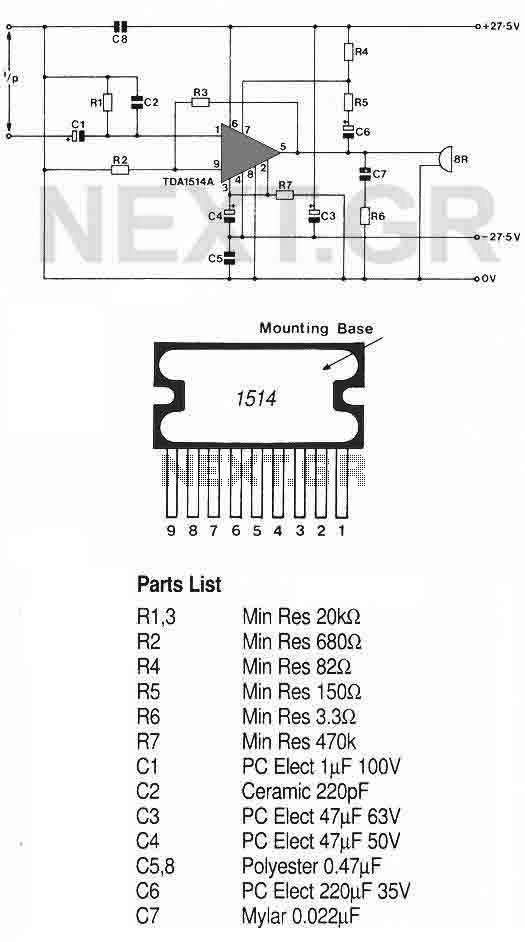
Guitar Amp
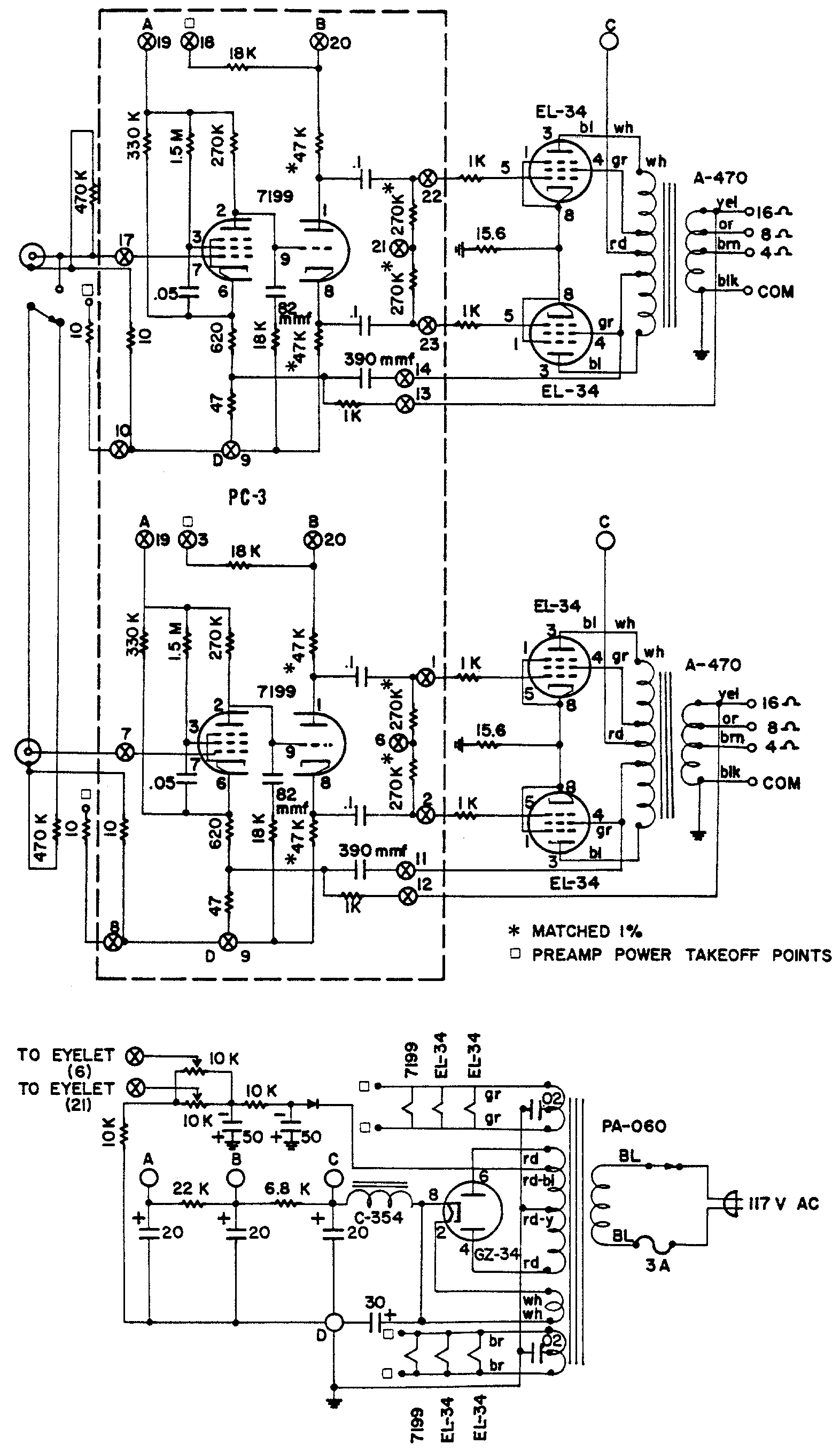
This amplifier exhibited hum and noise issues. To address this, capacitors were added to the power supply; however, the voltage levels were excessively high, resulting in sparks at the final tube socket pins. Consequently, the capacitors were removed.
The described amplifier circuit encountered issues primarily related to power supply noise and high voltage levels. The presence of hum and noise in audio amplifiers is often attributed to inadequate filtering in the power supply section. In this case, the addition of capacitors aimed to enhance the filtering capability, thereby reducing the noise.
However, the modification led to an unexpected increase in voltage levels, which can occur if the capacitors added were of inappropriate value or if they were not properly rated for the voltage present in the circuit. High voltage conditions can be detrimental, particularly in tube amplifiers, where excessive voltage can lead to arcing or sparking at the socket pins of the final output tubes. This phenomenon indicates that the voltage exceeded the safe operating limits of the components, potentially damaging the tubes or other circuit elements.
To resolve these issues in future designs, it is essential to select capacitors that are rated for the specific voltage levels present in the circuit. Additionally, implementing a voltage regulation mechanism or using capacitors with higher capacitance values may improve filtering without causing excessive voltage spikes. Properly sizing and placing these components within the circuit can help maintain stability and prevent noise while ensuring the safety and longevity of the amplifier's components.This amp had hum and nosise. So I added cpacitors at power supply, but Voltage was high. There was spark at final tube socket pins. So I pulled off capacitors. 🔗 External reference
The described amplifier circuit encountered issues primarily related to power supply noise and high voltage levels. The presence of hum and noise in audio amplifiers is often attributed to inadequate filtering in the power supply section. In this case, the addition of capacitors aimed to enhance the filtering capability, thereby reducing the noise.
However, the modification led to an unexpected increase in voltage levels, which can occur if the capacitors added were of inappropriate value or if they were not properly rated for the voltage present in the circuit. High voltage conditions can be detrimental, particularly in tube amplifiers, where excessive voltage can lead to arcing or sparking at the socket pins of the final output tubes. This phenomenon indicates that the voltage exceeded the safe operating limits of the components, potentially damaging the tubes or other circuit elements.
To resolve these issues in future designs, it is essential to select capacitors that are rated for the specific voltage levels present in the circuit. Additionally, implementing a voltage regulation mechanism or using capacitors with higher capacitance values may improve filtering without causing excessive voltage spikes. Properly sizing and placing these components within the circuit can help maintain stability and prevent noise while ensuring the safety and longevity of the amplifier's components.This amp had hum and nosise. So I added cpacitors at power supply, but Voltage was high. There was spark at final tube socket pins. So I pulled off capacitors. 🔗 External reference