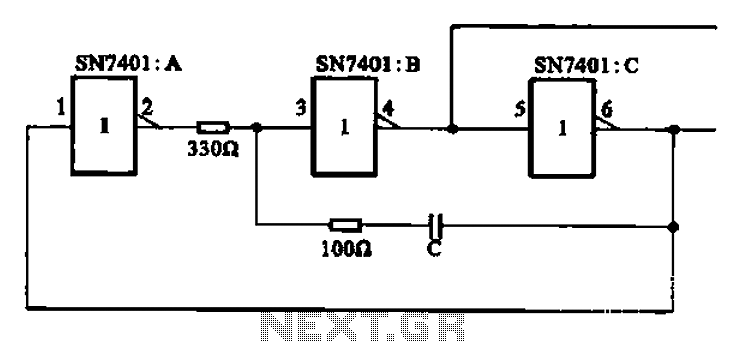
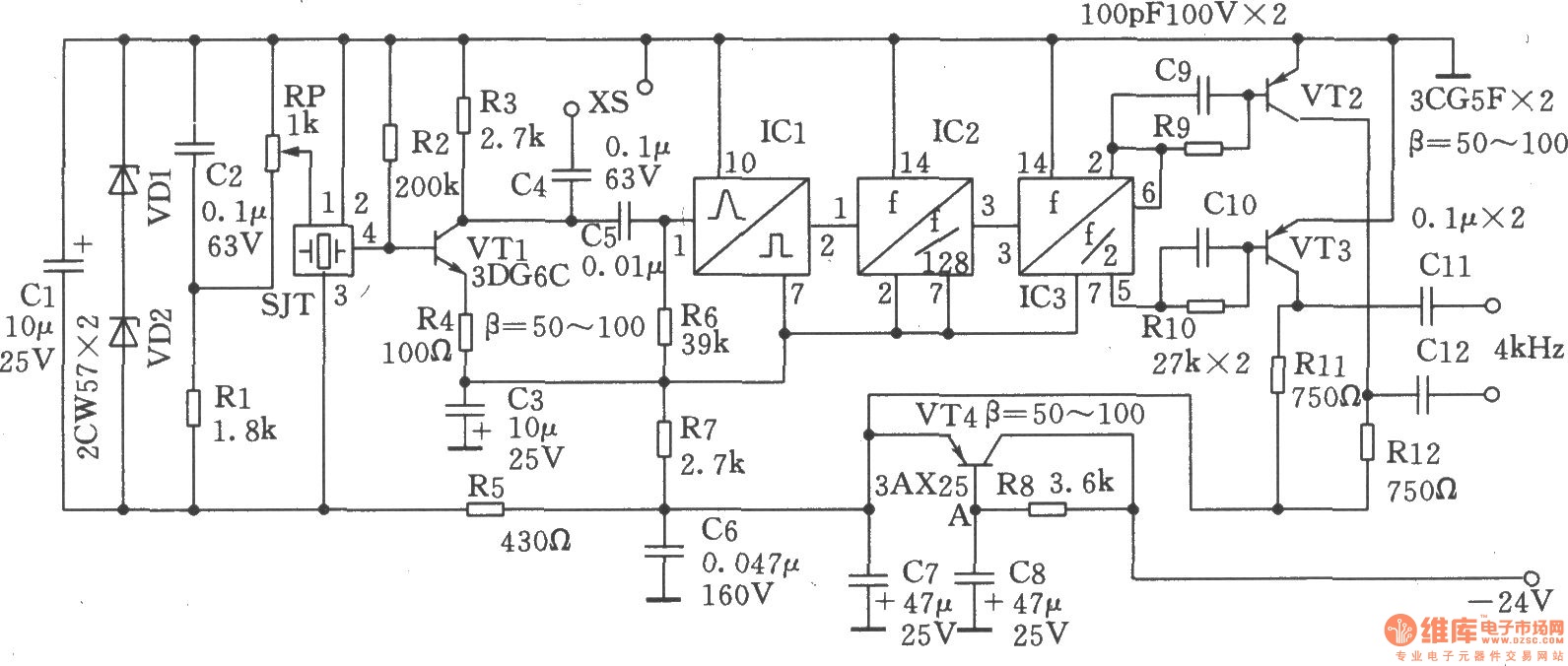
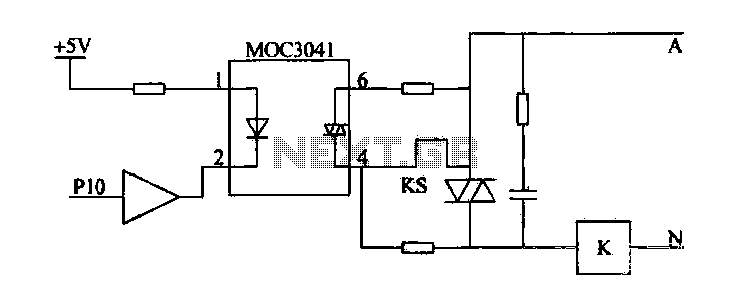
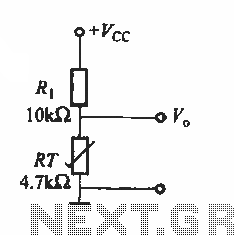
Inverting monostable circuit diagram
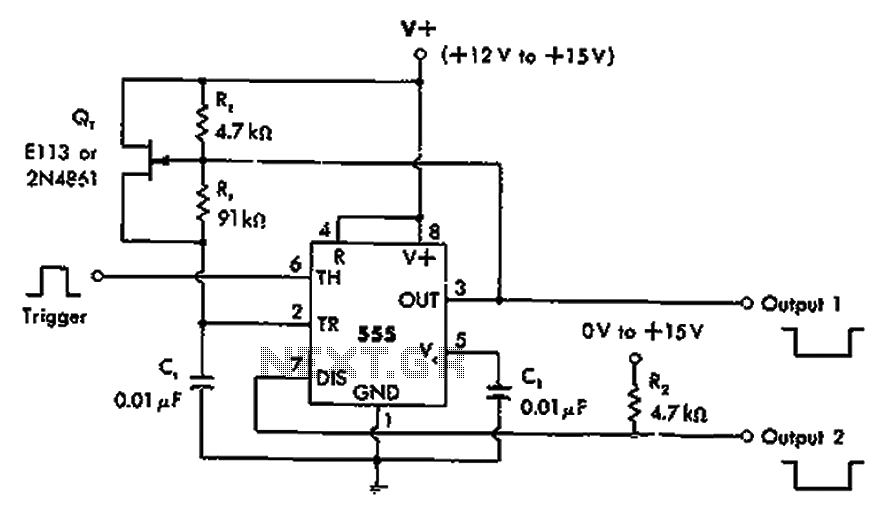
The timer 555 is activated by a positive trigger pulse, which results in negative output pulses. In scenarios where the duty cycle exceeds 99%, heavy loads can be disconnected from pin 7 without impacting timing accuracy, although loads exceeding pin 3 may affect timing precision.
The timer 555 is a versatile integrated circuit commonly used in various timing, delay, and oscillator applications. In a typical configuration, the 555 timer operates in either monostable or astable mode, depending on the desired output behavior. When triggered by a positive pulse at the trigger pin (pin 2), the timer transitions from its low state to a high state, producing a negative output pulse at the output pin (pin 3). This output pulse duration is determined by the external resistors and capacitors connected to the timer.
In applications where the duty cycle is maintained above 99%, the timer can effectively handle heavy loads connected to pin 7, which is the discharge pin. This feature allows for the separation of heavy loads from the timing components without compromising the accuracy of the timing cycle. However, care must be taken when loads exceed the specifications related to pin 3, as excessive loading can lead to inaccuracies in the timing intervals.
To ensure optimal performance, it is essential to select appropriate resistor and capacitor values to establish the desired timing characteristics while considering the load requirements. The 555 timer can be used in various circuits, including pulse-width modulation (PWM) applications, frequency generation, and timer circuits, making it a fundamental component in electronic design. Proper understanding of the connections and behavior of the 555 timer is crucial for achieving reliable and precise operation in diverse applications. As shown in the timer 555 is triggered by the positive trigger pulse, then a negative output pulses. In the absence of beating duty cycle greater than 99%. Heavy loads can be s eparated from the pin 7, will not affect the accuracy, but will affect the load exceeds 3 pin timing accuracy.
The timer 555 is a versatile integrated circuit commonly used in various timing, delay, and oscillator applications. In a typical configuration, the 555 timer operates in either monostable or astable mode, depending on the desired output behavior. When triggered by a positive pulse at the trigger pin (pin 2), the timer transitions from its low state to a high state, producing a negative output pulse at the output pin (pin 3). This output pulse duration is determined by the external resistors and capacitors connected to the timer.
In applications where the duty cycle is maintained above 99%, the timer can effectively handle heavy loads connected to pin 7, which is the discharge pin. This feature allows for the separation of heavy loads from the timing components without compromising the accuracy of the timing cycle. However, care must be taken when loads exceed the specifications related to pin 3, as excessive loading can lead to inaccuracies in the timing intervals.
To ensure optimal performance, it is essential to select appropriate resistor and capacitor values to establish the desired timing characteristics while considering the load requirements. The 555 timer can be used in various circuits, including pulse-width modulation (PWM) applications, frequency generation, and timer circuits, making it a fundamental component in electronic design. Proper understanding of the connections and behavior of the 555 timer is crucial for achieving reliable and precise operation in diverse applications. As shown in the timer 555 is triggered by the positive trigger pulse, then a negative output pulses. In the absence of beating duty cycle greater than 99%. Heavy loads can be s eparated from the pin 7, will not affect the accuracy, but will affect the load exceeds 3 pin timing accuracy.