
Hall-effect-compass
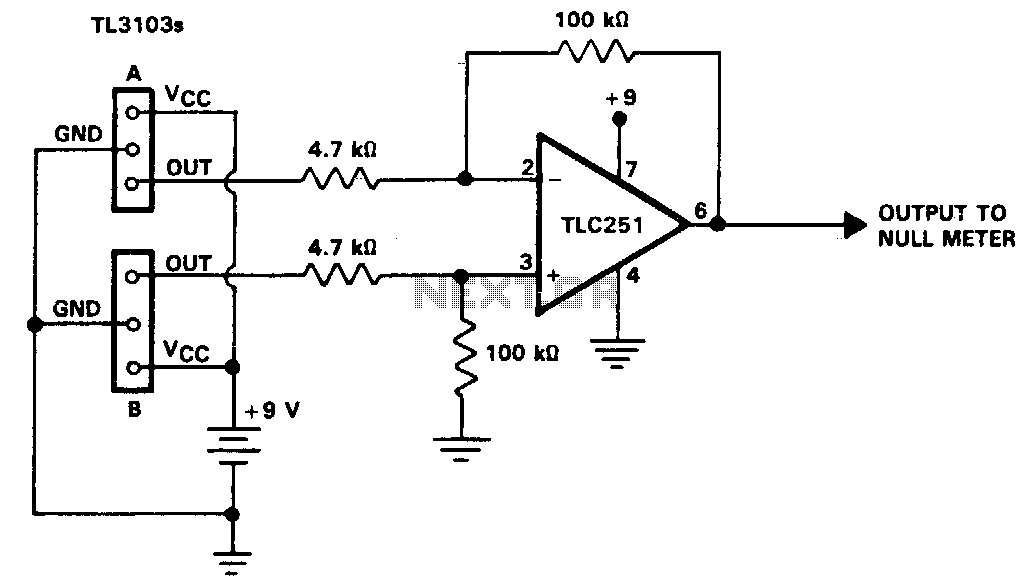
The TL3103 linear Hall-effect device can be used as a compass. By definition, the north pole of a magnet is the pole that is attracted to the magnetic north pole of the Earth. The north pole of a magnet repels the north-seeking pole of a compass. By convention, lines of flux emanate from the north pole of a magnet and enter the south pole. The circuit of the compass is shown. By using two TL3103 devices instead of one, sensitivity is doubled. With each device facing in opposite directions, device A provides a positive output while the output of device B is negative in relation to the zero magnetic field level. This configuration yields a differential signal that can be applied to the TLC251 operational amplifier. The op-amp is configured as a difference amplifier with a gain of 20. Its output is directed to a null meter or a bridge balance indicator circuit.
The TL3103 linear Hall-effect sensor operates by detecting the presence and intensity of magnetic fields. This device is particularly useful in navigation applications, such as compasses, where accurate detection of the Earth's magnetic field is critical. In the described circuit, two TL3103 sensors are strategically positioned to enhance sensitivity and provide a more accurate reading of the magnetic field.
When the two sensors are oriented in opposite directions, they can effectively measure the magnetic field's polarity and strength. Device A, facing one direction, will register a positive voltage output in the presence of a magnetic field, while device B, facing the opposite direction, will produce a negative voltage output under the same conditions. This differential output is crucial for determining the direction of the magnetic field relative to the sensors.
The differential signal generated by the two TL3103 devices is then fed into the TLC251 operational amplifier. This op-amp is configured as a difference amplifier, which amplifies the difference between the two input signals. The gain of 20 ensures that even small variations in the magnetic field can be detected, making the system highly sensitive. The amplified output from the op-amp can then be connected to a null meter or a bridge balance indicator circuit, which provides a visual representation of the magnetic field's direction and intensity. This setup is beneficial for applications requiring precise navigation data, such as in robotics, drones, and other autonomous systems.The TL3103 linear Hall-effect device can be used as a compass. By definition, the north pole of a magnet is the pole that is attracted by the magnetic north pole of the earth. The north pole of a magnet repels the north-seeking pole of a compass. By convention, lines of flux emanate from the north pole of a magnet and enter the south pole. The circuit of the compass is shown. By using two TL3103 devices instead of one, we achieve twice the sensitivity. With each device facing the opposite direction, device A would have a position output while the output of device B would be negative with respect to the zero magnetic field level. This gives a differential signal to apply to the TLC251 op amp. The op amp is connected as a difference amplifier with a gain of 20. Its output is applied to a null meter or a bridge balance indicator circuit.
The TL3103 linear Hall-effect sensor operates by detecting the presence and intensity of magnetic fields. This device is particularly useful in navigation applications, such as compasses, where accurate detection of the Earth's magnetic field is critical. In the described circuit, two TL3103 sensors are strategically positioned to enhance sensitivity and provide a more accurate reading of the magnetic field.
When the two sensors are oriented in opposite directions, they can effectively measure the magnetic field's polarity and strength. Device A, facing one direction, will register a positive voltage output in the presence of a magnetic field, while device B, facing the opposite direction, will produce a negative voltage output under the same conditions. This differential output is crucial for determining the direction of the magnetic field relative to the sensors.
The differential signal generated by the two TL3103 devices is then fed into the TLC251 operational amplifier. This op-amp is configured as a difference amplifier, which amplifies the difference between the two input signals. The gain of 20 ensures that even small variations in the magnetic field can be detected, making the system highly sensitive. The amplified output from the op-amp can then be connected to a null meter or a bridge balance indicator circuit, which provides a visual representation of the magnetic field's direction and intensity. This setup is beneficial for applications requiring precise navigation data, such as in robotics, drones, and other autonomous systems.The TL3103 linear Hall-effect device can be used as a compass. By definition, the north pole of a magnet is the pole that is attracted by the magnetic north pole of the earth. The north pole of a magnet repels the north-seeking pole of a compass. By convention, lines of flux emanate from the north pole of a magnet and enter the south pole. The circuit of the compass is shown. By using two TL3103 devices instead of one, we achieve twice the sensitivity. With each device facing the opposite direction, device A would have a position output while the output of device B would be negative with respect to the zero magnetic field level. This gives a differential signal to apply to the TLC251 op amp. The op amp is connected as a difference amplifier with a gain of 20. Its output is applied to a null meter or a bridge balance indicator circuit.