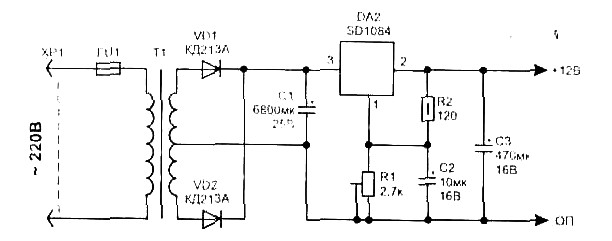
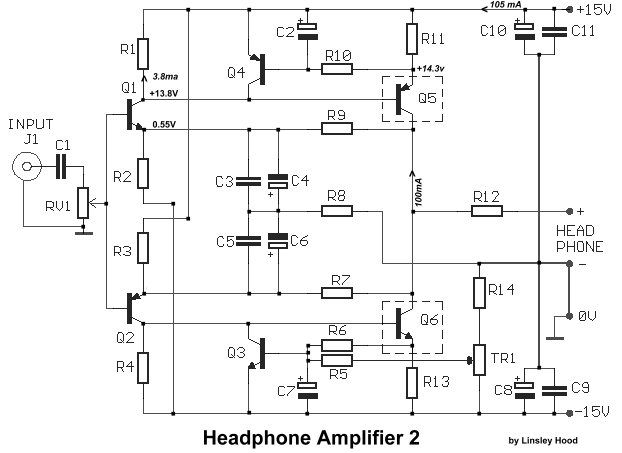
headphone class a amplifier
A small headphone amplifier is a valuable device capable of driving multiple pairs of headphones. The headphone amplifier's task is simplified due to the relatively low output power requirements and the manageable load characteristics. Headphones generally have an impedance ranging from 50 ohms to a typical 600 ohms and only require a maximum of 1-2V RMS for normal operation.
The headphone amplifier circuit typically consists of several key components designed to enhance audio signal quality while providing sufficient power to drive headphones effectively. The input stage often includes a buffer or preamplifier to accommodate various audio sources, ensuring that the signal is adequately conditioned before amplification. Operational amplifiers (op-amps) are frequently employed in this stage due to their high input impedance and low output impedance characteristics.
Following the input stage, a gain stage amplifies the signal to the required level. This is usually accomplished using additional op-amps configured in a non-inverting or inverting amplifier configuration, depending on the desired gain and circuit design. Feedback resistors are used to set the gain, allowing for flexibility in adjustment based on the specific requirements of the headphones being used.
The output stage is critical for driving the headphones. It often includes a class A or class AB amplifier configuration, which provides low distortion and high fidelity. Capacitive coupling may be employed at the output to block any DC offset, ensuring that only the AC audio signal reaches the headphones. Furthermore, a low-pass filter may be integrated to eliminate high-frequency noise, improving sound clarity.
Power supply considerations are also essential in headphone amplifier design. A regulated power supply is recommended to maintain consistent voltage levels, which helps prevent distortion and ensures optimal performance. Additionally, bypass capacitors are often placed close to the power supply pins of the op-amps to filter out noise and stabilize the power supply.
Thermal management is another aspect that should not be overlooked. Adequate heat sinking may be necessary for high-power applications to prevent overheating and ensure reliability during prolonged use.
In summary, the design of a headphone amplifier involves careful selection and arrangement of components to achieve the desired audio performance while meeting the specific impedance and power requirements of various headphones.It is a very useful thing , to have a small headphone amplifier , capable of driving a couple of pairs phones. Fortunately, the headphone amp has a much easier job to do, in that neither the output power requirements nor the load characteristics are so severe, since headphones typically have a load, impedance , higher of 50 ohm, (typical 600 ohm), and only require 1-2V RMS.
max, for normal output.. 🔗 External reference
The headphone amplifier circuit typically consists of several key components designed to enhance audio signal quality while providing sufficient power to drive headphones effectively. The input stage often includes a buffer or preamplifier to accommodate various audio sources, ensuring that the signal is adequately conditioned before amplification. Operational amplifiers (op-amps) are frequently employed in this stage due to their high input impedance and low output impedance characteristics.
Following the input stage, a gain stage amplifies the signal to the required level. This is usually accomplished using additional op-amps configured in a non-inverting or inverting amplifier configuration, depending on the desired gain and circuit design. Feedback resistors are used to set the gain, allowing for flexibility in adjustment based on the specific requirements of the headphones being used.
The output stage is critical for driving the headphones. It often includes a class A or class AB amplifier configuration, which provides low distortion and high fidelity. Capacitive coupling may be employed at the output to block any DC offset, ensuring that only the AC audio signal reaches the headphones. Furthermore, a low-pass filter may be integrated to eliminate high-frequency noise, improving sound clarity.
Power supply considerations are also essential in headphone amplifier design. A regulated power supply is recommended to maintain consistent voltage levels, which helps prevent distortion and ensures optimal performance. Additionally, bypass capacitors are often placed close to the power supply pins of the op-amps to filter out noise and stabilize the power supply.
Thermal management is another aspect that should not be overlooked. Adequate heat sinking may be necessary for high-power applications to prevent overheating and ensure reliability during prolonged use.
In summary, the design of a headphone amplifier involves careful selection and arrangement of components to achieve the desired audio performance while meeting the specific impedance and power requirements of various headphones.It is a very useful thing , to have a small headphone amplifier , capable of driving a couple of pairs phones. Fortunately, the headphone amp has a much easier job to do, in that neither the output power requirements nor the load characteristics are so severe, since headphones typically have a load, impedance , higher of 50 ohm, (typical 600 ohm), and only require 1-2V RMS.
max, for normal output.. 🔗 External reference