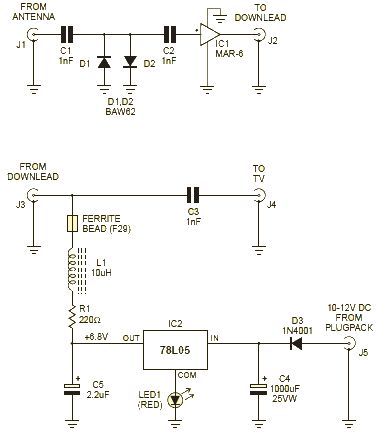
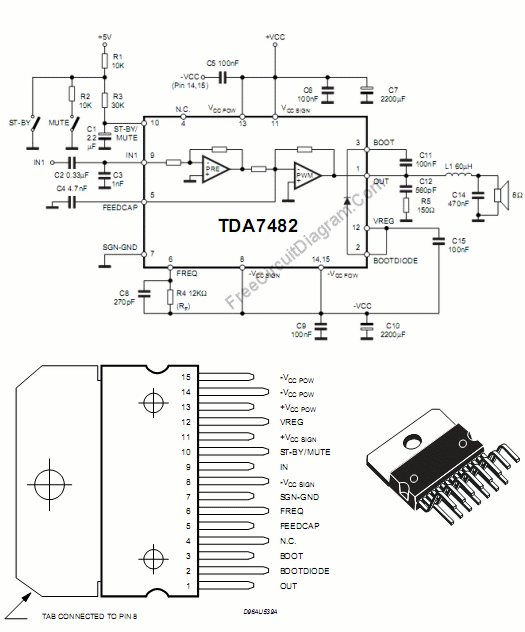
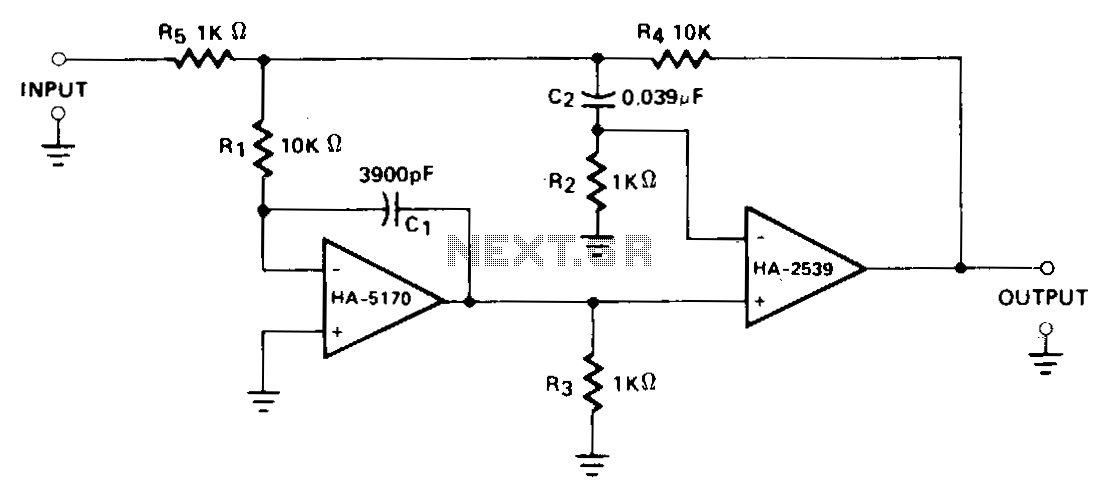
Broadcast band RF amplifier
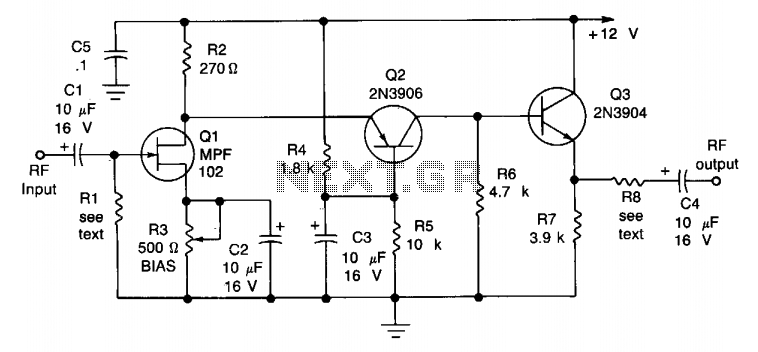
The circuit exhibits a frequency response that spans from 100 Hz to 3 MHz, with a gain of approximately 30 dB. The field-effect transistor Q1 is arranged in a common-source self-biased configuration, while an optional resistor R1 allows for the adjustment of input impedance to a desired level, typically set to 50 ohms. The signal is then directly coupled to Q2, which operates as a common-base circuit that effectively isolates the input and output stages, contributing to the amplifier's notable stability. Q3 serves as an emitter follower, providing a low output impedance of around 50 ohms. To achieve a higher output impedance, resistor R8 can be included, affecting the impedance according to the formula: R8 - Rout - 50. Alternatively, the output capacitor C4 can be connected directly to the emitter of Q3.
The circuit described employs a frequency response that is essential for various audio and RF applications, allowing it to effectively amplify signals within the specified range. The use of a field-effect transistor (FET) in the common-source configuration provides high input impedance and significant voltage gain, making it suitable for interfacing with high-impedance sources. The optional resistor R1 plays a critical role in defining the input impedance, which can be tailored to suit specific requirements, enhancing the circuit's versatility.
The direct coupling of the signal to Q2 ensures minimal signal loss and maintains the integrity of the amplified output. The common-base configuration of Q2 is particularly advantageous for achieving high-frequency performance, as it offers low input capacitance and improved bandwidth. This configuration allows for effective isolation between the input and output stages, which is vital for preventing feedback and ensuring stable operation across the frequency range.
Q3, functioning as an emitter follower, provides a low output impedance, which is crucial for driving subsequent stages or loads without significant signal degradation. The typical output impedance of around 50 ohms makes it compatible with standard RF and audio applications. The inclusion of resistor R8 allows for adjustments to the output impedance, enabling the circuit to interface with various loads or to match specific requirements in different applications.
In scenarios where higher output impedance is necessary, the formula R8 - Rout - 50 provides a straightforward method for calculating the required resistance. Alternatively, connecting output capacitor C4 directly to the emitter of Q3 allows for a simplified output stage, which may be preferable in certain designs where impedance matching is not critical. This flexibility in design choices enhances the overall functionality and adaptability of the circuit for diverse electronic applications.The circuit has a frequency response ranging from 100 Hz to 3 MHz; gain is about 30 dB. Field-effect transistor Ql is configured in the common-source self-biased mode; optional resistor Rl sets the input impedance to any desired value. Commonly, it will be 50 ohms. The signal is then direct-coupled to Q2, a common-base circuit that isolates the input and output stages and provides the amplifier's exceptional stability.
Q3 functions as an emitter follower, to provide low output impedance (about 50 ohms). For higher output impedance, include resistor R8. It will affect impedance according to this formula: R8 - Rout-50. Otherwise, connect output capacitor C4 directly to the emitter of Q3.
The circuit described employs a frequency response that is essential for various audio and RF applications, allowing it to effectively amplify signals within the specified range. The use of a field-effect transistor (FET) in the common-source configuration provides high input impedance and significant voltage gain, making it suitable for interfacing with high-impedance sources. The optional resistor R1 plays a critical role in defining the input impedance, which can be tailored to suit specific requirements, enhancing the circuit's versatility.
The direct coupling of the signal to Q2 ensures minimal signal loss and maintains the integrity of the amplified output. The common-base configuration of Q2 is particularly advantageous for achieving high-frequency performance, as it offers low input capacitance and improved bandwidth. This configuration allows for effective isolation between the input and output stages, which is vital for preventing feedback and ensuring stable operation across the frequency range.
Q3, functioning as an emitter follower, provides a low output impedance, which is crucial for driving subsequent stages or loads without significant signal degradation. The typical output impedance of around 50 ohms makes it compatible with standard RF and audio applications. The inclusion of resistor R8 allows for adjustments to the output impedance, enabling the circuit to interface with various loads or to match specific requirements in different applications.
In scenarios where higher output impedance is necessary, the formula R8 - Rout - 50 provides a straightforward method for calculating the required resistance. Alternatively, connecting output capacitor C4 directly to the emitter of Q3 allows for a simplified output stage, which may be preferable in certain designs where impedance matching is not critical. This flexibility in design choices enhances the overall functionality and adaptability of the circuit for diverse electronic applications.The circuit has a frequency response ranging from 100 Hz to 3 MHz; gain is about 30 dB. Field-effect transistor Ql is configured in the common-source self-biased mode; optional resistor Rl sets the input impedance to any desired value. Commonly, it will be 50 ohms. The signal is then direct-coupled to Q2, a common-base circuit that isolates the input and output stages and provides the amplifier's exceptional stability.
Q3 functions as an emitter follower, to provide low output impedance (about 50 ohms). For higher output impedance, include resistor R8. It will affect impedance according to this formula: R8 - Rout-50. Otherwise, connect output capacitor C4 directly to the emitter of Q3.