
Burst-power-control
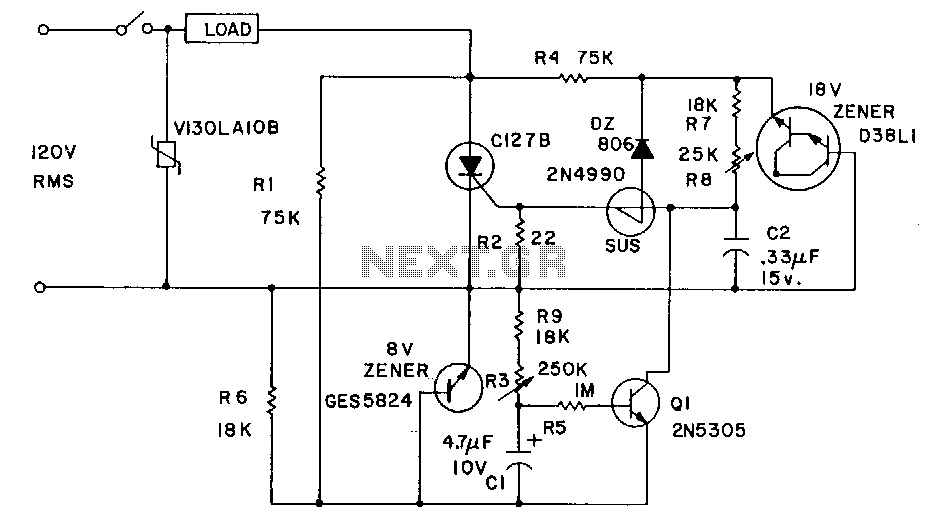
Industrial applications sometimes require that power be briefly applied to a load following the closure of a switch, such as a microswitch or foot switch. The load could be a heating element used for sealing plastic bags, a DC motor that is indexed or stepped with each application of power, or a DC solenoid that is energized for a brief time, such as in a staple gun. The phase angle at which the SCR triggers is determined by the charging rate of capacitor C2 through resistor R7 and potentiometer R5. When the breakover voltage of the gate triggering device, a silicon unilateral switch, is reached, the SCR turns on. The average DC voltage supplied to the load is determined by the setting of R5.
In this circuit design, the primary function is to control the application of power to various loads in industrial settings. The system typically utilizes a silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) as the main switching component, which allows for precise control over the timing of the power application. The operation begins with the closure of a switch, which could be a microswitch or a foot switch, that initiates the charging of capacitor C2 through resistor R7 and potentiometer R5.
The charging rate of C2 is critical as it affects the phase angle at which the SCR is triggered. The potentiometer R5 allows for fine-tuning of the charging rate, thereby adjusting the timing of the SCR's conduction. When the voltage across C2 reaches the breakover voltage of the gate triggering device, the SCR conducts, allowing current to flow to the load. This load can vary from heating elements, which require a brief application of power for processes like sealing, to DC motors and solenoids that may need to be energized momentarily for specific tasks.
The average DC voltage delivered to the load is influenced by the setting of the potentiometer R5, which provides versatility in controlling the power delivered, depending on the requirements of the application. The circuit's design ensures that the loads receive power only for the necessary duration, thereby enhancing efficiency and reducing energy consumption in industrial operations. This type of control is particularly useful in applications where precise timing is essential for operational effectiveness.Industrial applications sometimes require that power be only briefly applied to a load following the closure of a switch, such as a microswitch or foot switch. The load could be a heating element for use in sealing plastic bags, a de motor that is indexed or stepped with each application of power, or a de solenoid which is to be energized for a brief time-for example, a staple gun.
The phase angle at which the SCR triggers on is determined by the charging rate of C2 through R7 and potentiometer RS. When the breakover voltage of the gate triggering device, a silicon unilateral switch, is reached, the SCR turns on.
The average de voltage to the load is determined by the setting of RS.
In this circuit design, the primary function is to control the application of power to various loads in industrial settings. The system typically utilizes a silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) as the main switching component, which allows for precise control over the timing of the power application. The operation begins with the closure of a switch, which could be a microswitch or a foot switch, that initiates the charging of capacitor C2 through resistor R7 and potentiometer R5.
The charging rate of C2 is critical as it affects the phase angle at which the SCR is triggered. The potentiometer R5 allows for fine-tuning of the charging rate, thereby adjusting the timing of the SCR's conduction. When the voltage across C2 reaches the breakover voltage of the gate triggering device, the SCR conducts, allowing current to flow to the load. This load can vary from heating elements, which require a brief application of power for processes like sealing, to DC motors and solenoids that may need to be energized momentarily for specific tasks.
The average DC voltage delivered to the load is influenced by the setting of the potentiometer R5, which provides versatility in controlling the power delivered, depending on the requirements of the application. The circuit's design ensures that the loads receive power only for the necessary duration, thereby enhancing efficiency and reducing energy consumption in industrial operations. This type of control is particularly useful in applications where precise timing is essential for operational effectiveness.Industrial applications sometimes require that power be only briefly applied to a load following the closure of a switch, such as a microswitch or foot switch. The load could be a heating element for use in sealing plastic bags, a de motor that is indexed or stepped with each application of power, or a de solenoid which is to be energized for a brief time-for example, a staple gun.
The phase angle at which the SCR triggers on is determined by the charging rate of C2 through R7 and potentiometer RS. When the breakover voltage of the gate triggering device, a silicon unilateral switch, is reached, the SCR turns on.
The average de voltage to the load is determined by the setting of RS.