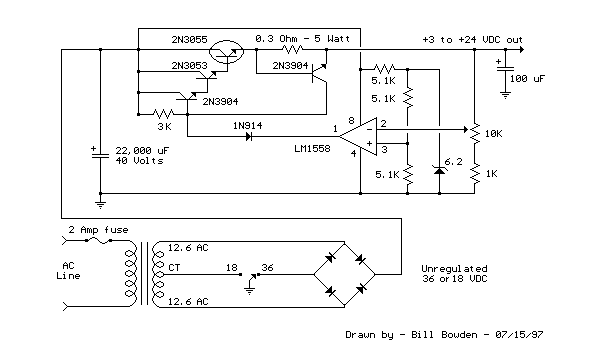
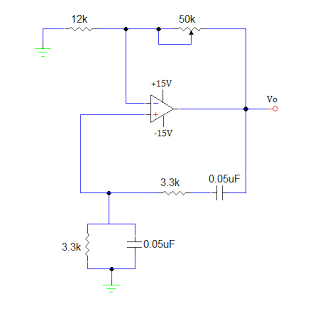
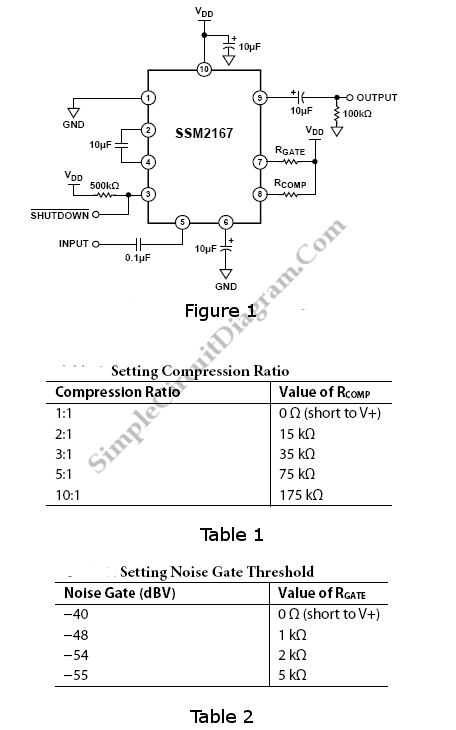
Improved 3 Transistor Audio Amp
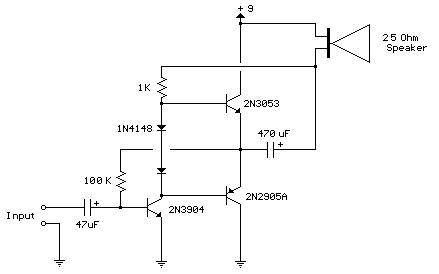
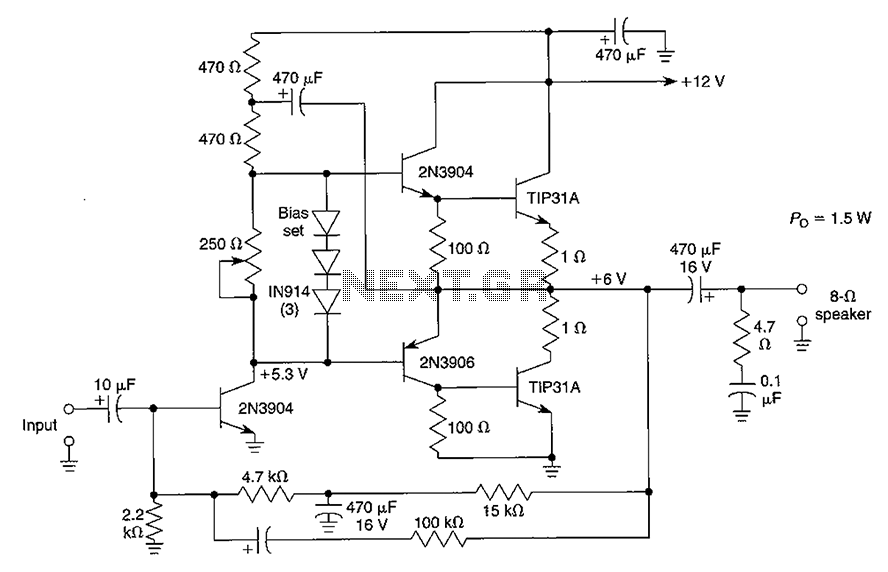
Improved 3 Transistor Audio Amplifier. The load resistor for the driver transistor is connected directly to the positive supply. This configuration has a disadvantage in that as the output moves positive, the voltage drop across...
The improved three-transistor audio amplifier circuit is designed to enhance audio signal amplification while addressing common issues associated with traditional amplifier designs. The circuit typically consists of three transistors configured in a way that optimizes performance and minimizes distortion.
In this configuration, the driver transistor's load resistor is connected directly to the positive supply voltage. While this approach simplifies the circuit design and can improve response time, it introduces a potential drawback. As the output signal transitions positively, the voltage drop across the load resistor can lead to a reduction in the effective output swing, potentially limiting the amplifier's ability to handle dynamic audio signals without clipping.
To mitigate this issue, careful selection of the load resistor and biasing resistors is essential. The load resistor should be chosen to ensure that it provides sufficient current to the driver transistor while maintaining a balance between output power and linearity. Additionally, the use of feedback mechanisms can help stabilize the gain and improve overall linearity, further enhancing audio fidelity.
The overall architecture may also incorporate capacitive coupling at the input and output stages to block DC offsets and prevent unwanted biasing of subsequent stages. This ensures that only the AC audio signal is amplified, preserving the integrity of the audio signal throughout the amplification process.
In summary, the improved three-transistor audio amplifier is a robust design that leverages the advantages of direct load connection while addressing the inherent challenges associated with output voltage swings. Proper component selection and circuit design considerations are crucial for achieving optimal performance in audio applications.Improved 3 Transistor Audio Amp , The load resistor for the driver transistor is tied directly to the + supply. This has a disadvantage in that as the output moves positive, the drop across.. 🔗 External reference
The improved three-transistor audio amplifier circuit is designed to enhance audio signal amplification while addressing common issues associated with traditional amplifier designs. The circuit typically consists of three transistors configured in a way that optimizes performance and minimizes distortion.
In this configuration, the driver transistor's load resistor is connected directly to the positive supply voltage. While this approach simplifies the circuit design and can improve response time, it introduces a potential drawback. As the output signal transitions positively, the voltage drop across the load resistor can lead to a reduction in the effective output swing, potentially limiting the amplifier's ability to handle dynamic audio signals without clipping.
To mitigate this issue, careful selection of the load resistor and biasing resistors is essential. The load resistor should be chosen to ensure that it provides sufficient current to the driver transistor while maintaining a balance between output power and linearity. Additionally, the use of feedback mechanisms can help stabilize the gain and improve overall linearity, further enhancing audio fidelity.
The overall architecture may also incorporate capacitive coupling at the input and output stages to block DC offsets and prevent unwanted biasing of subsequent stages. This ensures that only the AC audio signal is amplified, preserving the integrity of the audio signal throughout the amplification process.
In summary, the improved three-transistor audio amplifier is a robust design that leverages the advantages of direct load connection while addressing the inherent challenges associated with output voltage swings. Proper component selection and circuit design considerations are crucial for achieving optimal performance in audio applications.Improved 3 Transistor Audio Amp , The load resistor for the driver transistor is tied directly to the + supply. This has a disadvantage in that as the output moves positive, the drop across.. 🔗 External reference