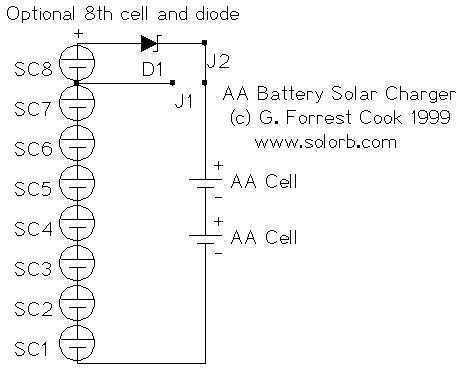
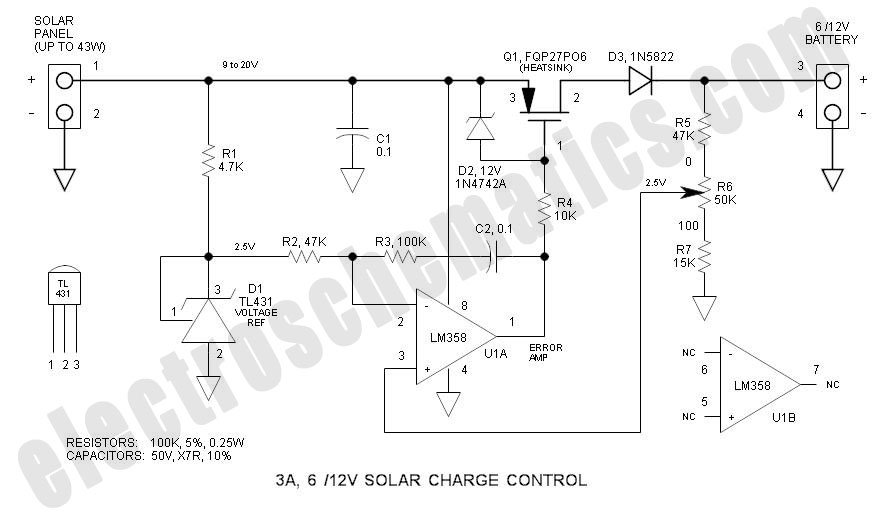
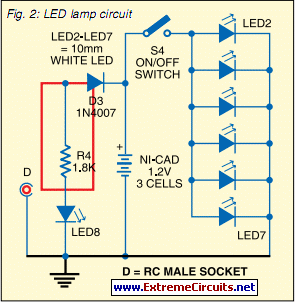
Solar Tracker
This solar tracker circuit is an open-source design that allows for modifications according to individual preferences. A video is available that provides additional useful information regarding the features included in the solar tracker, as well as those that may require further implementation.
The solar tracker circuit is designed to optimize the positioning of solar panels to maximize exposure to sunlight throughout the day. It typically employs a dual-axis tracking system, which allows the panels to move both horizontally and vertically, following the sun's path. The core components of such a circuit usually include light-dependent resistors (LDRs) for detecting sunlight intensity, a microcontroller for processing the input signals, and motor drivers to control the movement of the solar panels.
The LDRs are strategically placed on the solar panel to sense the light intensity from different directions. When one side receives more light than the other, the microcontroller interprets this data and sends signals to the motor drivers, which activate the motors to adjust the panel's angle accordingly. This process ensures that the solar panels are always oriented towards the sun, thereby enhancing energy capture efficiency.
Additionally, the circuit may feature a power supply section that includes a battery management system to store excess energy generated during peak sunlight hours. This stored energy can be used to power the tracker during periods of low sunlight or at night.
For users looking to customize the circuit, the open-source nature allows for modifications in the code running on the microcontroller, enabling the implementation of additional features such as weather sensors or remote monitoring capabilities. The accompanying video provides insights into these features and demonstrates how to make the necessary adjustments for specific requirements. Overall, the solar tracker circuit represents a valuable tool for improving solar energy harnessing capabilities.This solar tracker circuit is an open source circuit and anyone may edit the circuit to his/her own preference. Watch the video for other useful information regarding features the solar tracker does and does not include that you may have to implement yourself.
🔗 External reference
The solar tracker circuit is designed to optimize the positioning of solar panels to maximize exposure to sunlight throughout the day. It typically employs a dual-axis tracking system, which allows the panels to move both horizontally and vertically, following the sun's path. The core components of such a circuit usually include light-dependent resistors (LDRs) for detecting sunlight intensity, a microcontroller for processing the input signals, and motor drivers to control the movement of the solar panels.
The LDRs are strategically placed on the solar panel to sense the light intensity from different directions. When one side receives more light than the other, the microcontroller interprets this data and sends signals to the motor drivers, which activate the motors to adjust the panel's angle accordingly. This process ensures that the solar panels are always oriented towards the sun, thereby enhancing energy capture efficiency.
Additionally, the circuit may feature a power supply section that includes a battery management system to store excess energy generated during peak sunlight hours. This stored energy can be used to power the tracker during periods of low sunlight or at night.
For users looking to customize the circuit, the open-source nature allows for modifications in the code running on the microcontroller, enabling the implementation of additional features such as weather sensors or remote monitoring capabilities. The accompanying video provides insights into these features and demonstrates how to make the necessary adjustments for specific requirements. Overall, the solar tracker circuit represents a valuable tool for improving solar energy harnessing capabilities.This solar tracker circuit is an open source circuit and anyone may edit the circuit to his/her own preference. Watch the video for other useful information regarding features the solar tracker does and does not include that you may have to implement yourself.
🔗 External reference