
Battery-splitter
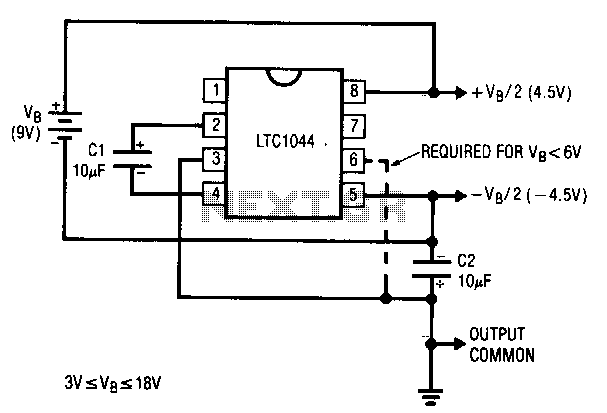
A common requirement in many systems is to obtain both positive and negative supplies from a single battery. For applications with small current needs, the circuit illustrated provides a straightforward solution. It generates symmetrical output voltages of ±, each equal to one-half of the input voltage. The output voltages are referenced to pin 3, which serves as the output common. If the input voltage between pin 8 and pin 5 exceeds 6 V, pin 6 should also be connected to pin 3, as indicated by the dashed line. For higher current demands, an LT1010 buffer is utilized. The splitter circuit can source or sink up to ±150 mA while maintaining a quiescent current of only 5 mA. The output capacitor, C2, can be sized as needed to absorb current transients. An input capacitor is also employed on the buffer to prevent high-frequency instability that may arise from high source impedance.
The described circuit is a dual-output voltage splitter that efficiently derives both positive and negative voltages from a single DC battery supply. The circuit configuration typically employs an operational amplifier or a dedicated voltage splitter IC, such as the LT1010, to achieve the desired output characteristics.
The circuit's fundamental operation is based on the principle of virtual ground, where the output common at pin 3 serves as a reference point for the generated output voltages. By connecting the input voltage across pins 8 and 5, the circuit divides the input voltage in half, creating symmetrical outputs. The output voltages are crucial in applications requiring dual polarity for operational amplifiers, sensors, or other electronic components.
The additional connection from pin 6 to pin 3, activated when the input voltage exceeds 6 V, ensures stability and proper operation under varying load conditions. This feature is particularly important in applications where the input voltage may fluctuate, as it helps maintain consistent output levels.
The LT1010 buffer enhances the circuit's performance by isolating the output from the input, allowing for higher current sourcing and sinking capabilities. This buffer is essential when the load demands exceed the limits of the primary circuit, ensuring that the output remains stable without affecting the input voltage.
The output capacitor, C2, plays a significant role in transient response. It acts as a reservoir that can quickly provide or absorb charge during sudden changes in load, thereby preventing voltage dips or spikes that could affect circuit performance. The size of C2 can be adjusted based on the expected load transients, ensuring robust operation across a range of conditions.
Additionally, an input capacitor is included to mitigate high-frequency instability. This capacitor helps filter out noise and prevents oscillations that could arise from the high source impedance associated with the input. Overall, this voltage splitter circuit is a versatile solution for generating dual power supplies from a single battery, catering to various electronic applications where dual polarity is required.A common need in many systems is to obtain positive and negative supplies from a single battery. Where current requirements are small, the circuit shown is a simple solution. It provides symmetrical ± output voltages, both equal to one half the input voltage. The output voltages are referenced to pin 3, output common. If the input voltage between pin 8 and pin 5 exceeds 6 V, pin 6 should also be connected to pin 3, as shown by the dashed line. Higher current requirements are served by an LT1010 buffer. The splitter circuit can source or sink up to ±150 mA with only 5 mA quiescent current. The output capacitor, C2, can be made as large as necessary to absorb current transients. An input capacitor is also used on the buffer to avoid high frequency instability that can be caused by high source impedance.
The described circuit is a dual-output voltage splitter that efficiently derives both positive and negative voltages from a single DC battery supply. The circuit configuration typically employs an operational amplifier or a dedicated voltage splitter IC, such as the LT1010, to achieve the desired output characteristics.
The circuit's fundamental operation is based on the principle of virtual ground, where the output common at pin 3 serves as a reference point for the generated output voltages. By connecting the input voltage across pins 8 and 5, the circuit divides the input voltage in half, creating symmetrical outputs. The output voltages are crucial in applications requiring dual polarity for operational amplifiers, sensors, or other electronic components.
The additional connection from pin 6 to pin 3, activated when the input voltage exceeds 6 V, ensures stability and proper operation under varying load conditions. This feature is particularly important in applications where the input voltage may fluctuate, as it helps maintain consistent output levels.
The LT1010 buffer enhances the circuit's performance by isolating the output from the input, allowing for higher current sourcing and sinking capabilities. This buffer is essential when the load demands exceed the limits of the primary circuit, ensuring that the output remains stable without affecting the input voltage.
The output capacitor, C2, plays a significant role in transient response. It acts as a reservoir that can quickly provide or absorb charge during sudden changes in load, thereby preventing voltage dips or spikes that could affect circuit performance. The size of C2 can be adjusted based on the expected load transients, ensuring robust operation across a range of conditions.
Additionally, an input capacitor is included to mitigate high-frequency instability. This capacitor helps filter out noise and prevents oscillations that could arise from the high source impedance associated with the input. Overall, this voltage splitter circuit is a versatile solution for generating dual power supplies from a single battery, catering to various electronic applications where dual polarity is required.A common need in many systems is to obtain positive and negative supplies from a single battery. Where current requirements are small, the circuit shown is a simple solution. It provides symmetrical ± output voltages, both equal to one half the input voltage. The output voltages are referenced to pin 3, output common. If the input voltage between pin 8 and pin 5 exceeds 6 V, pin 6 should also be connected to pin 3, as shown by the dashed line. Higher current requirements are served by an LT1010 buffer. The splitter circuit can source or sink up to ±150 mA with only 5 mA quiescent current. The output capacitor, C2, can be made as large as necessary to absorb current transients. An input capacitor is also used on the buffer to avoid high frequency instability that can be caused by high source impedance.