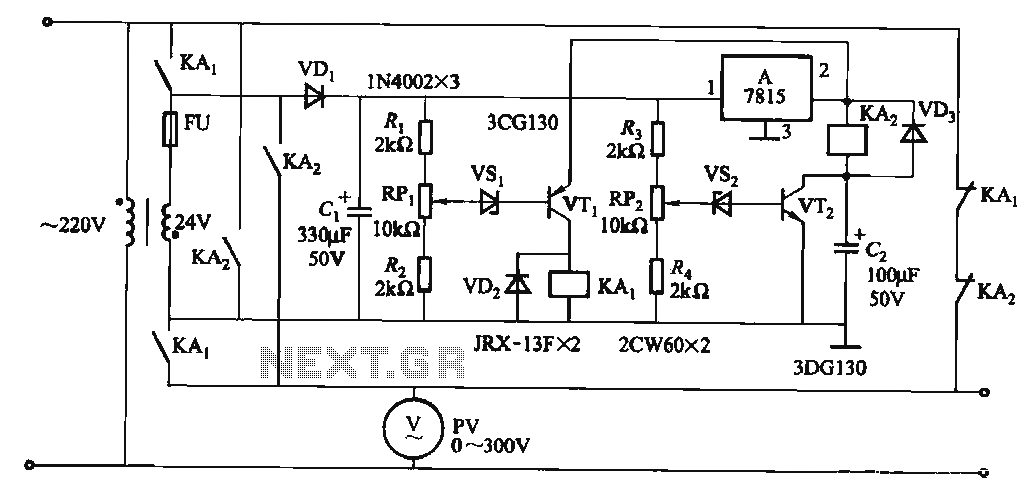
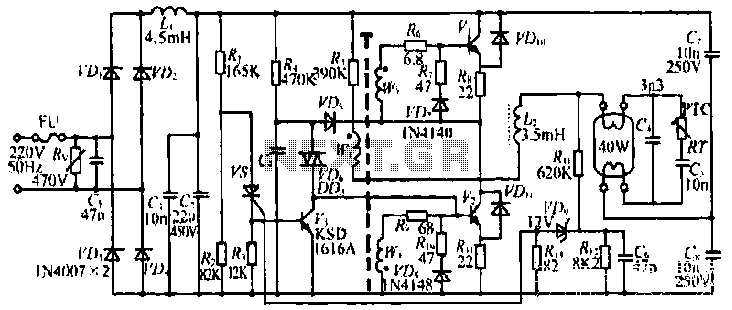
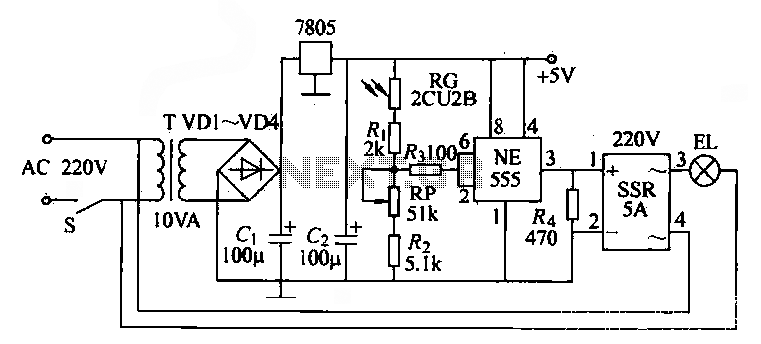
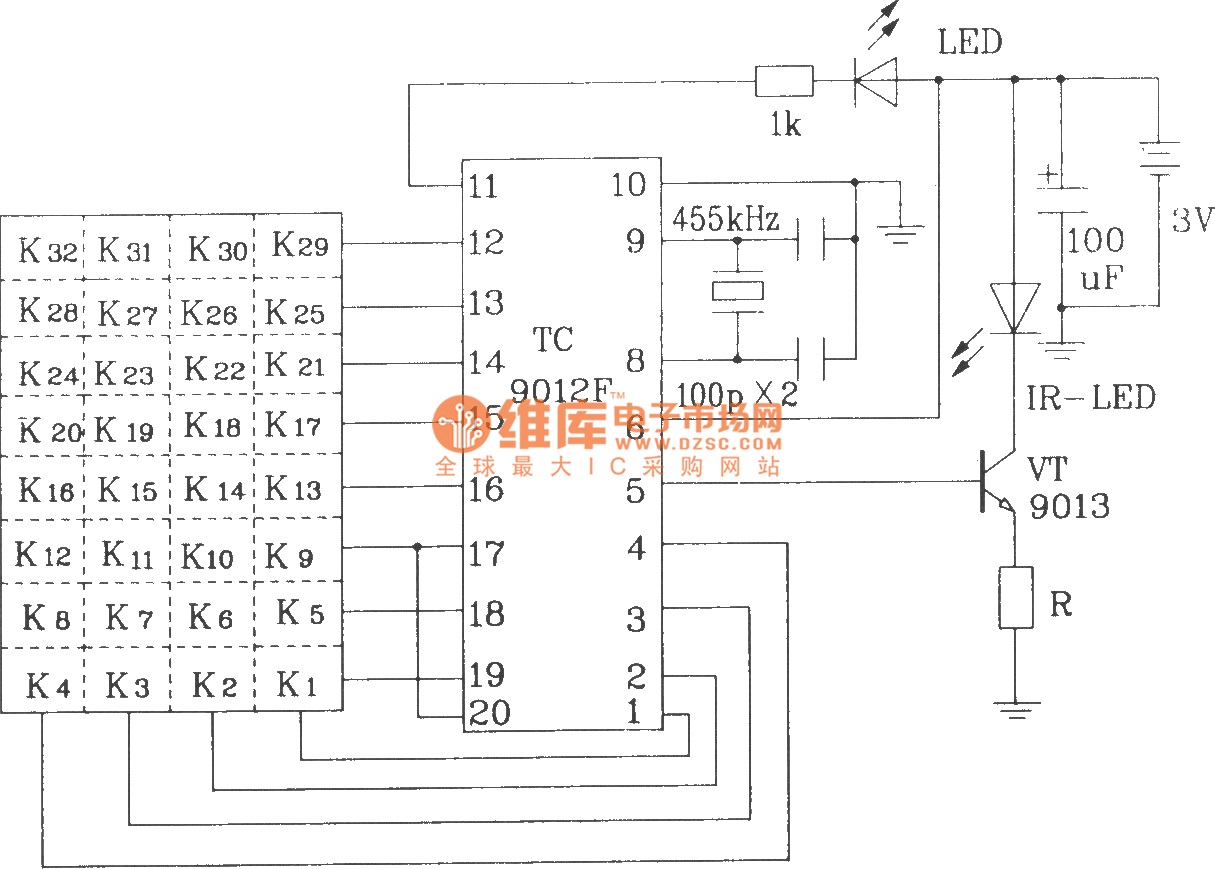
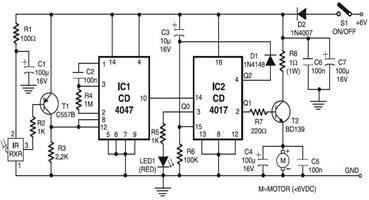
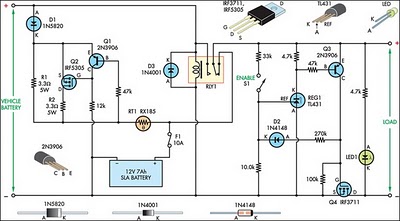
Booster circuit

This circuit illustrates a simple boost converter, which is powered by an oscillating signal generated by the NE555 timer. The signal is amplified through a VT transistor to drive a booster transformer. This step-up transformer increases the oscillating signal, which is then rectified to obtain a high-voltage DC output.
The described circuit operates on the principle of boosting a low-voltage signal to a higher voltage level using a combination of an NE555 timer, a transistor, and a transformer. The NE555 timer is configured in astable mode to generate a continuous square wave output. This oscillating signal is crucial for the operation of the subsequent components.
The VT transistor serves as a switch that modulates the current flowing through the primary winding of the booster transformer. When the NE555 timer outputs a high signal, the transistor turns on, allowing current to flow through the transformer. This current induces a magnetic field in the transformer core, which is essential for transferring energy to the secondary winding.
The transformer is designed to step up the voltage, meaning that the output voltage across the secondary winding will be significantly higher than the input voltage applied to the primary winding. The turns ratio of the transformer determines the magnitude of this voltage increase.
After the signal has been stepped up by the transformer, it is still in an AC form. A rectifier circuit, typically composed of diodes, is used to convert the AC voltage into a pulsating DC voltage. Depending on the design, additional filtering components, such as capacitors, can be included to smooth the rectified output, resulting in a more stable DC voltage.
This simple boost circuit is often utilized in applications requiring higher voltage levels from a lower voltage source, such as in battery-powered devices or in scenarios where compact, efficient power conversion is necessary. The design's effectiveness relies on the careful selection of components, including the NE555 timer configuration, the specifications of the transistor, and the characteristics of the transformer used.It illustrates a simple boost circuit, which is supplied by an oscillating signal generated NE555 via VT transistor to drive booster transformer , a step-up transformer to increase the oscillation signal is then rectified DC high voltage can be obtained.
The described circuit operates on the principle of boosting a low-voltage signal to a higher voltage level using a combination of an NE555 timer, a transistor, and a transformer. The NE555 timer is configured in astable mode to generate a continuous square wave output. This oscillating signal is crucial for the operation of the subsequent components.
The VT transistor serves as a switch that modulates the current flowing through the primary winding of the booster transformer. When the NE555 timer outputs a high signal, the transistor turns on, allowing current to flow through the transformer. This current induces a magnetic field in the transformer core, which is essential for transferring energy to the secondary winding.
The transformer is designed to step up the voltage, meaning that the output voltage across the secondary winding will be significantly higher than the input voltage applied to the primary winding. The turns ratio of the transformer determines the magnitude of this voltage increase.
After the signal has been stepped up by the transformer, it is still in an AC form. A rectifier circuit, typically composed of diodes, is used to convert the AC voltage into a pulsating DC voltage. Depending on the design, additional filtering components, such as capacitors, can be included to smooth the rectified output, resulting in a more stable DC voltage.
This simple boost circuit is often utilized in applications requiring higher voltage levels from a lower voltage source, such as in battery-powered devices or in scenarios where compact, efficient power conversion is necessary. The design's effectiveness relies on the careful selection of components, including the NE555 timer configuration, the specifications of the transistor, and the characteristics of the transformer used.It illustrates a simple boost circuit, which is supplied by an oscillating signal generated NE555 via VT transistor to drive booster transformer , a step-up transformer to increase the oscillation signal is then rectified DC high voltage can be obtained.