H Bridge design for robotics and motion control systems
H-bridge applications for robots, robotics, and motor control. This post focuses on the low-side switch element.
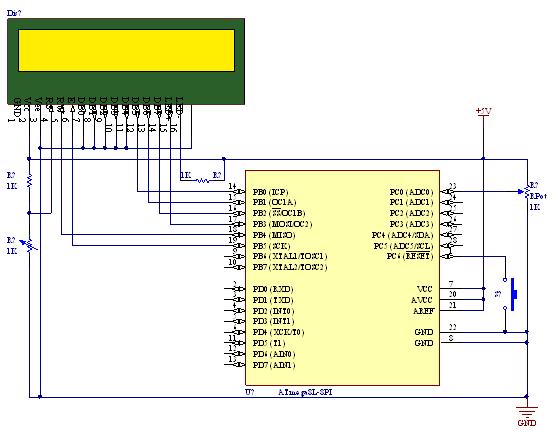
H-bridges are widely utilized in robotics and motor control applications to enable bidirectional control of DC motors. An H-bridge consists of four switches arranged in a configuration that allows current to flow in either direction through the motor, facilitating forward and reverse rotation. The low-side switch element specifically refers to the switches connected to the ground side of the motor circuit.
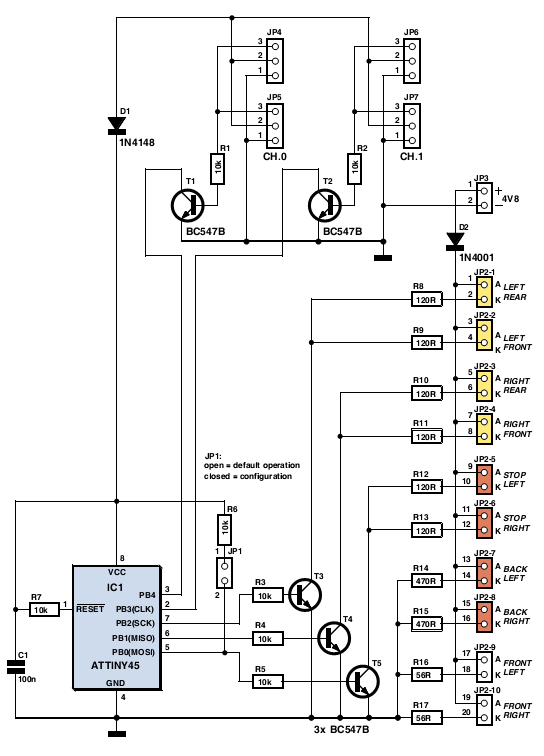
In a typical H-bridge configuration, two low-side switches are employed, which are often implemented using MOSFETs or bipolar junction transistors (BJTs). When one low-side switch is turned on, it completes the circuit, allowing current to flow through the motor in one direction. Conversely, activating the other low-side switch reverses the current flow, enabling the motor to rotate in the opposite direction. This control method is essential for applications requiring precise motor direction and speed control.
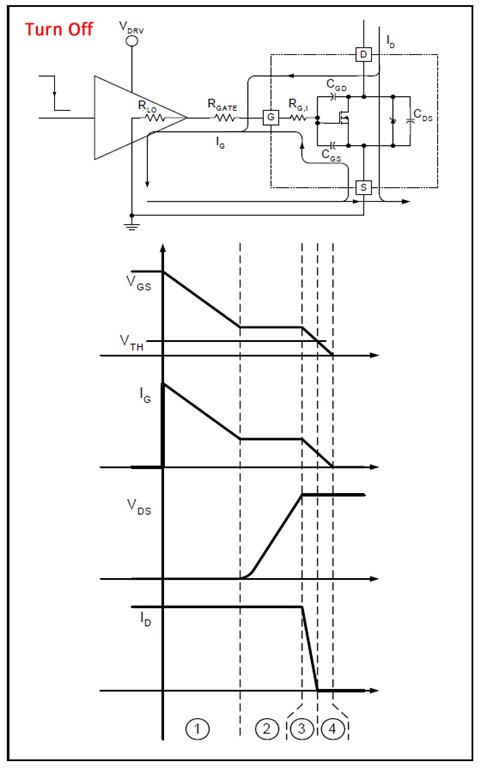
The low-side switch configuration offers several advantages, including simpler drive circuitry and reduced complexity in the control logic. Additionally, it helps to minimize the risk of shoot-through conditions, which can occur if both high-side and low-side switches are activated simultaneously. Proper design considerations must be made regarding the gate drive signals to ensure that the switches are turned on and off at the appropriate times, preventing damage to the components and ensuring efficient operation.
In summary, the low-side switch element in an H-bridge plays a critical role in the effective control of motors in robotic applications. Its ability to manage current flow direction is fundamental to achieving the desired motion control, making it a vital component in modern robotics and automation systems.H bridge applications for robots, robotics, and motor control. This post focuses on the low side switch element. 🔗 External reference
H-bridges are widely utilized in robotics and motor control applications to enable bidirectional control of DC motors. An H-bridge consists of four switches arranged in a configuration that allows current to flow in either direction through the motor, facilitating forward and reverse rotation. The low-side switch element specifically refers to the switches connected to the ground side of the motor circuit.
In a typical H-bridge configuration, two low-side switches are employed, which are often implemented using MOSFETs or bipolar junction transistors (BJTs). When one low-side switch is turned on, it completes the circuit, allowing current to flow through the motor in one direction. Conversely, activating the other low-side switch reverses the current flow, enabling the motor to rotate in the opposite direction. This control method is essential for applications requiring precise motor direction and speed control.
The low-side switch configuration offers several advantages, including simpler drive circuitry and reduced complexity in the control logic. Additionally, it helps to minimize the risk of shoot-through conditions, which can occur if both high-side and low-side switches are activated simultaneously. Proper design considerations must be made regarding the gate drive signals to ensure that the switches are turned on and off at the appropriate times, preventing damage to the components and ensuring efficient operation.
In summary, the low-side switch element in an H-bridge plays a critical role in the effective control of motors in robotic applications. Its ability to manage current flow direction is fundamental to achieving the desired motion control, making it a vital component in modern robotics and automation systems.H bridge applications for robots, robotics, and motor control. This post focuses on the low side switch element. 🔗 External reference