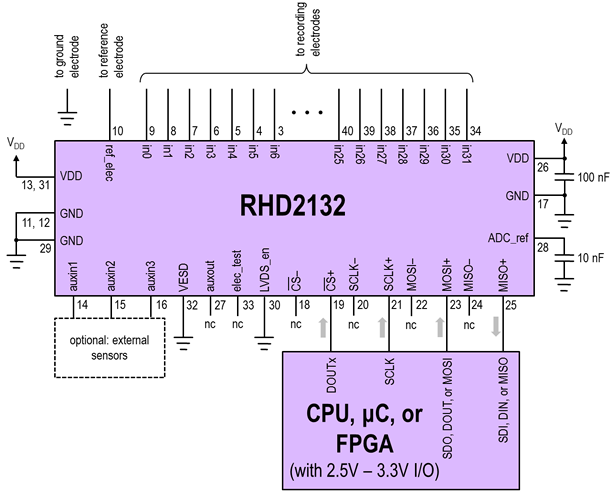
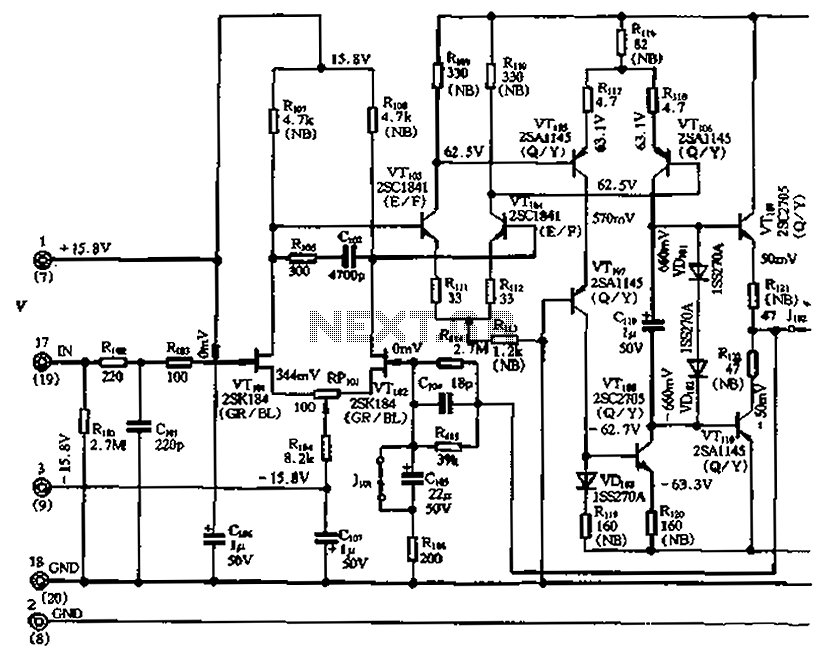
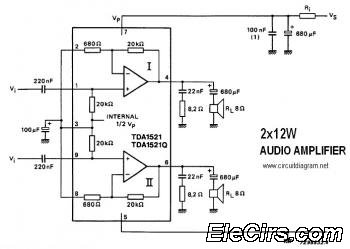
Accelerometer Signal Amplifier
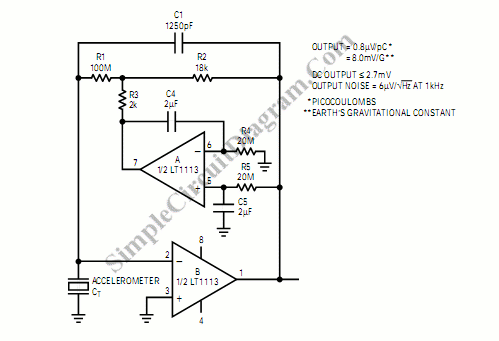
An inverting mode amplifier is required for precision accelerometers due to their typical charge output characteristics. This amplifier is utilized to convert charge into voltage.
An inverting mode amplifier is a critical component in applications involving precision accelerometers, which often produce a charge output as a response to acceleration. The primary function of the inverting amplifier in this context is to convert the charge generated by the accelerometer into a corresponding voltage signal that can be easily processed and analyzed.
The inverting amplifier configuration typically consists of an operational amplifier (op-amp), a feedback resistor (Rf), and an input resistor (Rin). The input charge from the accelerometer is converted to a voltage by the relationship defined by the equation Vout = - (Rf/Rin) * Vin, where Vin represents the input voltage derived from the charge. The negative sign indicates that the output signal is inverted relative to the input signal.
To ensure precision in the conversion process, it is essential to select appropriate values for Rin and Rf. The gain of the amplifier can be adjusted by changing the ratio of these resistors, allowing for flexibility in application based on the specific characteristics of the accelerometer being used.
Furthermore, the design must account for factors such as bandwidth, noise performance, and stability, which are critical for maintaining the integrity of the signal in high-precision applications. The power supply for the op-amp should also be considered, ensuring that it meets the requirements for the desired output voltage range.
In summary, the inverting mode amplifier serves as an essential interface between precision accelerometers and the electronic systems that utilize their output, facilitating the conversion of charge to a usable voltage signal while maintaining accuracy and reliability in measurement.Inverting mode amplifier is needed by precision accelerometers because that usually charge output device. This amplifier is used to convert charge into voltage.. 🔗 External reference
An inverting mode amplifier is a critical component in applications involving precision accelerometers, which often produce a charge output as a response to acceleration. The primary function of the inverting amplifier in this context is to convert the charge generated by the accelerometer into a corresponding voltage signal that can be easily processed and analyzed.
The inverting amplifier configuration typically consists of an operational amplifier (op-amp), a feedback resistor (Rf), and an input resistor (Rin). The input charge from the accelerometer is converted to a voltage by the relationship defined by the equation Vout = - (Rf/Rin) * Vin, where Vin represents the input voltage derived from the charge. The negative sign indicates that the output signal is inverted relative to the input signal.
To ensure precision in the conversion process, it is essential to select appropriate values for Rin and Rf. The gain of the amplifier can be adjusted by changing the ratio of these resistors, allowing for flexibility in application based on the specific characteristics of the accelerometer being used.
Furthermore, the design must account for factors such as bandwidth, noise performance, and stability, which are critical for maintaining the integrity of the signal in high-precision applications. The power supply for the op-amp should also be considered, ensuring that it meets the requirements for the desired output voltage range.
In summary, the inverting mode amplifier serves as an essential interface between precision accelerometers and the electronic systems that utilize their output, facilitating the conversion of charge to a usable voltage signal while maintaining accuracy and reliability in measurement.Inverting mode amplifier is needed by precision accelerometers because that usually charge output device. This amplifier is used to convert charge into voltage.. 🔗 External reference