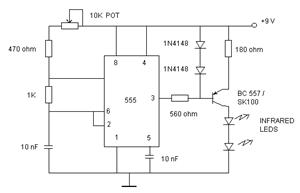
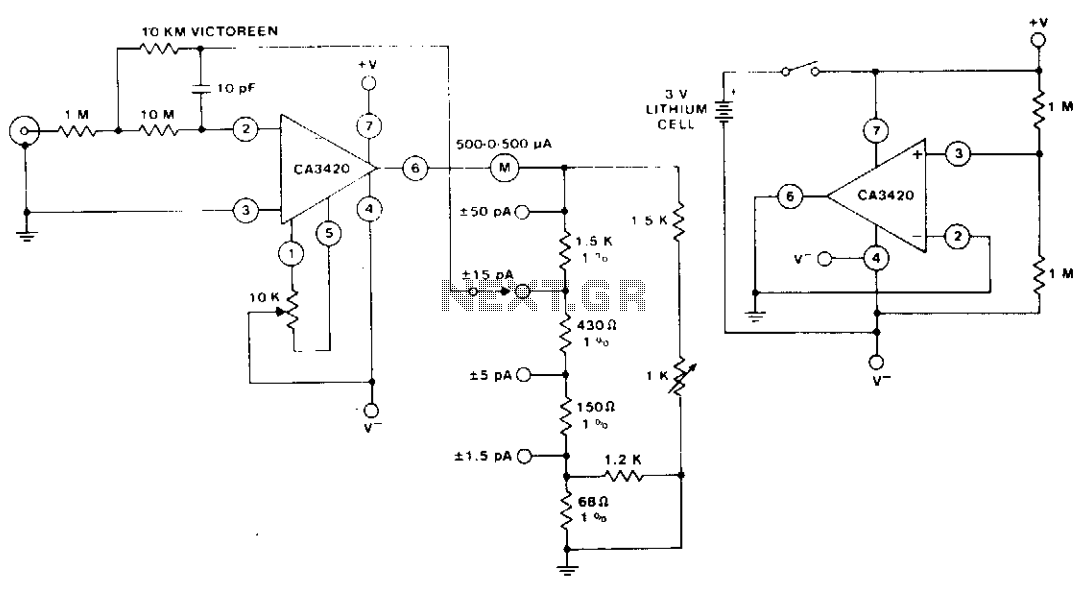
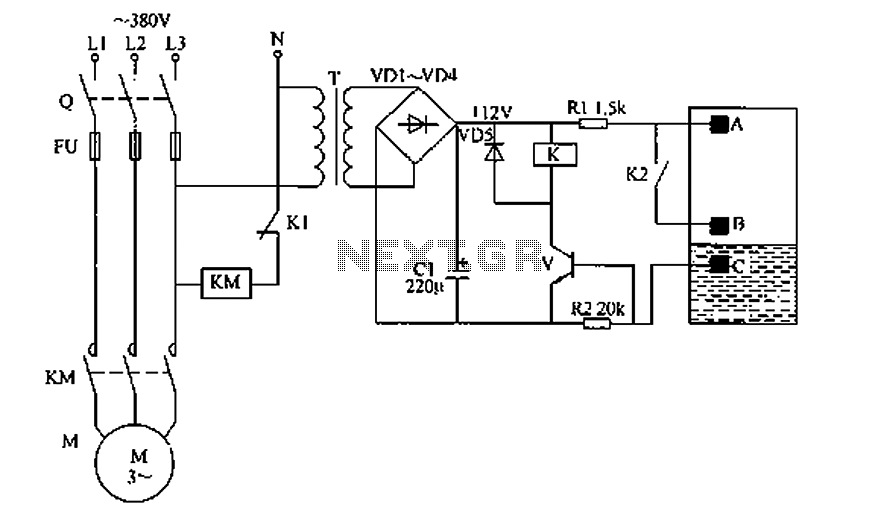
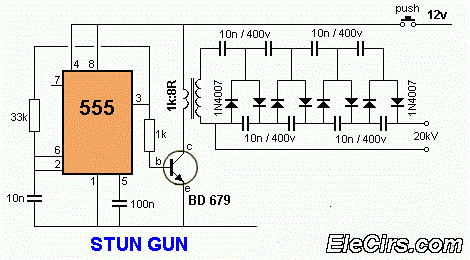
General Purpose Amplifier circuit diagram
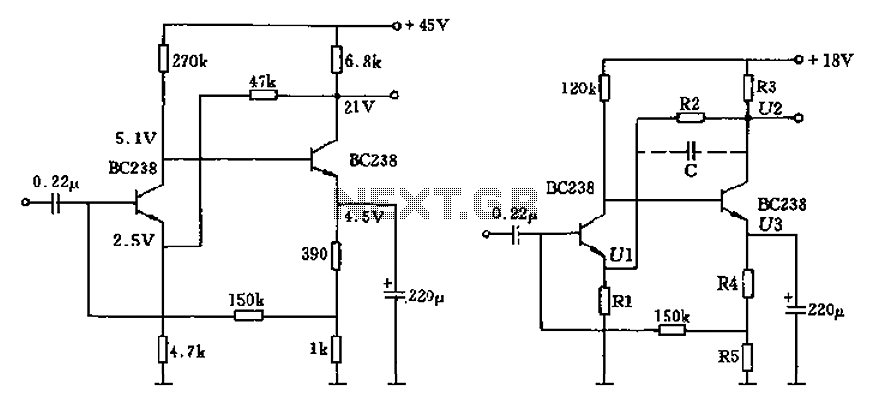
The circuit characteristic involves the elimination of external input resistors, which reduces the influence on the stabilization of the working point. It also employs two DC negative feedback loops. Additionally, the output from the second stage connects to the extreme base, while the collector of the second stage is linked to the emitter of the first stage.
The described circuit features a unique configuration that enhances performance by removing external input resistors. This modification significantly minimizes the variability associated with the working point stabilization, allowing for more consistent circuit behavior. The implementation of two DC negative feedback loops serves to further stabilize the circuit's operation, improving linearity and reducing distortion.
In this configuration, the first stage operates as a signal amplifier, where the output is derived from the extreme base. This arrangement ensures that the signal is amplified before being processed by the second stage. The second stage, which follows the first, receives its input from the collector of the first stage. By linking the collector of the second stage back to the emitter of the first stage, the circuit creates a feedback path that enhances stability and linearity.
The use of negative feedback in this circuit is crucial, as it helps to counteract any variations in the output that may arise due to changes in temperature or supply voltage. By continuously feeding a portion of the output back into the input, the circuit can maintain a more stable operational point, leading to improved performance across a range of conditions.
This circuit design is particularly beneficial in applications requiring high fidelity and precision, such as audio amplification or signal processing systems. The elimination of external resistors and the strategic use of feedback contribute to a more reliable and efficient circuit, ultimately resulting in superior performance. Circuit characteristic is the elimination of the external input resistors, thereby reducing the element of the working point stabilization, also uses two DC negative feedback; the second stage exit from the first stage of the extreme base and collector from the second stage to the first stage emitter.
The described circuit features a unique configuration that enhances performance by removing external input resistors. This modification significantly minimizes the variability associated with the working point stabilization, allowing for more consistent circuit behavior. The implementation of two DC negative feedback loops serves to further stabilize the circuit's operation, improving linearity and reducing distortion.
In this configuration, the first stage operates as a signal amplifier, where the output is derived from the extreme base. This arrangement ensures that the signal is amplified before being processed by the second stage. The second stage, which follows the first, receives its input from the collector of the first stage. By linking the collector of the second stage back to the emitter of the first stage, the circuit creates a feedback path that enhances stability and linearity.
The use of negative feedback in this circuit is crucial, as it helps to counteract any variations in the output that may arise due to changes in temperature or supply voltage. By continuously feeding a portion of the output back into the input, the circuit can maintain a more stable operational point, leading to improved performance across a range of conditions.
This circuit design is particularly beneficial in applications requiring high fidelity and precision, such as audio amplification or signal processing systems. The elimination of external resistors and the strategic use of feedback contribute to a more reliable and efficient circuit, ultimately resulting in superior performance. Circuit characteristic is the elimination of the external input resistors, thereby reducing the element of the working point stabilization, also uses two DC negative feedback; the second stage exit from the first stage of the extreme base and collector from the second stage to the first stage emitter.