FET VOLTMETER 1
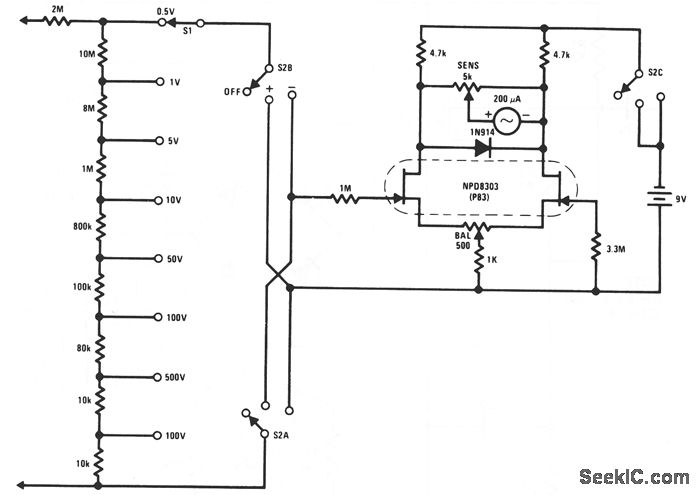
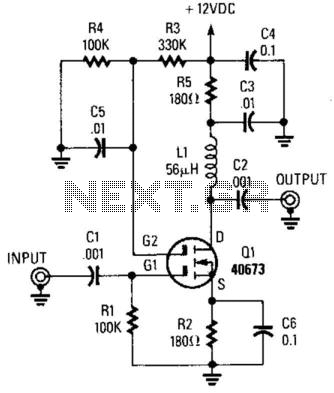
This FET voltmeter (FETVM) serves as a replacement for the vacuum tube voltmeter (VTVM) and eliminates the need for a standard line cord. Additionally, the drift rates of field-effect transistors (FETs) are significantly better than those of vacuum tube circuits, enabling a full-scale voltage range of 0.5 V, which is typically unachievable with most vacuum tubes. The low leakage and low noise characteristics of the NPD8303 transistor make it particularly suitable for this application.
The FET voltmeter employs advanced solid-state technology to provide accurate voltage measurements with enhanced stability and reduced noise. The design utilizes the NPD8303, a low-noise N-channel depletion-mode FET, which contributes to the overall performance by minimizing thermal drift and bias current variations. This is crucial for precision measurement applications where even minor fluctuations can lead to significant errors.
The circuit configuration includes a high-impedance input stage, designed to ensure that the voltmeter does not load the circuit under test. The output stage may include an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for digital readouts or a simple analog display for direct voltage readings. The choice of components and layout is optimized to maintain low noise levels and high linearity across the operating range.
Powering the FETVM can be achieved through a battery or a low-voltage power supply, further enhancing its portability and usability in various field applications. The elimination of a line cord not only simplifies the design but also increases the safety and convenience of the instrument, making it ideal for both laboratory and field environments.
Overall, the FET voltmeter represents a significant advancement over traditional vacuum tube voltmeters, offering improved performance, ease of use, and versatility in a compact form factor.This FETVM replaces the function of the VTVM and rids the instrument of the usual line cord. In addition, FET drift rates are far superior to vacuum tube circuits, allowing a 0. 5 V full-scale range which is impractical with most vacuum tubes. The low leakage, low noise NPD8303 is ideal for this application. 🔗 External reference
The FET voltmeter employs advanced solid-state technology to provide accurate voltage measurements with enhanced stability and reduced noise. The design utilizes the NPD8303, a low-noise N-channel depletion-mode FET, which contributes to the overall performance by minimizing thermal drift and bias current variations. This is crucial for precision measurement applications where even minor fluctuations can lead to significant errors.
The circuit configuration includes a high-impedance input stage, designed to ensure that the voltmeter does not load the circuit under test. The output stage may include an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for digital readouts or a simple analog display for direct voltage readings. The choice of components and layout is optimized to maintain low noise levels and high linearity across the operating range.
Powering the FETVM can be achieved through a battery or a low-voltage power supply, further enhancing its portability and usability in various field applications. The elimination of a line cord not only simplifies the design but also increases the safety and convenience of the instrument, making it ideal for both laboratory and field environments.
Overall, the FET voltmeter represents a significant advancement over traditional vacuum tube voltmeters, offering improved performance, ease of use, and versatility in a compact form factor.This FETVM replaces the function of the VTVM and rids the instrument of the usual line cord. In addition, FET drift rates are far superior to vacuum tube circuits, allowing a 0. 5 V full-scale range which is impractical with most vacuum tubes. The low leakage, low noise NPD8303 is ideal for this application. 🔗 External reference