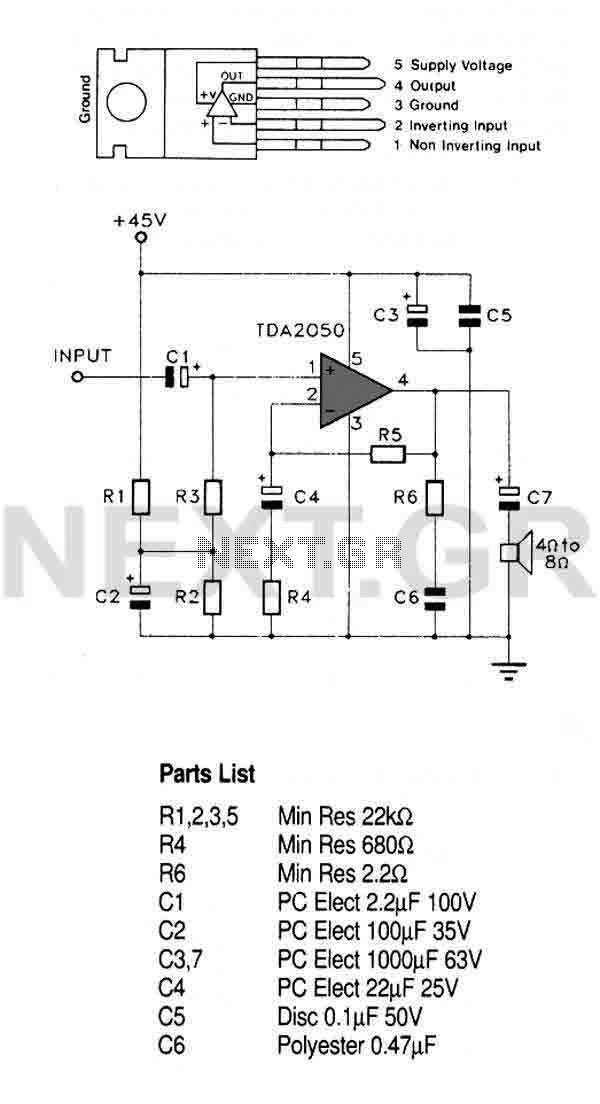
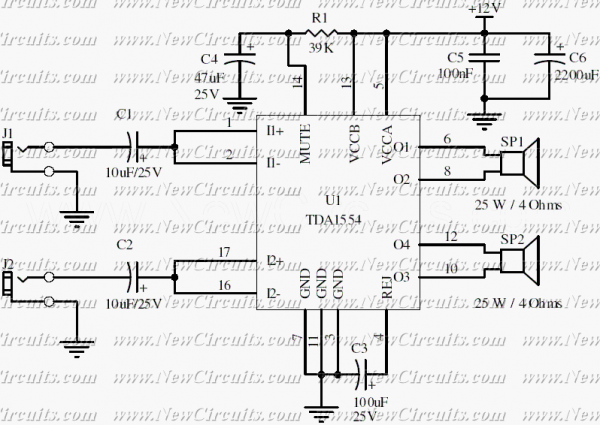
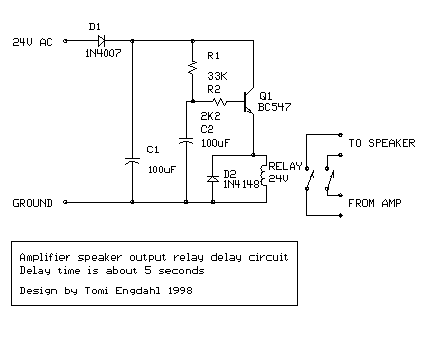
Four quadrant photo-conductive detector amplifier
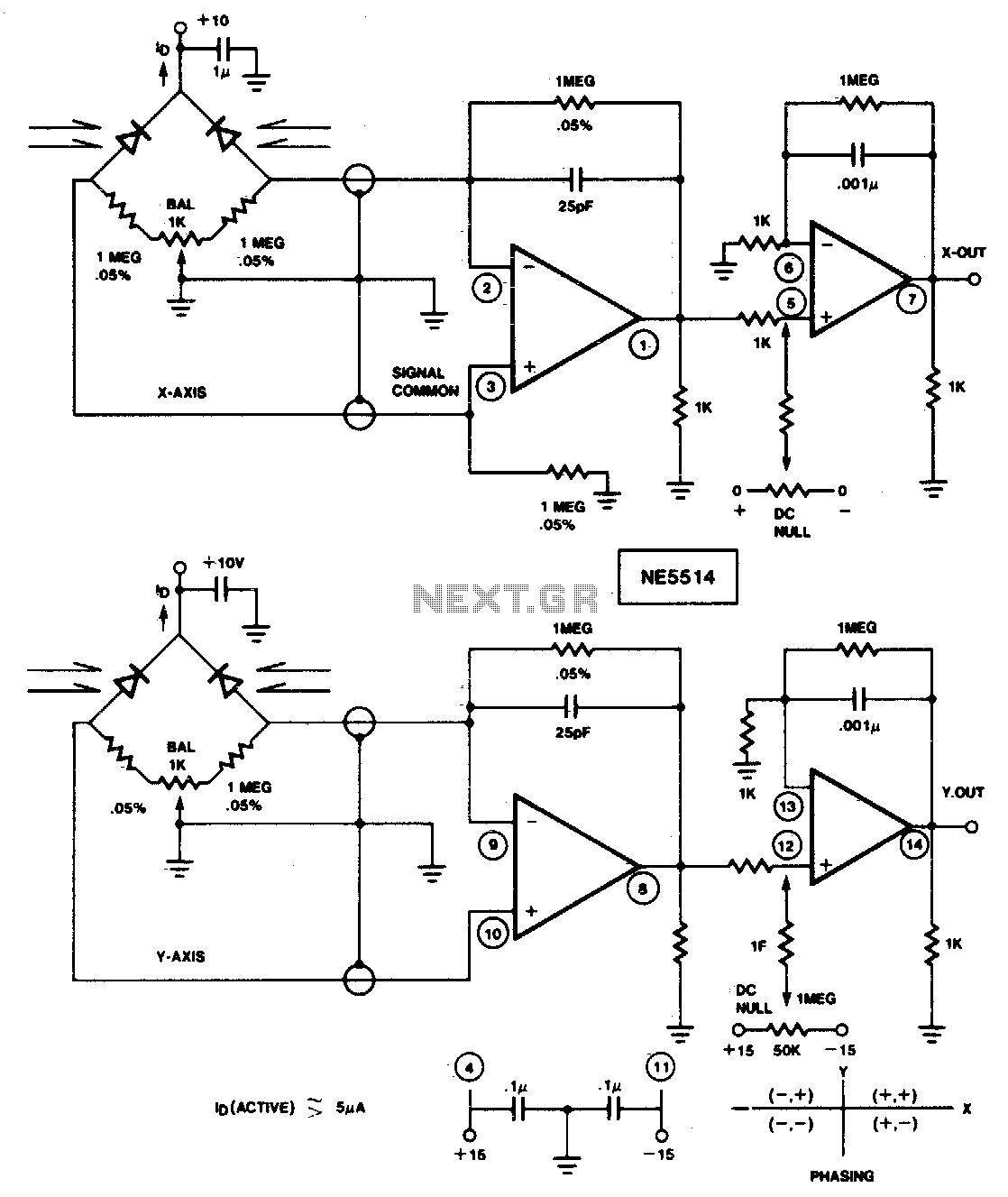
This circuit is designed to detect four-quadrant motion of a light source. By appropriately summing the signals from the X and Y axes, the resulting four-quadrant output can be utilized with an X-Y plotter, oscilloscope, or computer for simulation purposes. The integrated circuit used in this application is the NE/SE5514.
The circuit operates by utilizing photodetectors aligned along the X and Y axes to capture the intensity of light. Each photodetector generates a voltage proportional to the light intensity it detects. The NE/SE5514 integrated circuit is essential for processing these signals, as it features differential inputs that allow for precise summation of the X and Y signals.
In a typical configuration, two photodiodes are positioned to face the light source, one aligned horizontally (X-axis) and the other vertically (Y-axis). The output voltages from these photodiodes are fed into the NE/SE5514, which performs the necessary signal conditioning and amplification. The output from the IC reflects the position of the light source in a four-quadrant coordinate system, enabling accurate tracking of its motion.
The summed output can be connected to an X-Y plotter, which graphically represents the light source's movement across a two-dimensional plane. Alternatively, the output can be directed to an oscilloscope to visualize the changes in voltage over time, or to a computer for further analysis and simulation. This versatility makes the circuit suitable for various applications, including robotic vision systems, light tracking mechanisms, and experimental setups in optics research.
In summary, this circuit provides a compact and efficient solution for sensing and visualizing the motion of a light source in a four-quadrant space, leveraging the capabilities of the NE/SE5514 integrated circuit for optimal performance.Use this circuit to sense four quadrant motion of a light source By proper summing of the signals from the X and Y axes, four quadrant output may be fed to an X-Y plotter, oscilloscope, or computer for simulation. IC = NE/SE5514.
The circuit operates by utilizing photodetectors aligned along the X and Y axes to capture the intensity of light. Each photodetector generates a voltage proportional to the light intensity it detects. The NE/SE5514 integrated circuit is essential for processing these signals, as it features differential inputs that allow for precise summation of the X and Y signals.
In a typical configuration, two photodiodes are positioned to face the light source, one aligned horizontally (X-axis) and the other vertically (Y-axis). The output voltages from these photodiodes are fed into the NE/SE5514, which performs the necessary signal conditioning and amplification. The output from the IC reflects the position of the light source in a four-quadrant coordinate system, enabling accurate tracking of its motion.
The summed output can be connected to an X-Y plotter, which graphically represents the light source's movement across a two-dimensional plane. Alternatively, the output can be directed to an oscilloscope to visualize the changes in voltage over time, or to a computer for further analysis and simulation. This versatility makes the circuit suitable for various applications, including robotic vision systems, light tracking mechanisms, and experimental setups in optics research.
In summary, this circuit provides a compact and efficient solution for sensing and visualizing the motion of a light source in a four-quadrant space, leveraging the capabilities of the NE/SE5514 integrated circuit for optimal performance.Use this circuit to sense four quadrant motion of a light source By proper summing of the signals from the X and Y axes, four quadrant output may be fed to an X-Y plotter, oscilloscope, or computer for simulation. IC = NE/SE5514.