Circuit Project: Sound Activated Switch II
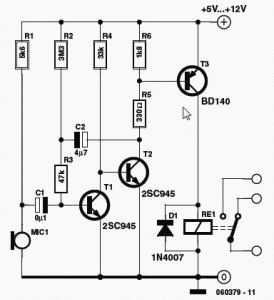
This sound-activated switch allows for control through sound, which can be beneficial not only in robotics but also in home automation applications.
The sound-activated switch operates by detecting specific sound frequencies or patterns, typically using a microphone or a sound sensor. Upon receiving a sound signal that meets predefined criteria, the switch activates an output device, such as a light or motor. This functionality is particularly advantageous in scenarios where hands-free operation is desired, enhancing convenience and accessibility.
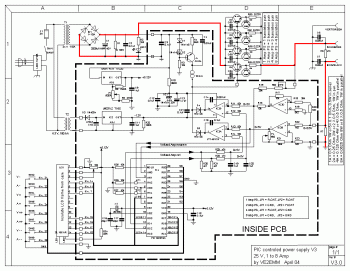
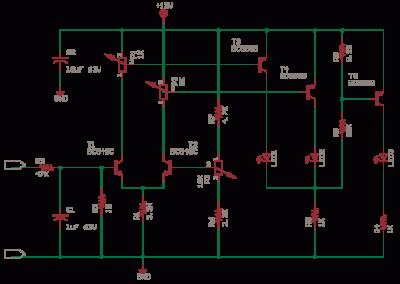
The circuit generally consists of several key components: a microphone or sound sensor, an amplifier to boost the audio signal, a microcontroller or comparator to process the sound input, and a relay or transistor to control the output device. The microphone captures ambient sound, and the amplifier increases the signal strength for better detection. The microcontroller is programmed to recognize specific sound patterns, triggering a high or low output signal based on the detection. This output then activates the relay or transistor, allowing current to flow to the connected device, thereby enabling it to perform the desired action.
For home automation, this technology can be integrated into various systems, such as lighting control, alarm systems, or even as a trigger for smart home devices. The sound-activated switch can be customized to respond to different sounds, making it versatile for various applications. Additionally, the circuit can be designed to include features such as adjustable sensitivity, which allows users to set the threshold for sound detection according to their environment.
Overall, the sound-activated switch represents an innovative approach to control mechanisms, leveraging audio signals for practical applications in both robotics and home automation.With this sound activated switch, control by sound may be very useful, not just on a robot but also for a bit of home automation, for example a sound-acti.. 🔗 External reference
The sound-activated switch operates by detecting specific sound frequencies or patterns, typically using a microphone or a sound sensor. Upon receiving a sound signal that meets predefined criteria, the switch activates an output device, such as a light or motor. This functionality is particularly advantageous in scenarios where hands-free operation is desired, enhancing convenience and accessibility.
The circuit generally consists of several key components: a microphone or sound sensor, an amplifier to boost the audio signal, a microcontroller or comparator to process the sound input, and a relay or transistor to control the output device. The microphone captures ambient sound, and the amplifier increases the signal strength for better detection. The microcontroller is programmed to recognize specific sound patterns, triggering a high or low output signal based on the detection. This output then activates the relay or transistor, allowing current to flow to the connected device, thereby enabling it to perform the desired action.
For home automation, this technology can be integrated into various systems, such as lighting control, alarm systems, or even as a trigger for smart home devices. The sound-activated switch can be customized to respond to different sounds, making it versatile for various applications. Additionally, the circuit can be designed to include features such as adjustable sensitivity, which allows users to set the threshold for sound detection according to their environment.
Overall, the sound-activated switch represents an innovative approach to control mechanisms, leveraging audio signals for practical applications in both robotics and home automation.With this sound activated switch, control by sound may be very useful, not just on a robot but also for a bit of home automation, for example a sound-acti.. 🔗 External reference