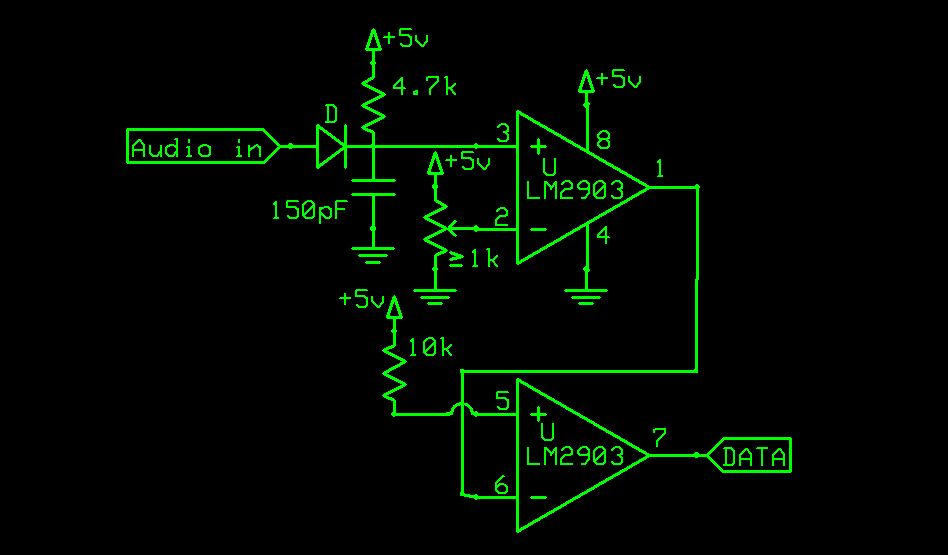
Construction of the Mk1 Receiver
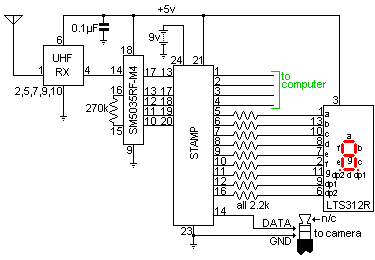
The remote control receiver is a custom design based on a pre-built 433MHz UHF radio receiver, a decoder chip and a BASIC Stamp. The Stamp is expensive, but easy to work with. The receiver requires 8.5mA, plus 1.5mA for each LED (individual or segment) that is lit for a maximum of up to 23mA. In practice it is between 13 and 16mA. Pressing a button on the remote transmitter causes the receiver to consume an extra 0.2mA. In the power saving mode the PBASIC nap instruction is used in combination with turning all the LEDs off to reduce power consumption to 4mA. The battery should last about 30 hours of on-time.
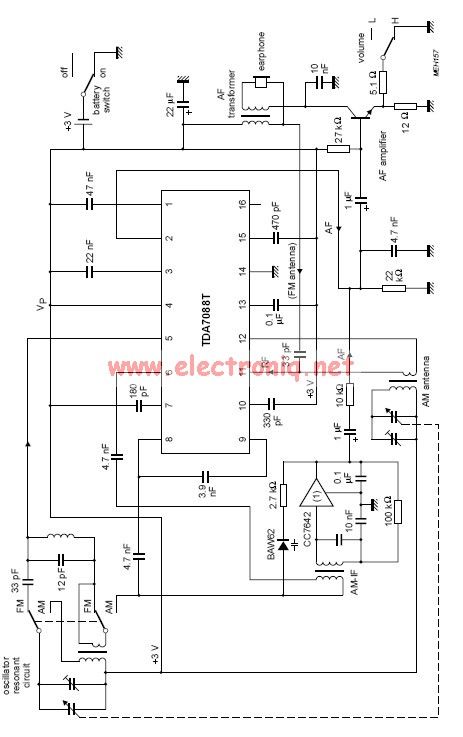
The remote control receiver circuit is designed around a 433MHz UHF radio receiver module, which is responsible for receiving signals from a remote transmitter. The integration of a decoder chip is crucial for interpreting the received data, allowing for effective communication between the remote control and the receiver. The BASIC Stamp microcontroller serves as the central processing unit, managing the overall functionality of the circuit and providing a user-friendly programming environment.
Power consumption is a critical aspect of this design. The receiver operates at a nominal current of 8.5mA, with additional current draw depending on the number of LEDs activated—1.5mA per LED. In practical scenarios, the total current consumption typically ranges from 13mA to 16mA, depending on the operational state of the LEDs. When a button on the remote is pressed, the receiver experiences a slight increase in current consumption, approximately 0.2mA, due to the processing of the received signal.
To enhance energy efficiency, the circuit employs a 'power saving' mode activated by the PBASIC nap instruction. This mode effectively reduces the current consumption to 4mA by turning off all LEDs, thus prolonging the battery life. The design anticipates a battery life of approximately 30 hours under typical usage conditions, making it suitable for applications where battery replacement is inconvenient.
Overall, this remote control receiver circuit combines a robust design with efficient power management, making it a practical solution for wireless control applications. The choice of components and their configuration ensures reliable performance while maintaining ease of use and programming flexibility.The remote control receiver is a custom design based on a pre-built 433MHz UHF radio receiver, a decoder chip and a BASIC Stamp. The Stamp is expensive, but easy to work with. The receiver requires 8.5mA, plus 1.5mA for each LED (individual or segment) that is lit for a maximum of up to 23mA.
In practice it is between 13 and 16mA. Pressing a button on the remote transmitter causes the receiver to consume an extra 0.2mA. In the `power saving` mode the PBASIC `nap` instruction is used in combination with turning all the LEDs off to reduce power consumption to 4mA. The battery should last about 30 hours of on-time. 🔗 External reference
The remote control receiver circuit is designed around a 433MHz UHF radio receiver module, which is responsible for receiving signals from a remote transmitter. The integration of a decoder chip is crucial for interpreting the received data, allowing for effective communication between the remote control and the receiver. The BASIC Stamp microcontroller serves as the central processing unit, managing the overall functionality of the circuit and providing a user-friendly programming environment.
Power consumption is a critical aspect of this design. The receiver operates at a nominal current of 8.5mA, with additional current draw depending on the number of LEDs activated—1.5mA per LED. In practical scenarios, the total current consumption typically ranges from 13mA to 16mA, depending on the operational state of the LEDs. When a button on the remote is pressed, the receiver experiences a slight increase in current consumption, approximately 0.2mA, due to the processing of the received signal.
To enhance energy efficiency, the circuit employs a 'power saving' mode activated by the PBASIC nap instruction. This mode effectively reduces the current consumption to 4mA by turning off all LEDs, thus prolonging the battery life. The design anticipates a battery life of approximately 30 hours under typical usage conditions, making it suitable for applications where battery replacement is inconvenient.
Overall, this remote control receiver circuit combines a robust design with efficient power management, making it a practical solution for wireless control applications. The choice of components and their configuration ensures reliable performance while maintaining ease of use and programming flexibility.The remote control receiver is a custom design based on a pre-built 433MHz UHF radio receiver, a decoder chip and a BASIC Stamp. The Stamp is expensive, but easy to work with. The receiver requires 8.5mA, plus 1.5mA for each LED (individual or segment) that is lit for a maximum of up to 23mA.
In practice it is between 13 and 16mA. Pressing a button on the remote transmitter causes the receiver to consume an extra 0.2mA. In the `power saving` mode the PBASIC `nap` instruction is used in combination with turning all the LEDs off to reduce power consumption to 4mA. The battery should last about 30 hours of on-time. 🔗 External reference