FPGA / CPLD 16x2 LCD Interface Circuit
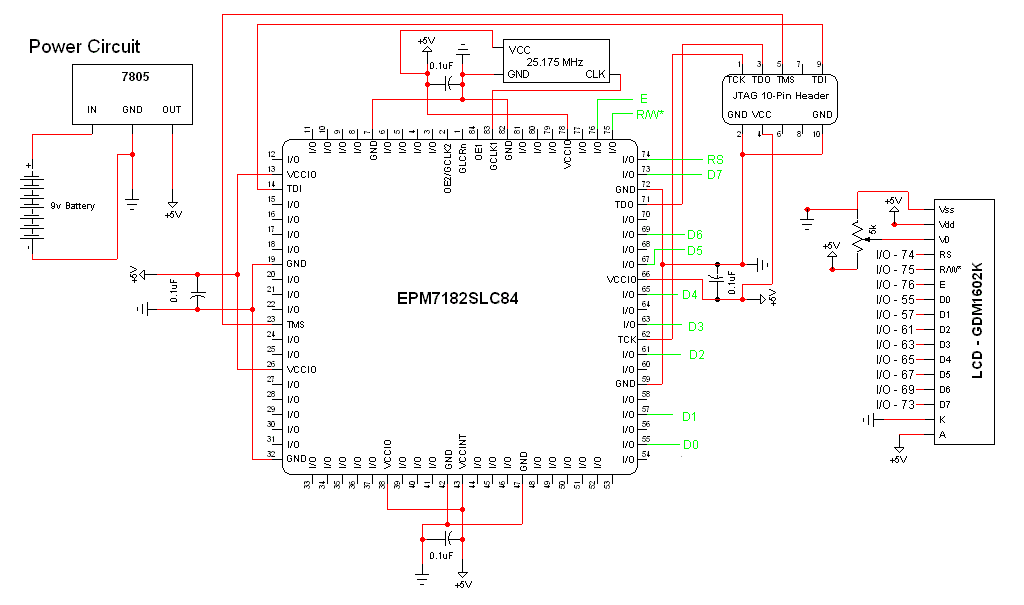
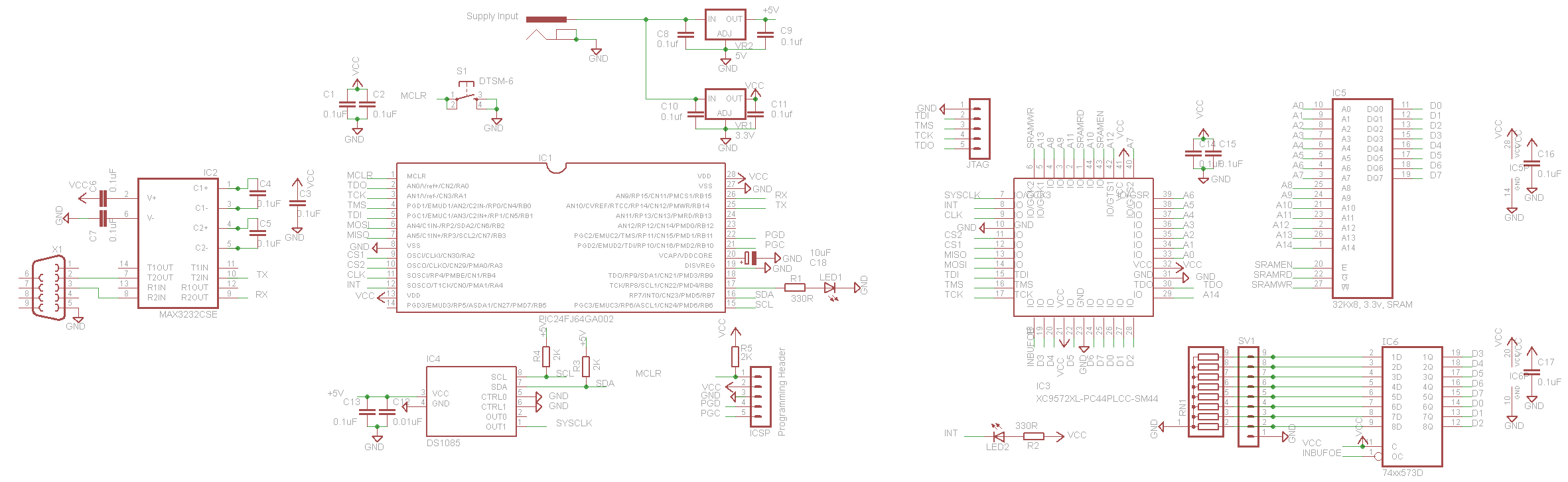
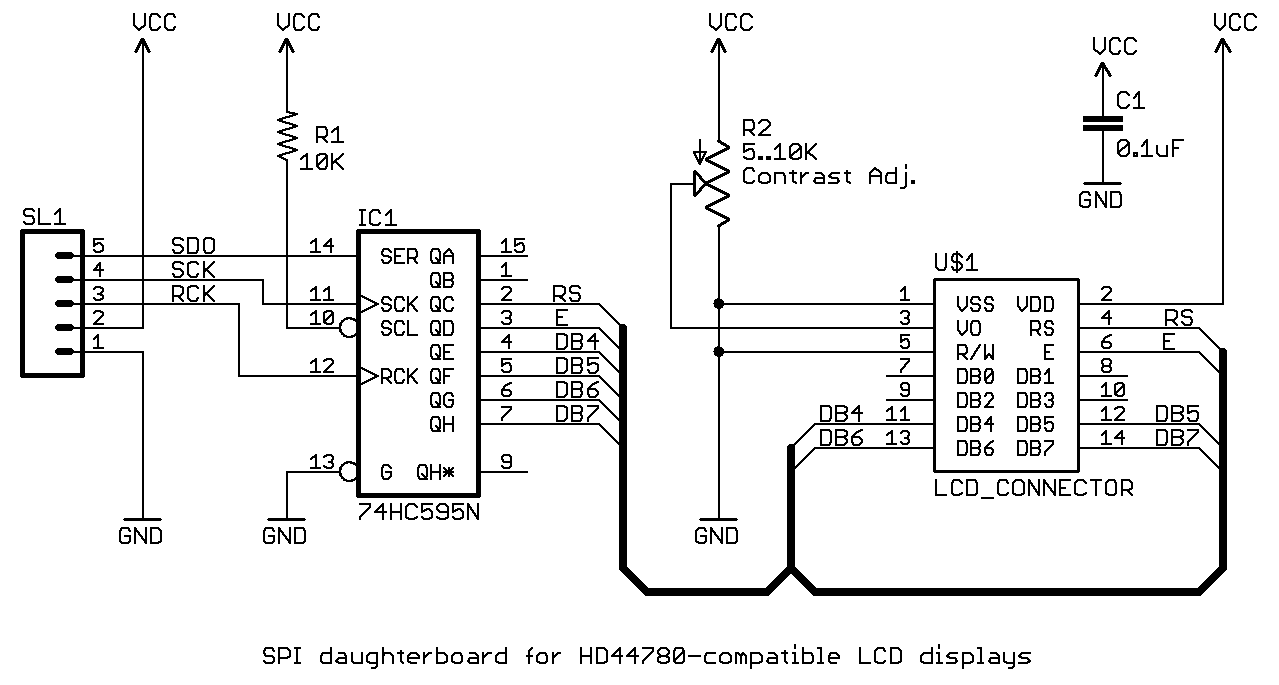
Description: The schematic for this project is a modified version of the CPLD development board schematic. Several new components have been added for this project, and the completed schematic is presented below. The primary components in the schematic include the CPLD development board, a 16x2 LCD (HD44780), and a ByteBlasterMV. The 16x2 LCD requires 11 digital I/O connections to the CPLD/FPGA when configured in 8-bit mode (only 7 connections are needed in 4-bit mode). Since 8-bit mode is utilized, all connections are essential. The remaining pins of the LCD are for power connections and contrast adjustment via a 5kΩ trimpot. This protoboard for the CPLD was developed previously and comprises a PLCC CPLD in a socket, along with power and JTAG connectors for programming. The oscillator selected for this project was chosen primarily due to its availability, as a timing device is necessary to maintain a reference time. Generally, any clock with a frequency above 10 MHz is suitable for this project.
The schematic integrates several critical components to facilitate the operation of the CPLD-based system. The CPLD development board serves as the core processing unit, enabling complex logic operations and interfacing with peripheral devices. The 16x2 LCD (HD44780) is a widely used display module that provides a user interface for outputting information. In the 8-bit configuration, it connects to the CPLD via 11 digital I/O lines, which include data, control, and enable signals, ensuring efficient communication between the CPLD and the display.
The ByteBlasterMV is employed as a programming interface, allowing for the configuration of the CPLD through JTAG. This connection is vital for downloading the programmed logic into the CPLD, enabling it to execute the desired functions as defined in the design.
Power supply considerations are essential, with the LCD requiring a stable voltage and current for proper operation. The inclusion of a 5kΩ trimpot for contrast adjustment allows for fine-tuning the display visibility based on ambient lighting conditions.
The oscillator is a crucial component, providing the necessary clock signal for the CPLD to synchronize its operations. The choice of an oscillator with a frequency above 10 MHz ensures that the system operates efficiently, meeting timing requirements for the various logic functions implemented within the CPLD.
Overall, this schematic represents a well-thought-out integration of components that work together to create a functional CPLD-based project, allowing for both programming flexibility and user interaction through the LCD display.The schematic for this project is a modified version of the CPLD dev board schematic. There are a few new parts added for this project and you can see the completed schematic for this project below. The main parts in the schematic are the CPLD Dev Board, 16x2 LCD (HD44780) and ByteBlasterMV. The 16x2 LCD makes 11 digital I/O connections to the CPLD/FPGA when used in 8-bit mode (In 4-bit mode, only 7 connections are necessary). Since we`re using 8-bit mode all of these connections are necessary. The rest of the LCD`s pins are power connection and contrast from the 5k © trimpot. This protoboard for a cpld was developed by me a few years ago. It`s really just a PLCC CPLD in a socket with power and JTAG connectors for programming. This oscillator was chosen mostly at random. We needed some type of timing device to keep a reference to time and I had this one laying around. Generally if you can find a clock above 10 MHz you`ll be fine for this project. 🔗 External reference
The schematic integrates several critical components to facilitate the operation of the CPLD-based system. The CPLD development board serves as the core processing unit, enabling complex logic operations and interfacing with peripheral devices. The 16x2 LCD (HD44780) is a widely used display module that provides a user interface for outputting information. In the 8-bit configuration, it connects to the CPLD via 11 digital I/O lines, which include data, control, and enable signals, ensuring efficient communication between the CPLD and the display.
The ByteBlasterMV is employed as a programming interface, allowing for the configuration of the CPLD through JTAG. This connection is vital for downloading the programmed logic into the CPLD, enabling it to execute the desired functions as defined in the design.
Power supply considerations are essential, with the LCD requiring a stable voltage and current for proper operation. The inclusion of a 5kΩ trimpot for contrast adjustment allows for fine-tuning the display visibility based on ambient lighting conditions.
The oscillator is a crucial component, providing the necessary clock signal for the CPLD to synchronize its operations. The choice of an oscillator with a frequency above 10 MHz ensures that the system operates efficiently, meeting timing requirements for the various logic functions implemented within the CPLD.
Overall, this schematic represents a well-thought-out integration of components that work together to create a functional CPLD-based project, allowing for both programming flexibility and user interaction through the LCD display.The schematic for this project is a modified version of the CPLD dev board schematic. There are a few new parts added for this project and you can see the completed schematic for this project below. The main parts in the schematic are the CPLD Dev Board, 16x2 LCD (HD44780) and ByteBlasterMV. The 16x2 LCD makes 11 digital I/O connections to the CPLD/FPGA when used in 8-bit mode (In 4-bit mode, only 7 connections are necessary). Since we`re using 8-bit mode all of these connections are necessary. The rest of the LCD`s pins are power connection and contrast from the 5k © trimpot. This protoboard for a cpld was developed by me a few years ago. It`s really just a PLCC CPLD in a socket with power and JTAG connectors for programming. This oscillator was chosen mostly at random. We needed some type of timing device to keep a reference to time and I had this one laying around. Generally if you can find a clock above 10 MHz you`ll be fine for this project. 🔗 External reference