
Dual-liquid-level-detector
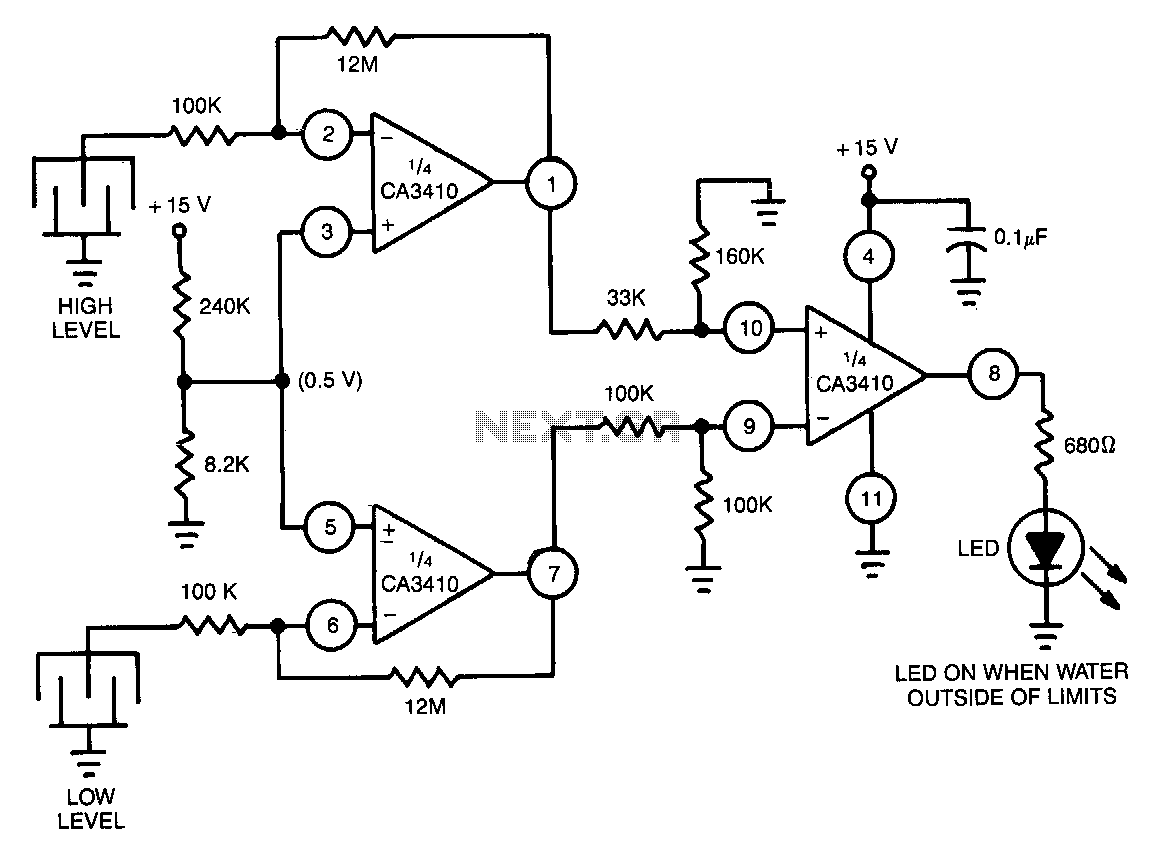
Utilizes the CA3410 quad BiMOS operational amplifier to detect small currents. Due to the low input current of the op-amp, a current as small as 1 pA flowing through the sensor will cause the converter's output to vary by approximately 10 to 12 V.
The circuit employs the CA3410, which is known for its high input impedance and low bias current characteristics, making it particularly suitable for applications involving the measurement of minute currents. The configuration of the op-amp in this setup is typically as a differential amplifier or as part of a transimpedance amplifier, which converts the sensed current into a voltage output.
In this circuit, the small current is sensed through a resistor or a specialized sensor that translates the current flow into a voltage drop. The CA3410 amplifies this voltage drop, leveraging its high gain to output a significant voltage change. The output voltage range of 10 to 12 V in response to a 1 pA input current indicates a high sensitivity and gain factor, which is crucial for applications in precision measurements, such as in biomedical instrumentation or sensitive environmental monitoring.
The circuit design should also include appropriate feedback mechanisms to stabilize the gain and prevent oscillations. Additionally, filtering components may be integrated to eliminate noise and enhance the signal integrity. Overall, the CA3410-based circuit provides an effective solution for sensing and amplifying ultra-low currents, making it an essential component in various electronic measurement systems.Uses CA3410 quad BiMOS op amp to sense small currents. Because the op amp"s input current is low, a current of only 1 p.A passing through the sensor will change the converter"s output by as much as 10 to 12 V.
The circuit employs the CA3410, which is known for its high input impedance and low bias current characteristics, making it particularly suitable for applications involving the measurement of minute currents. The configuration of the op-amp in this setup is typically as a differential amplifier or as part of a transimpedance amplifier, which converts the sensed current into a voltage output.
In this circuit, the small current is sensed through a resistor or a specialized sensor that translates the current flow into a voltage drop. The CA3410 amplifies this voltage drop, leveraging its high gain to output a significant voltage change. The output voltage range of 10 to 12 V in response to a 1 pA input current indicates a high sensitivity and gain factor, which is crucial for applications in precision measurements, such as in biomedical instrumentation or sensitive environmental monitoring.
The circuit design should also include appropriate feedback mechanisms to stabilize the gain and prevent oscillations. Additionally, filtering components may be integrated to eliminate noise and enhance the signal integrity. Overall, the CA3410-based circuit provides an effective solution for sensing and amplifying ultra-low currents, making it an essential component in various electronic measurement systems.Uses CA3410 quad BiMOS op amp to sense small currents. Because the op amp"s input current is low, a current of only 1 p.A passing through the sensor will change the converter"s output by as much as 10 to 12 V.