
Digital-frequency-meter
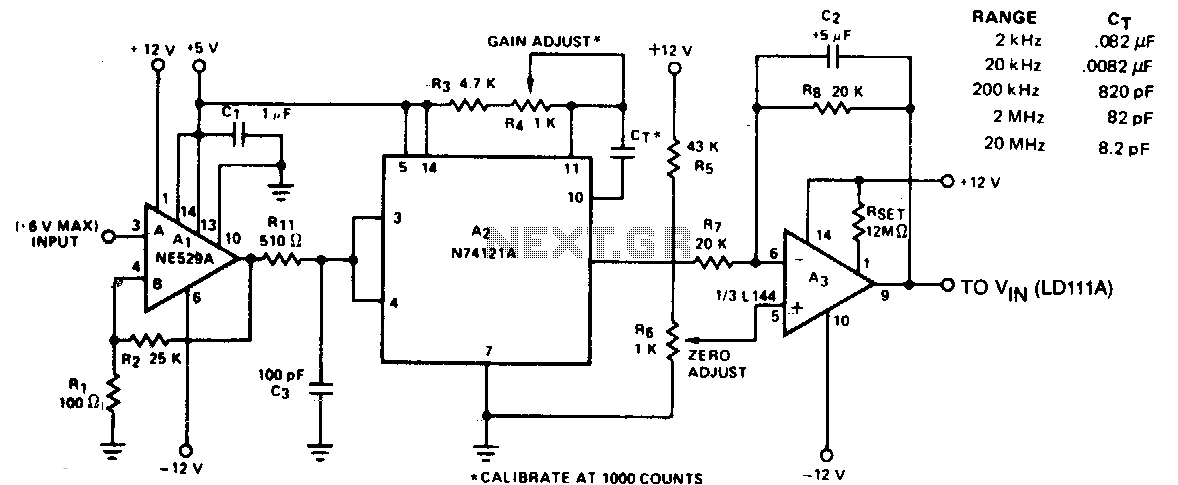
The circuit converts frequency to voltage by taking the average DC value of the pulses from the 74121 monostable multivibrator. The one-shot is triggered by the positive-going AC signal at the input of the 529 comparator. The amplifier functions as a DC filter and also provides zeroing. This circuit will maintain an accuracy of 2% over a range of five decades. The input signal to the comparator should be greater than 0.1 V peak-to-peak and less than 12 V peak-to-peak for proper operation.
The described circuit is a frequency-to-voltage converter that utilizes a 74121 monostable multivibrator to generate a corresponding DC voltage based on the frequency of an incoming AC signal. The 74121 is a dual retriggerable monostable multivibrator, which can produce a pulse of a specific duration in response to an input trigger. In this configuration, the positive-going edge of the AC signal triggers the monostable, generating a series of output pulses.
These output pulses are then fed into a 529 comparator, which is designed to compare the incoming AC signal against a reference voltage. The comparator's function is crucial as it determines the accuracy of the frequency-to-voltage conversion. The output of the comparator provides a clean, digital representation of the frequency of the incoming AC signal, which is then processed by the subsequent circuitry.
The amplifier connected to the output of the comparator serves two primary functions: it acts as a DC filter to smooth out the pulsed output from the monostable multivibrator and provides zeroing capability to ensure that the output voltage can be accurately calibrated to zero when no input signal is present. This filtering is essential for achieving a stable DC voltage that accurately represents the average frequency of the input signal.
To ensure proper operation, the input signal to the comparator must meet specific voltage requirements, being greater than 0.1 V peak-to-peak and less than 12 V peak-to-peak. Adhering to these voltage levels is critical for the circuit's performance and accuracy, as signals outside this range may lead to erroneous outputs or non-functional behavior.
Overall, this circuit design achieves a reliable frequency-to-voltage conversion with an impressive accuracy of 2% across five decades of frequency range, making it suitable for various applications in electronic measurement and control systems.The circuit converts frequency to voltage by taking the average de value of the pulses from the 7 4121 monostable multivibrator. The one shot is triggered by the positive-going ac signal at the input of the 529 comparator. The amplifier acts as a de filter, and also provides zeroing. This circuit will maintain an accuracy of2% over 5 decades of range. The input signal to the comparator should be greater than 0.1 V pkpk, and less than 12 V pk-pk for proper operation.
The described circuit is a frequency-to-voltage converter that utilizes a 74121 monostable multivibrator to generate a corresponding DC voltage based on the frequency of an incoming AC signal. The 74121 is a dual retriggerable monostable multivibrator, which can produce a pulse of a specific duration in response to an input trigger. In this configuration, the positive-going edge of the AC signal triggers the monostable, generating a series of output pulses.
These output pulses are then fed into a 529 comparator, which is designed to compare the incoming AC signal against a reference voltage. The comparator's function is crucial as it determines the accuracy of the frequency-to-voltage conversion. The output of the comparator provides a clean, digital representation of the frequency of the incoming AC signal, which is then processed by the subsequent circuitry.
The amplifier connected to the output of the comparator serves two primary functions: it acts as a DC filter to smooth out the pulsed output from the monostable multivibrator and provides zeroing capability to ensure that the output voltage can be accurately calibrated to zero when no input signal is present. This filtering is essential for achieving a stable DC voltage that accurately represents the average frequency of the input signal.
To ensure proper operation, the input signal to the comparator must meet specific voltage requirements, being greater than 0.1 V peak-to-peak and less than 12 V peak-to-peak. Adhering to these voltage levels is critical for the circuit's performance and accuracy, as signals outside this range may lead to erroneous outputs or non-functional behavior.
Overall, this circuit design achieves a reliable frequency-to-voltage conversion with an impressive accuracy of 2% across five decades of frequency range, making it suitable for various applications in electronic measurement and control systems.The circuit converts frequency to voltage by taking the average de value of the pulses from the 7 4121 monostable multivibrator. The one shot is triggered by the positive-going ac signal at the input of the 529 comparator. The amplifier acts as a de filter, and also provides zeroing. This circuit will maintain an accuracy of2% over 5 decades of range. The input signal to the comparator should be greater than 0.1 V pkpk, and less than 12 V pk-pk for proper operation.