
Digital Dice Project
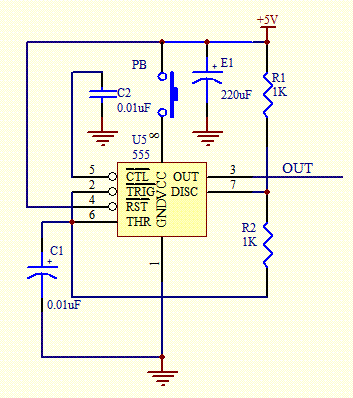
This digital dice electronic project utilizes a combination of a 555 timer, a 7490 decade counter, a 7483 4-bit binary adder, a 7447 BCD to 7-segment decoder, and a 7-segment display to show the digit.
The digital dice project is designed to simulate the random output of a traditional dice using electronic components. The core of the project is the 555 timer, configured in astable mode, which generates a continuous square wave signal. This signal serves as the clock input for the 7490 decade counter. The 7490 is a versatile decade counter that counts from 0 to 9 and resets upon reaching 10, making it ideal for simulating dice rolls.
The output from the 7490 is fed into a 7483 4-bit binary adder, which can be used to manipulate the count if additional features, such as scoring or multiple dice rolls, are desired. However, in a basic dice simulation, the output of the 7490 can be directly converted to a Binary-Coded Decimal (BCD) format.
To display the result of the dice roll, the output from the 7490 is connected to the 7447 BCD to 7-segment decoder. This component translates the BCD output into a format suitable for driving a 7-segment display. The 7447 decoder activates the appropriate segments of the 7-segment display to visually represent the number rolled, from 1 to 6, simulating a standard dice.
The entire circuit can be powered by a standard DC power supply, and the components are typically mounted on a breadboard or printed circuit board (PCB) for stability and ease of use. Additional features such as reset buttons or sound output can be integrated to enhance the user experience. Overall, this digital dice project exemplifies the integration of various logic components to create an engaging and functional electronic device.This Digital Dice electronic project uses a combination of 555 timer, 7490 decade counter, 7483 4-bit binary adder, 7447 BCD to 7 Segment Decoder and the 7 segment display the digit 🔗 External reference
The digital dice project is designed to simulate the random output of a traditional dice using electronic components. The core of the project is the 555 timer, configured in astable mode, which generates a continuous square wave signal. This signal serves as the clock input for the 7490 decade counter. The 7490 is a versatile decade counter that counts from 0 to 9 and resets upon reaching 10, making it ideal for simulating dice rolls.
The output from the 7490 is fed into a 7483 4-bit binary adder, which can be used to manipulate the count if additional features, such as scoring or multiple dice rolls, are desired. However, in a basic dice simulation, the output of the 7490 can be directly converted to a Binary-Coded Decimal (BCD) format.
To display the result of the dice roll, the output from the 7490 is connected to the 7447 BCD to 7-segment decoder. This component translates the BCD output into a format suitable for driving a 7-segment display. The 7447 decoder activates the appropriate segments of the 7-segment display to visually represent the number rolled, from 1 to 6, simulating a standard dice.
The entire circuit can be powered by a standard DC power supply, and the components are typically mounted on a breadboard or printed circuit board (PCB) for stability and ease of use. Additional features such as reset buttons or sound output can be integrated to enhance the user experience. Overall, this digital dice project exemplifies the integration of various logic components to create an engaging and functional electronic device.This Digital Dice electronic project uses a combination of 555 timer, 7490 decade counter, 7483 4-bit binary adder, 7447 BCD to 7 Segment Decoder and the 7 segment display the digit 🔗 External reference

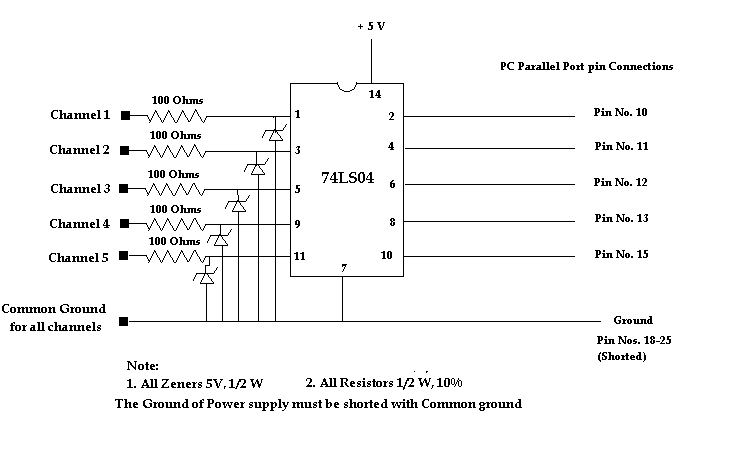
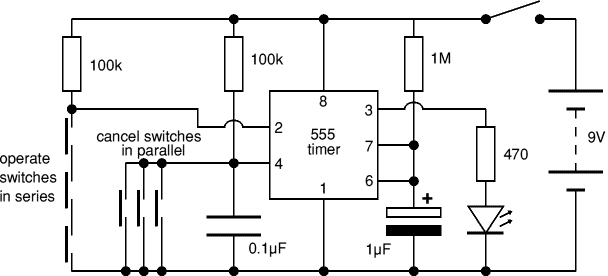
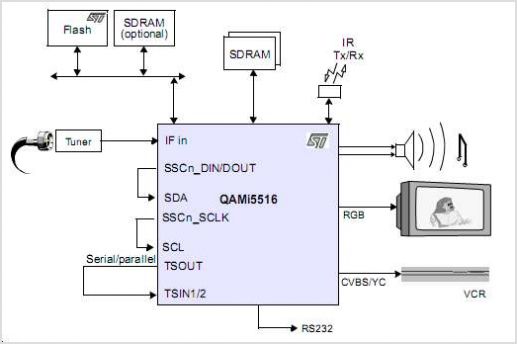

.png)