
Flood-alarm-or-temperature-monitor
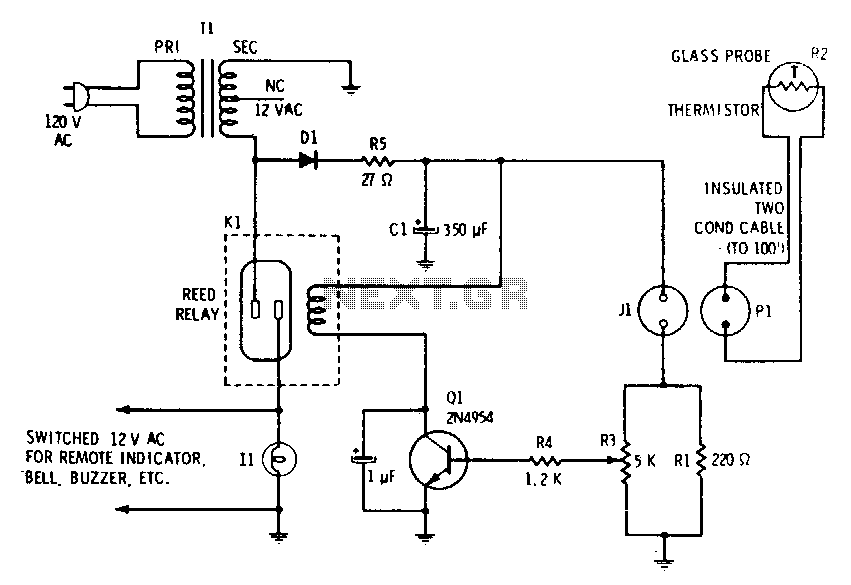
A filtered 15 V DC supply is applied to a series circuit that includes a thermistor (R2) and a parallel combination of resistors (R1 and R3). The transistor (Q1) functions as a switch, with its state controlled by the setting of the potentiometer (R3). Initially, R3 is adjusted to allow just enough current to flow into the base of Q1 to turn it on when the thermistor is exposed to air. As the resistance of the thermistor decreases, the voltage at the base of Q1 increases. When the base current reaches the predetermined level, the transistor conducts, allowing current to flow through the reed relay coil, which closes the contacts of the reed relay. The base current of transistor Q1 is influenced by the environmental conditions surrounding the thermistor.
In this circuit, the thermistor R2 serves as a temperature sensor, responding to changes in its environment. When the temperature rises, the resistance of the thermistor decreases, leading to an increase in voltage at the base of the transistor Q1. The potentiometer R3 allows for fine-tuning of the base current, ensuring that the transistor operates within the desired threshold for activation.
The parallel resistors R1 and R3 create a voltage divider, which is essential for setting the correct base voltage for Q1. The configuration allows for flexibility in adjusting the sensitivity of the circuit to temperature changes. When the thermistor detects a temperature change, the corresponding change in resistance alters the voltage across R3, thereby influencing the base current of Q1.
The reed relay, which is activated by the current flowing through its coil when Q1 conducts, provides an effective means of controlling higher power loads with the low power signal from the transistor. This arrangement is particularly useful in applications where isolation between the control circuit and the load circuit is necessary.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a simple yet effective method of using a thermistor in conjunction with a transistor switch and a relay to control devices based on temperature variations, demonstrating the principles of temperature sensing and electronic switching in practical applications.Filtered 15 V de is applied to a series circuit consisting of thermistor R2 and parallel combination of resistors Rl and R3. Transistor Ql acts as a switch whose state is determined by the setting of potentiometer R3, which is first set so just enough current flows into the base to switch on when the thermistor is in contact with air.
When the resistance of the thermistor decreases, the voltage at the base of Ql rises. When the base current reaches the preset level, the transistor conducts and passes current through the reed relay coil, closing the reed relay contacts. Current at the base of transistor Ql is determined by the environment into which the termistor is inserted.
In this circuit, the thermistor R2 serves as a temperature sensor, responding to changes in its environment. When the temperature rises, the resistance of the thermistor decreases, leading to an increase in voltage at the base of the transistor Q1. The potentiometer R3 allows for fine-tuning of the base current, ensuring that the transistor operates within the desired threshold for activation.
The parallel resistors R1 and R3 create a voltage divider, which is essential for setting the correct base voltage for Q1. The configuration allows for flexibility in adjusting the sensitivity of the circuit to temperature changes. When the thermistor detects a temperature change, the corresponding change in resistance alters the voltage across R3, thereby influencing the base current of Q1.
The reed relay, which is activated by the current flowing through its coil when Q1 conducts, provides an effective means of controlling higher power loads with the low power signal from the transistor. This arrangement is particularly useful in applications where isolation between the control circuit and the load circuit is necessary.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a simple yet effective method of using a thermistor in conjunction with a transistor switch and a relay to control devices based on temperature variations, demonstrating the principles of temperature sensing and electronic switching in practical applications.Filtered 15 V de is applied to a series circuit consisting of thermistor R2 and parallel combination of resistors Rl and R3. Transistor Ql acts as a switch whose state is determined by the setting of potentiometer R3, which is first set so just enough current flows into the base to switch on when the thermistor is in contact with air.
When the resistance of the thermistor decreases, the voltage at the base of Ql rises. When the base current reaches the preset level, the transistor conducts and passes current through the reed relay coil, closing the reed relay contacts. Current at the base of transistor Ql is determined by the environment into which the termistor is inserted.