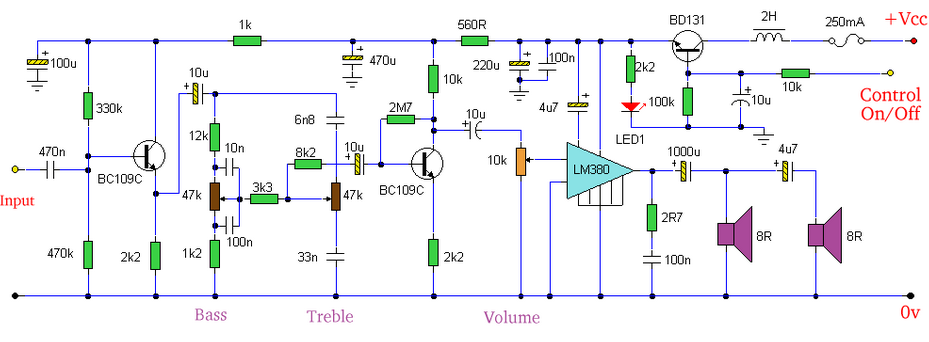
hard disk switch schematics
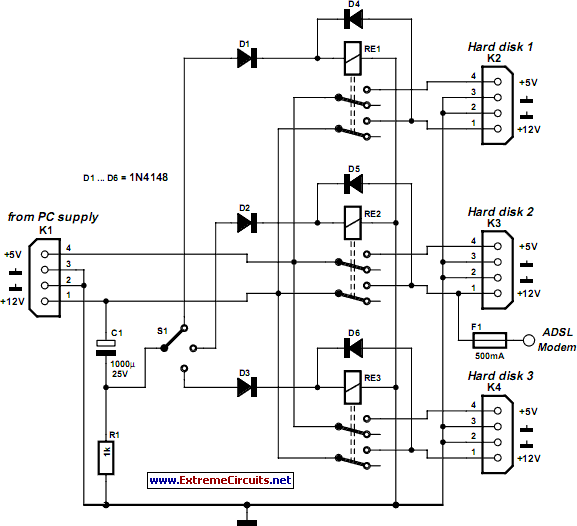
In today's environment, where viruses and other threats from the Internet are prevalent, it is essential to ensure that a personal computer (PC) remains secure from infections. This circuit was designed to facilitate the installation of multiple hard disks within a PC case, arranged in such a manner that viruses cannot transfer between disks. Specifically, three drives are installed: one for Internet use via ADSL, another for email, and a third for various applications. By ensuring that data from the Internet does not reach the third disk, it remains effectively protected against viruses. This solution has been successfully utilized for several years. An additional advantage is that if any operational issues arise with the computer, switching to another hard disk allows for easy troubleshooting. The circuit functions by selectively switching the power supply voltages (5 V and 12 V) of the hard disks, rendering any unpowered disk inactive. This method works seamlessly with S-ATA disks and is compatible with modern IDE drives, provided that only hard disks are connected to the relevant port, excluding CD-ROMs, DVD drives, or similar devices. The selection of the desired hard disk is accomplished using a rotary switch, which must be set to the appropriate position before powering on the computer. Upon powering up, one of three relays is activated via diodes D1, D2, or D3. Each relay is equipped with a hold circuit through a second diode (D4, D5, and D6), ensuring that the selected relay remains energized as long as the power supply voltage is present. After startup, electrolytic capacitor C1 charges through resistor R1, quickly bringing the common contact of the rotary switch to 0 V. This design feature prevents accidental switching of hard disks while the computer is operational. The ADSL modem receives power from the PC, which is only available when hard disk number 2 is selected, thereby restricting Internet access when any other disk is in use.
The circuit design employs a robust mechanism to enhance PC security by isolating hard disks from potential virus transmission. The use of a rotary switch simplifies the selection process for the user, ensuring that the configuration is set prior to system activation, which mitigates the risk of system instability caused by unintended disk switching. The relay system, controlled by diodes, provides reliable operation, maintaining the selected hard disk in an active state until the power is turned off, thereby preserving the integrity of the data on the inactive disks.
The inclusion of an electrolytic capacitor in the circuit aids in stabilizing the switch state during power-up, preventing any transient conditions that could lead to misoperation. Additionally, the design’s consideration for compatibility with both S-ATA and modern IDE drives ensures versatility in hard disk selection, accommodating a wide range of hardware configurations. The restriction of modem power to only one specific disk further enhances security by ensuring that Internet access is tightly controlled.
In summary, this circuit represents an effective solution for managing multiple hard disks within a PC, providing a practical approach to safeguarding against viruses while facilitating easy maintenance and troubleshooting. The careful arrangement of components and the use of established electronic principles contribute to a reliable and user-friendly design.In these times with viruses and other threats from the Internet it would be nice to have reassurance that the PC cannot be infected. That is why this circuit was designed. It makes it possible to install multiple hard disks inside the case of a PC, which are separated in such a way that viruses cannot move from one disk to another.
In this case th ere are three drives installed, one for use of the Internet via ADSL, one for working with email and one for other applications. If data from the Internet never arrives on the third disk, it is effectively protected against viruses.
The solution outlined here has been in satisfactory use for a couple of years. There is an additional benefit: if there are ever any problems with the operation of the computer, then it is very easy to change to another hard disk to check if the problem manifests itself there as well. In this case, fault finding can be made much easier. The circuit operates by only switching over the power supply voltages (5 V and 12 V) of the hard disks.
The hard disk is out of service without a power supply. This works without a problem with S-ATA disks. With IDE disks this only works with modern drives. There may only be a combination of hard disks on the relevant port and no CD-ROM, DVD-drive, CD-burner or something similar. The selection of the desired hard disk is done with a rotary switch. This has to be set to the correct position before the computer is switched on. When the power supply is turned on, one of three relays is driven via diode D1, D2 or D3. The relays are provided with a hold circuit via a second diode (D4, D5 and D6). In this way the selected relay remains energised as long as the power supply voltage is present. After switching on, electrolytic capacitor C1 is charged via R1, so that the common contact of the rotary switch is quickly at 0 V.
This prevents an accidental change of hard disk while the computer is in operation. The ADSL modem is powered from the PC. This power supply voltage is only present if hard disk number 2 is selected. This prevents the use of the Internet if one of the other disks is selected. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design employs a robust mechanism to enhance PC security by isolating hard disks from potential virus transmission. The use of a rotary switch simplifies the selection process for the user, ensuring that the configuration is set prior to system activation, which mitigates the risk of system instability caused by unintended disk switching. The relay system, controlled by diodes, provides reliable operation, maintaining the selected hard disk in an active state until the power is turned off, thereby preserving the integrity of the data on the inactive disks.
The inclusion of an electrolytic capacitor in the circuit aids in stabilizing the switch state during power-up, preventing any transient conditions that could lead to misoperation. Additionally, the design’s consideration for compatibility with both S-ATA and modern IDE drives ensures versatility in hard disk selection, accommodating a wide range of hardware configurations. The restriction of modem power to only one specific disk further enhances security by ensuring that Internet access is tightly controlled.
In summary, this circuit represents an effective solution for managing multiple hard disks within a PC, providing a practical approach to safeguarding against viruses while facilitating easy maintenance and troubleshooting. The careful arrangement of components and the use of established electronic principles contribute to a reliable and user-friendly design.In these times with viruses and other threats from the Internet it would be nice to have reassurance that the PC cannot be infected. That is why this circuit was designed. It makes it possible to install multiple hard disks inside the case of a PC, which are separated in such a way that viruses cannot move from one disk to another.
In this case th ere are three drives installed, one for use of the Internet via ADSL, one for working with email and one for other applications. If data from the Internet never arrives on the third disk, it is effectively protected against viruses.
The solution outlined here has been in satisfactory use for a couple of years. There is an additional benefit: if there are ever any problems with the operation of the computer, then it is very easy to change to another hard disk to check if the problem manifests itself there as well. In this case, fault finding can be made much easier. The circuit operates by only switching over the power supply voltages (5 V and 12 V) of the hard disks.
The hard disk is out of service without a power supply. This works without a problem with S-ATA disks. With IDE disks this only works with modern drives. There may only be a combination of hard disks on the relevant port and no CD-ROM, DVD-drive, CD-burner or something similar. The selection of the desired hard disk is done with a rotary switch. This has to be set to the correct position before the computer is switched on. When the power supply is turned on, one of three relays is driven via diode D1, D2 or D3. The relays are provided with a hold circuit via a second diode (D4, D5 and D6). In this way the selected relay remains energised as long as the power supply voltage is present. After switching on, electrolytic capacitor C1 is charged via R1, so that the common contact of the rotary switch is quickly at 0 V.
This prevents an accidental change of hard disk while the computer is in operation. The ADSL modem is powered from the PC. This power supply voltage is only present if hard disk number 2 is selected. This prevents the use of the Internet if one of the other disks is selected. 🔗 External reference