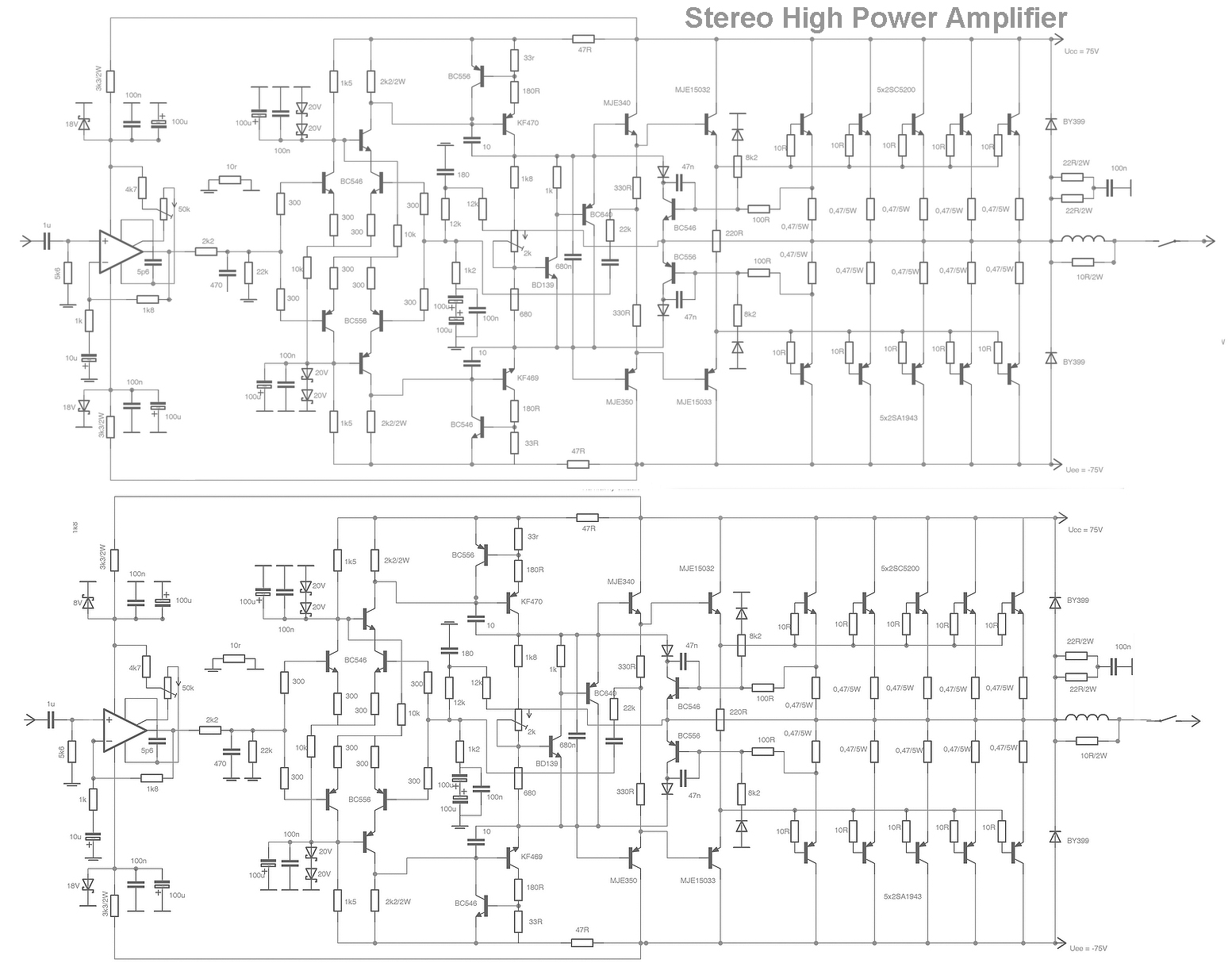
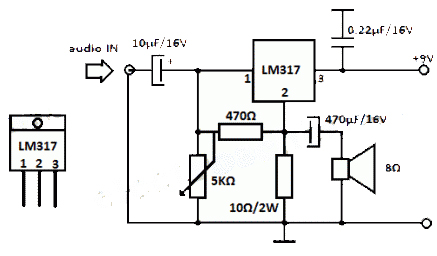
Audio-amplifier
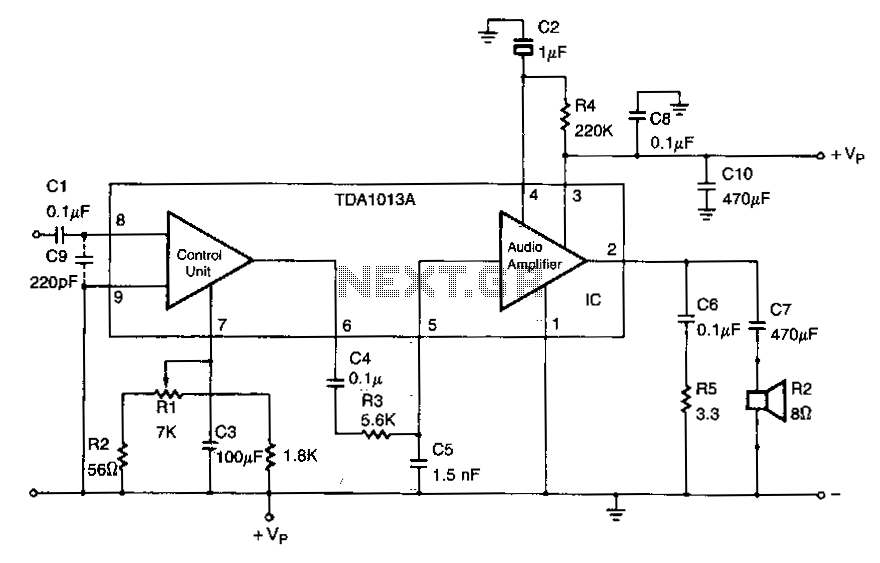
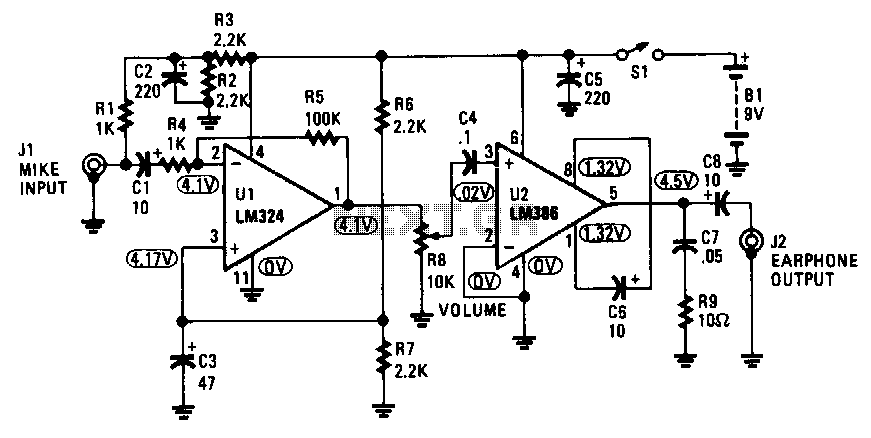
C9 is necessary to filter out RF input interferences. R3 in combination with C5 is used to limit the AF frequency bandwidth. The 470-f.IF power supply decoupling capacitor is C10.
C9 serves a critical role in the circuit by acting as a filter to eliminate radio frequency (RF) interferences that could disrupt the operation of sensitive components. This capacitor is typically placed in parallel with the RF input to ground, effectively shunting high-frequency noise away from the signal path. The choice of capacitance value for C9 is crucial, as it determines the cutoff frequency for the filtering action. A larger capacitance value will provide better attenuation of higher frequencies, while a smaller value may allow some interference to pass through.
R3, in conjunction with C5, forms a low-pass filter that limits the audio frequency (AF) bandwidth. This configuration is essential for ensuring that only the desired frequency range is amplified or processed, thereby enhancing the overall performance of the circuit. The values of R3 and C5 must be selected carefully to establish the desired cutoff frequency, which will define the bandwidth of the audio signal. By adjusting these components, the circuit designer can optimize the audio quality and prevent unwanted high-frequency signals from being amplified.
C10, the 470 µF power supply decoupling capacitor, is used to stabilize the power supply voltage by filtering out low-frequency noise and transients. It is placed close to the power supply pins of active components to provide a reservoir of charge that can be quickly accessed during sudden changes in current demand. This decoupling action helps maintain a steady voltage level, which is critical for the reliable operation of the circuit, especially in environments with fluctuating load conditions. The capacitance value of 470 µF is typically chosen to provide adequate filtering while balancing size and cost considerations. Proper placement and connection of C10 are vital to ensure its effectiveness in reducing power supply noise and improving overall circuit performance.C9 is necessary to filter-out rf input interferences. R3 in combination with C5 is used to limit the af frequency bandwidth. The 470-f.IF power supply decoupling capacitor is ClO.
C9 serves a critical role in the circuit by acting as a filter to eliminate radio frequency (RF) interferences that could disrupt the operation of sensitive components. This capacitor is typically placed in parallel with the RF input to ground, effectively shunting high-frequency noise away from the signal path. The choice of capacitance value for C9 is crucial, as it determines the cutoff frequency for the filtering action. A larger capacitance value will provide better attenuation of higher frequencies, while a smaller value may allow some interference to pass through.
R3, in conjunction with C5, forms a low-pass filter that limits the audio frequency (AF) bandwidth. This configuration is essential for ensuring that only the desired frequency range is amplified or processed, thereby enhancing the overall performance of the circuit. The values of R3 and C5 must be selected carefully to establish the desired cutoff frequency, which will define the bandwidth of the audio signal. By adjusting these components, the circuit designer can optimize the audio quality and prevent unwanted high-frequency signals from being amplified.
C10, the 470 µF power supply decoupling capacitor, is used to stabilize the power supply voltage by filtering out low-frequency noise and transients. It is placed close to the power supply pins of active components to provide a reservoir of charge that can be quickly accessed during sudden changes in current demand. This decoupling action helps maintain a steady voltage level, which is critical for the reliable operation of the circuit, especially in environments with fluctuating load conditions. The capacitance value of 470 µF is typically chosen to provide adequate filtering while balancing size and cost considerations. Proper placement and connection of C10 are vital to ensure its effectiveness in reducing power supply noise and improving overall circuit performance.C9 is necessary to filter-out rf input interferences. R3 in combination with C5 is used to limit the af frequency bandwidth. The 470-f.IF power supply decoupling capacitor is ClO.