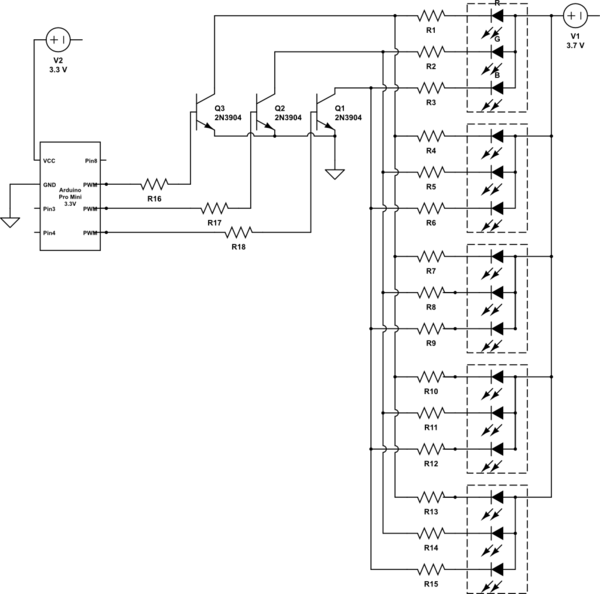
Delayed ON LED

This is a simple circuit where an LED turns on only after a predetermined time once the power supply is activated. Initially, when the power supply is turned on, the transistor remains off. The capacitor charges through the preset resistor R3, and when the voltage across capacitor C1 reaches a sufficient level, the transistor switches on, causing the LED to illuminate. The duration of the delay is adjustable by varying the resistance of the potentiometer R3.
This circuit operates on the principle of a time delay using a capacitor and a resistor in combination with a transistor switch. Upon activation of the power supply, the capacitor C1 begins charging through the potentiometer R3. The charging time is determined by the RC time constant, which is the product of the resistance (R3) and the capacitance (C1).
As the capacitor charges, the voltage across it increases gradually. The transistor, which is configured in a common emitter mode, remains in the cutoff region until the voltage across the capacitor exceeds the base-emitter threshold voltage of the transistor. Once this threshold is surpassed, the transistor enters saturation, allowing current to flow through the LED, thus illuminating it.
The adjustable nature of R3 allows for fine-tuning of the delay period, making this circuit versatile for various applications requiring time delays. Increasing the resistance of R3 will extend the time it takes for the capacitor to charge to the necessary voltage, thereby increasing the delay before the LED turns on. Conversely, decreasing R3 will shorten the delay.
This simple LED delay circuit can be utilized in applications such as timers, alarms, or any device where a delayed activation is beneficial. The choice of capacitor value also plays a crucial role in determining the delay; larger capacitance will result in longer delays, while smaller capacitance will yield shorter delays.Here is very simple circuit in which the LED becomes ON only after a preset time the power supply is switched ON. When the power supply is switched on the transistor will be OFF. The capacitor now charges via the preset R3 and when the voltage across C1 is sufficient, the transistor switches ON and LED glows.
The ON delay depends on the value of P OT R3. You can increase the time delay by increasing the resistance of POT R3. 🔗 External reference
This circuit operates on the principle of a time delay using a capacitor and a resistor in combination with a transistor switch. Upon activation of the power supply, the capacitor C1 begins charging through the potentiometer R3. The charging time is determined by the RC time constant, which is the product of the resistance (R3) and the capacitance (C1).
As the capacitor charges, the voltage across it increases gradually. The transistor, which is configured in a common emitter mode, remains in the cutoff region until the voltage across the capacitor exceeds the base-emitter threshold voltage of the transistor. Once this threshold is surpassed, the transistor enters saturation, allowing current to flow through the LED, thus illuminating it.
The adjustable nature of R3 allows for fine-tuning of the delay period, making this circuit versatile for various applications requiring time delays. Increasing the resistance of R3 will extend the time it takes for the capacitor to charge to the necessary voltage, thereby increasing the delay before the LED turns on. Conversely, decreasing R3 will shorten the delay.
This simple LED delay circuit can be utilized in applications such as timers, alarms, or any device where a delayed activation is beneficial. The choice of capacitor value also plays a crucial role in determining the delay; larger capacitance will result in longer delays, while smaller capacitance will yield shorter delays.Here is very simple circuit in which the LED becomes ON only after a preset time the power supply is switched ON. When the power supply is switched on the transistor will be OFF. The capacitor now charges via the preset R3 and when the voltage across C1 is sufficient, the transistor switches ON and LED glows.
The ON delay depends on the value of P OT R3. You can increase the time delay by increasing the resistance of POT R3. 🔗 External reference