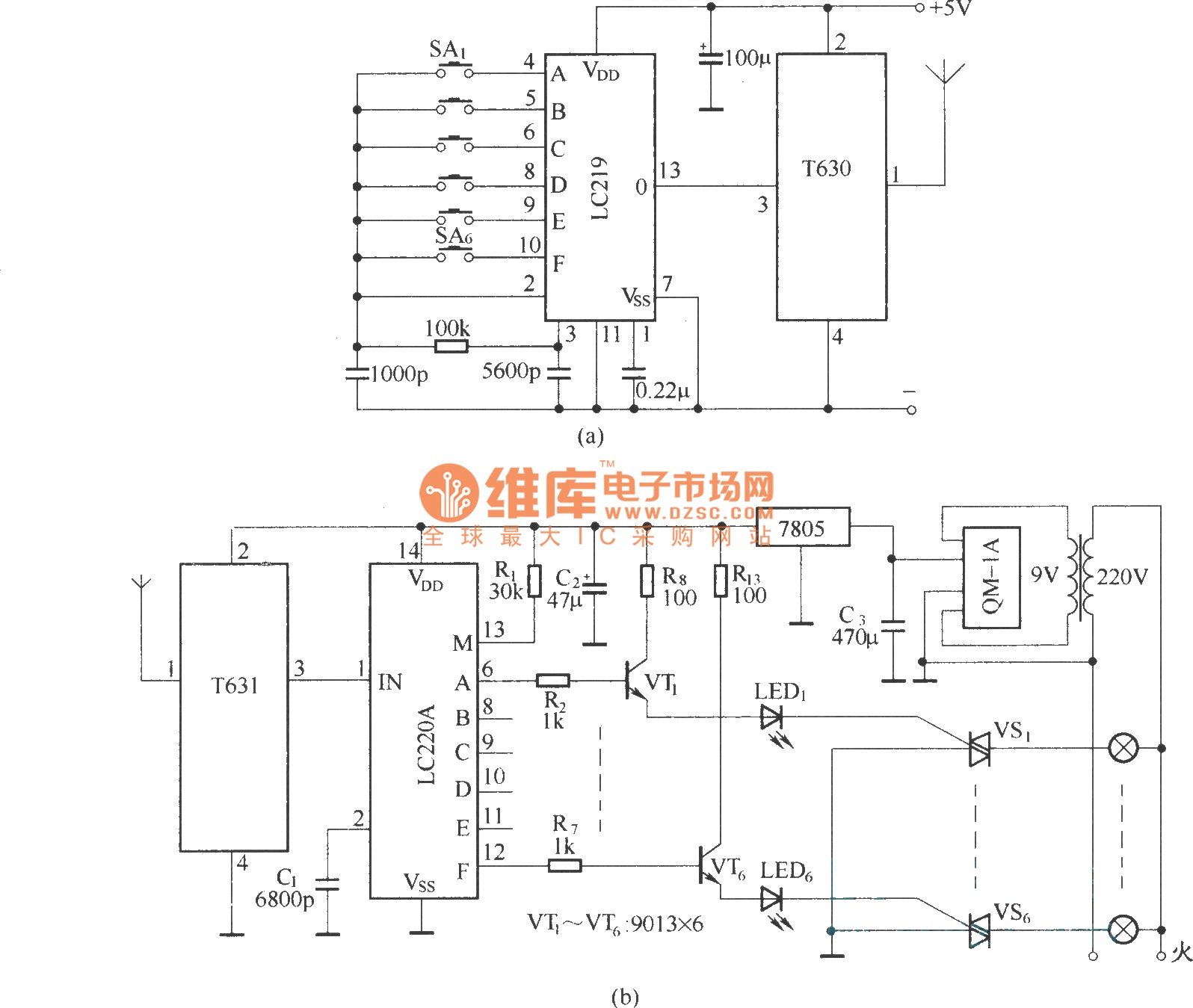
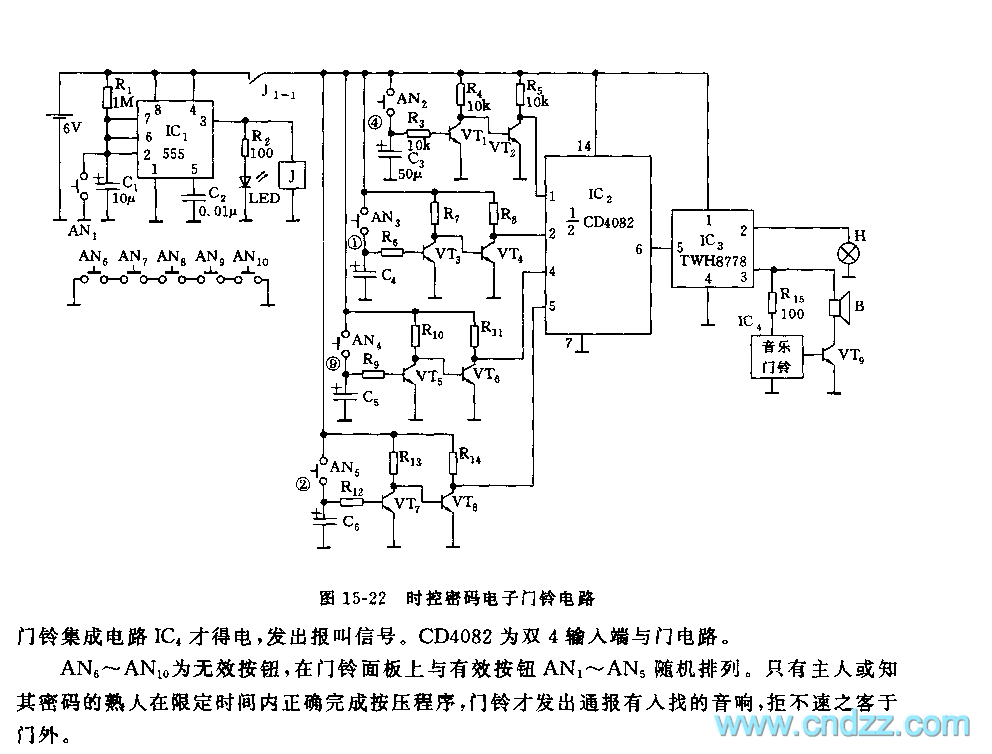
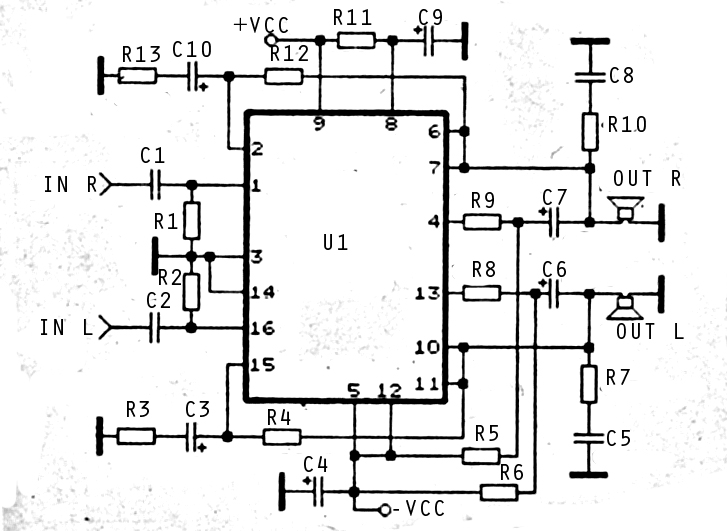
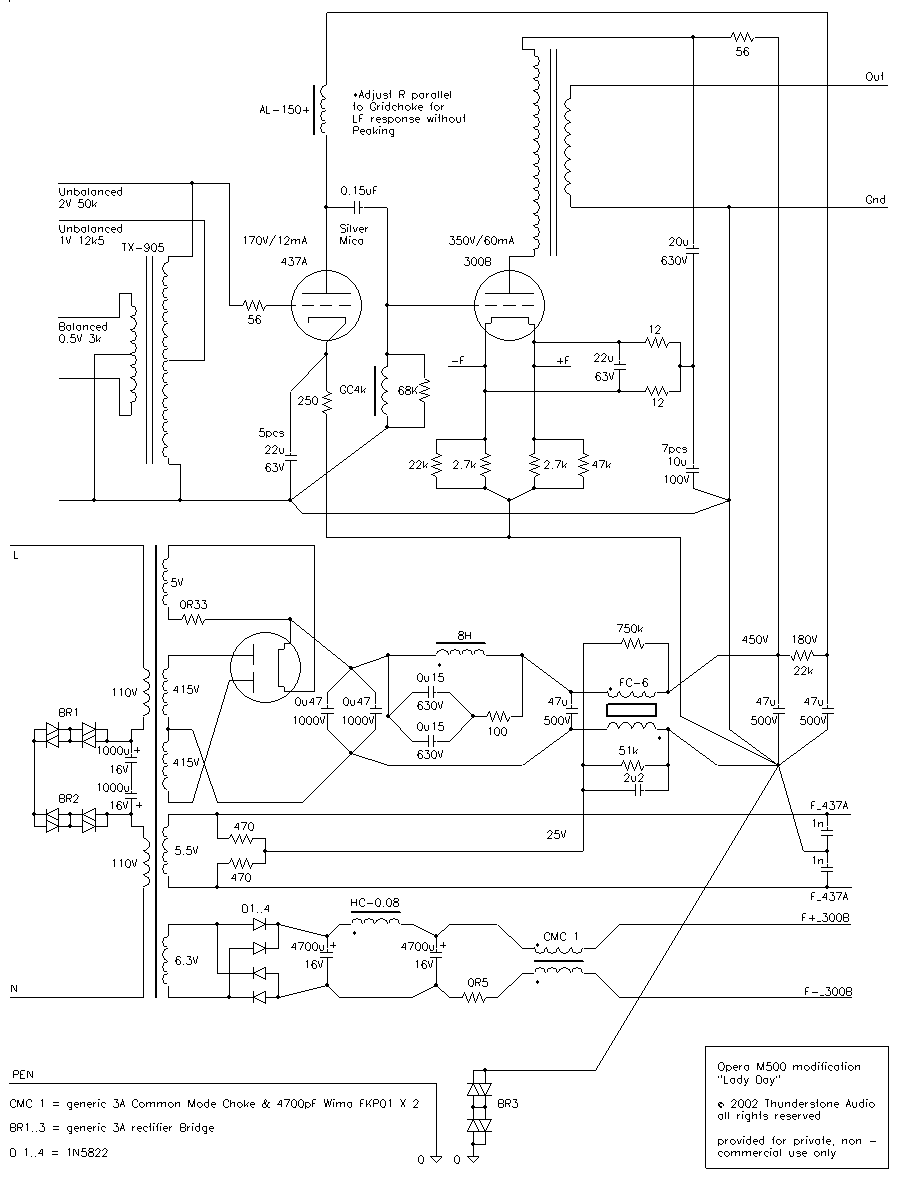
Improved Infrared Detector Circuit
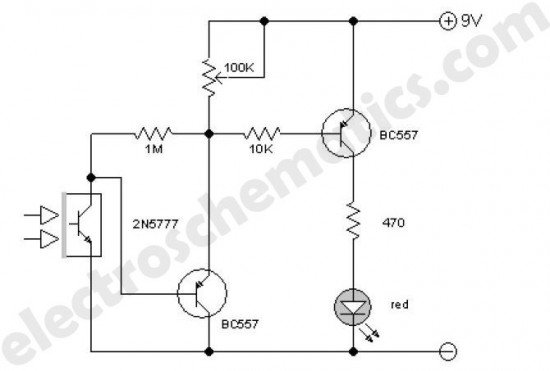
This enhanced infrared detector is designed for use with commercial infrared remote control handsets. This compact circuit is effective for quick go/no-go applications.
The infrared detector circuit is engineered to respond to signals emitted by infrared remote control devices, commonly used in consumer electronics. The core component of the circuit typically includes a photodiode or phototransistor, which detects infrared light. When an IR signal is transmitted from a remote control, the detector converts the light into an electrical signal.
To optimize the circuit's performance, it may integrate additional components such as operational amplifiers to amplify the received signal, filters to eliminate noise, and comparators to establish a threshold for signal detection. A microcontroller can also be incorporated to process the signal further, allowing for more complex functionalities such as decoding specific commands or interfacing with other electronic systems.
Power supply considerations are crucial for the circuit's operation. A stable voltage source, often from a battery or regulated power supply, ensures consistent performance. The circuit may also include power management features to minimize energy consumption, particularly important in battery-operated devices.
The physical layout of the circuit should ensure that the photodetector is positioned to have a clear line of sight to the remote control, maximizing its sensitivity and range. Additionally, the circuit design should account for environmental factors, such as ambient light interference, which could affect performance.
Overall, this infrared detector circuit represents a versatile solution for integrating remote control capabilities into various electronic devices, enhancing user experience and functionality.This improved infrared detector is specifically intended for use with commercial IR remote control handsets. This little circuit is useful for quick go/no-.. 🔗 External reference
The infrared detector circuit is engineered to respond to signals emitted by infrared remote control devices, commonly used in consumer electronics. The core component of the circuit typically includes a photodiode or phototransistor, which detects infrared light. When an IR signal is transmitted from a remote control, the detector converts the light into an electrical signal.
To optimize the circuit's performance, it may integrate additional components such as operational amplifiers to amplify the received signal, filters to eliminate noise, and comparators to establish a threshold for signal detection. A microcontroller can also be incorporated to process the signal further, allowing for more complex functionalities such as decoding specific commands or interfacing with other electronic systems.
Power supply considerations are crucial for the circuit's operation. A stable voltage source, often from a battery or regulated power supply, ensures consistent performance. The circuit may also include power management features to minimize energy consumption, particularly important in battery-operated devices.
The physical layout of the circuit should ensure that the photodetector is positioned to have a clear line of sight to the remote control, maximizing its sensitivity and range. Additionally, the circuit design should account for environmental factors, such as ambient light interference, which could affect performance.
Overall, this infrared detector circuit represents a versatile solution for integrating remote control capabilities into various electronic devices, enhancing user experience and functionality.This improved infrared detector is specifically intended for use with commercial IR remote control handsets. This little circuit is useful for quick go/no-.. 🔗 External reference