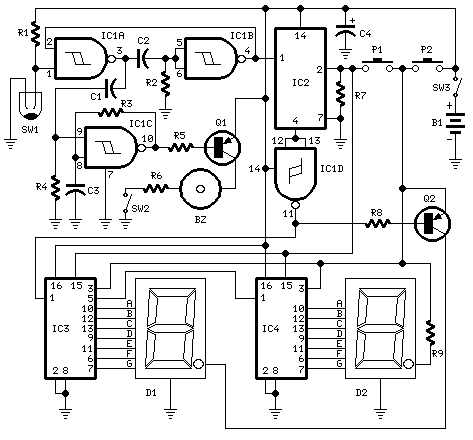
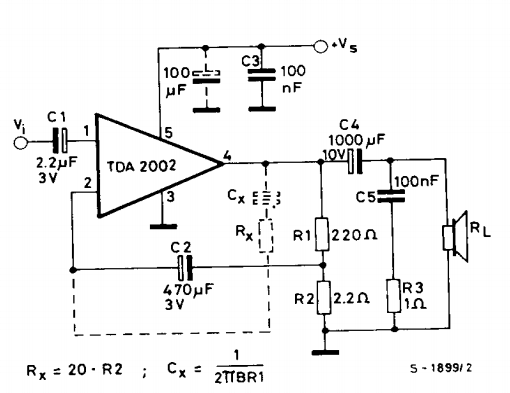
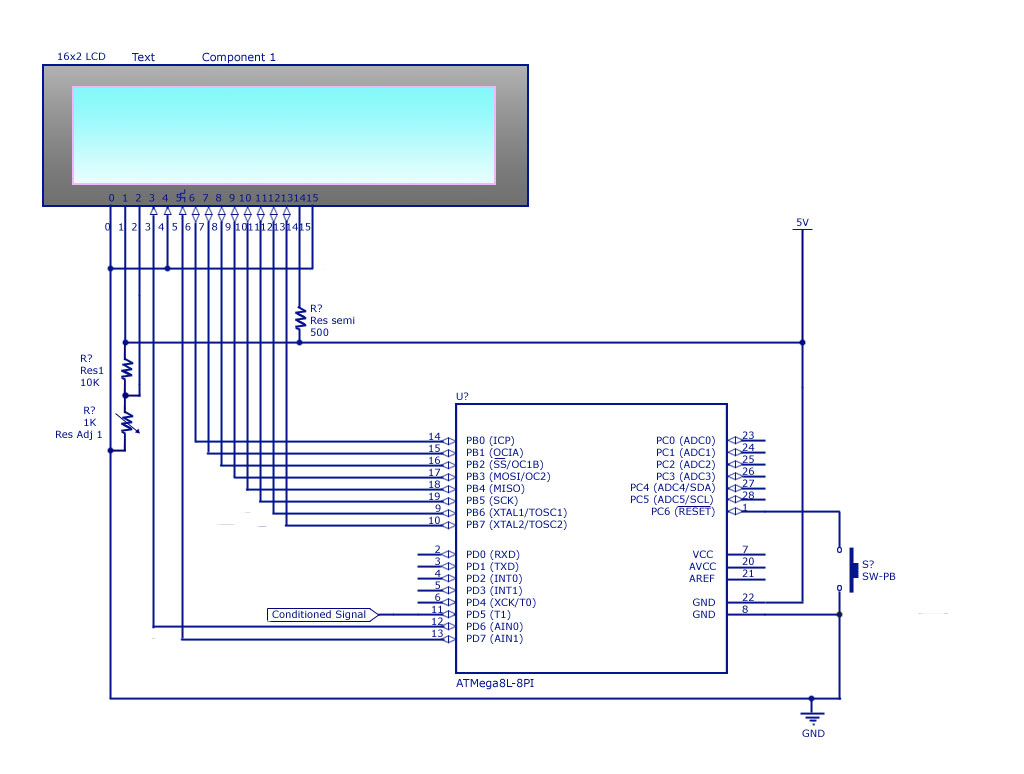
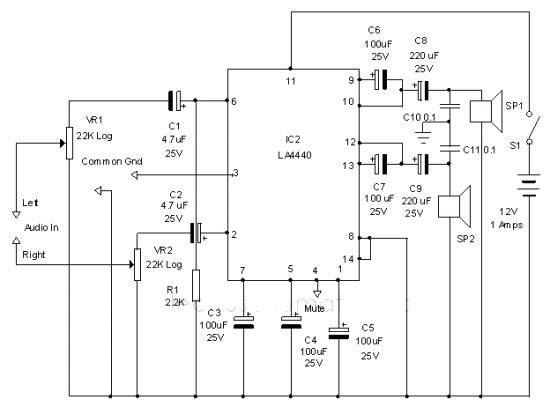
Digital display circuit configuration
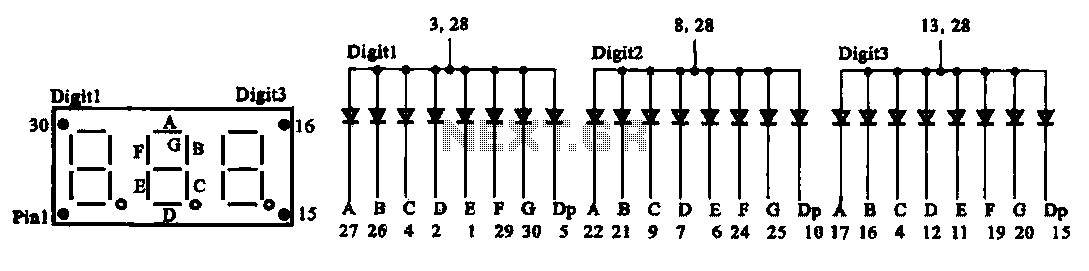
The document presents two types of digital display circuits. The first type (a) utilizes a common anode circuit configuration, while the second type (b) employs a common cathode circuit structure.
The common anode display circuit configuration consists of multiple light-emitting diodes (LEDs) connected in such a way that the anodes of all LEDs are connected to a positive voltage source. Each cathode is then connected to a control signal that determines whether the LED is turned on or off. This arrangement allows for a simplified control mechanism, as the common positive voltage can be maintained while individual LEDs are activated by grounding their respective cathodes.
In contrast, the common cathode display circuit configuration connects the cathodes of the LEDs to the ground, while the anodes are connected to a control signal that provides the positive voltage. In this setup, activating an LED requires applying a high signal to its anode, allowing current to flow from the anode to the cathode.
When designing these circuits, it is essential to consider the required current limiting resistors for each LED to prevent excessive current flow that could damage the components. The choice between a common anode and a common cathode configuration often depends on the specific application, the type of microcontroller or driving circuit used, and the desired control logic.
Both configurations can be effectively utilized in various applications, including seven-segment displays, alphanumeric displays, and other digital output devices, providing flexibility in design and implementation based on the project requirements.3 shows two kinds of digital display circuit, Total (a) adopt common anode circuit configuration, FIG. (B) the use of common cathode path structure.
The common anode display circuit configuration consists of multiple light-emitting diodes (LEDs) connected in such a way that the anodes of all LEDs are connected to a positive voltage source. Each cathode is then connected to a control signal that determines whether the LED is turned on or off. This arrangement allows for a simplified control mechanism, as the common positive voltage can be maintained while individual LEDs are activated by grounding their respective cathodes.
In contrast, the common cathode display circuit configuration connects the cathodes of the LEDs to the ground, while the anodes are connected to a control signal that provides the positive voltage. In this setup, activating an LED requires applying a high signal to its anode, allowing current to flow from the anode to the cathode.
When designing these circuits, it is essential to consider the required current limiting resistors for each LED to prevent excessive current flow that could damage the components. The choice between a common anode and a common cathode configuration often depends on the specific application, the type of microcontroller or driving circuit used, and the desired control logic.
Both configurations can be effectively utilized in various applications, including seven-segment displays, alphanumeric displays, and other digital output devices, providing flexibility in design and implementation based on the project requirements.3 shows two kinds of digital display circuit, Total (a) adopt common anode circuit configuration, FIG. (B) the use of common cathode path structure.