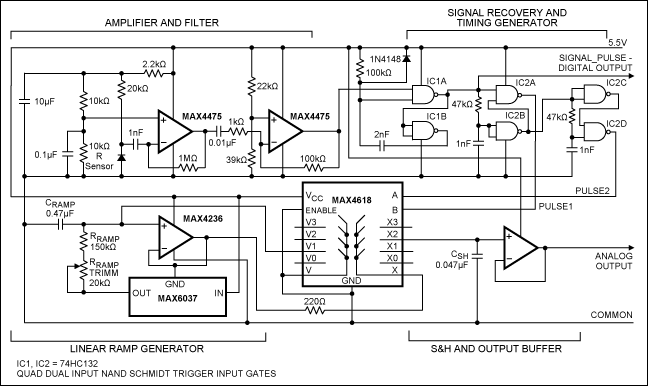
IR Link II
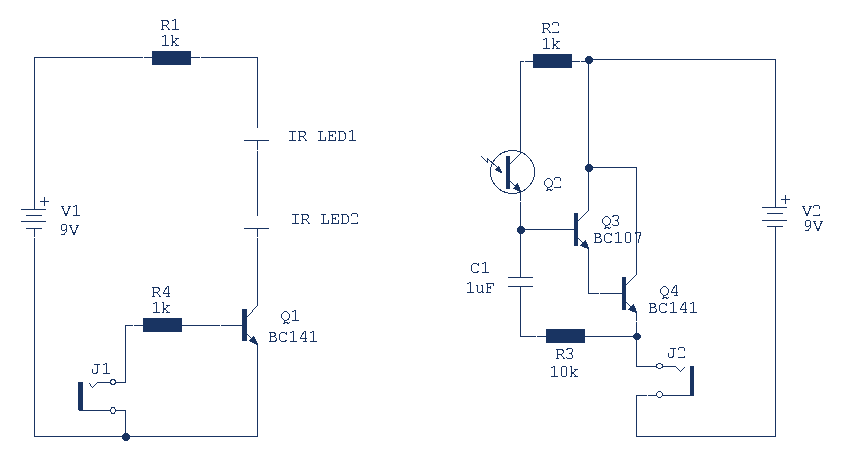
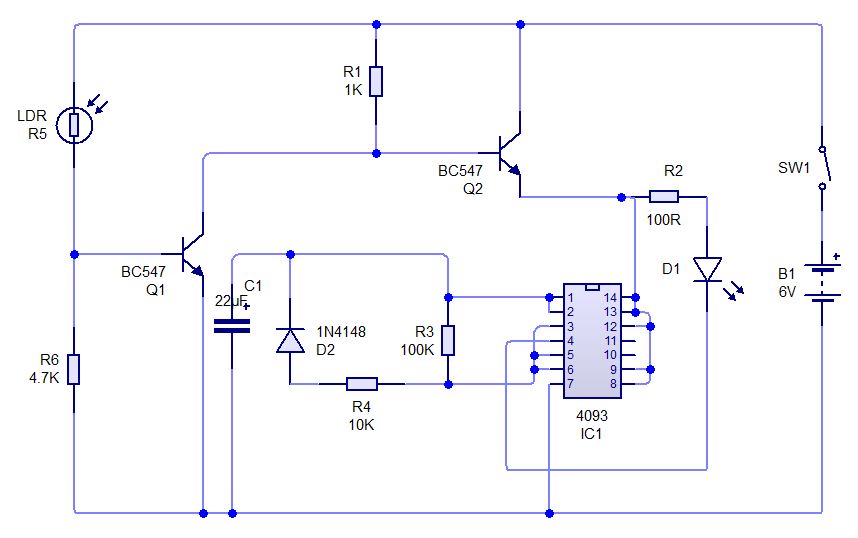
A basic Infra Red Link for audio communication for distances up to 3 meters. Transistors can be replaced with 2N3904 and 2N2222. In this circuit, Milan has created a basic Infra Red transmitter and receiver. The transmitter comprises a single amplifying stage driving two series connected IR LEDs. The input source is connected to J1. Please note that the device will pass a small DC current through it and also directly bias the transistor. A suitable device is therefore a high output crystal microphone. These can produce high output voltages up to 1.
The described circuit utilizes infrared (IR) technology to facilitate audio communication over short distances, specifically up to 3 meters. The core components include a transmitter and a receiver, with the transmitter being responsible for converting audio signals into infrared light signals for transmission.
The transmitter section is built around a single amplifying stage, which is crucial for boosting the audio signal before it is emitted as infrared light. The use of two series-connected IR LEDs allows for enhanced light output, improving the transmission range and reliability of the signal. These LEDs operate in the infrared spectrum, making them invisible to the naked eye while effectively transmitting audio information.
The input source, connected at J1, typically involves a high-output crystal microphone. This type of microphone is advantageous because it can generate sufficient output voltage—up to 1 volt—necessary for driving the amplifier stage. When the microphone picks up sound, it converts the acoustic energy into electrical signals, which are then amplified by the transistor.
Transistors, specifically the 2N3904 or 2N2222, can be utilized in this circuit configuration. These transistors serve as the amplifying element, where they are biased with a small DC current from the circuit. This biasing is essential for ensuring that the transistor operates correctly in the active region, allowing it to amplify the audio signals effectively.
The receiver section of the circuit, while not detailed in the original description, typically includes a photodiode or phototransistor that detects the infrared light emitted by the transmitter. The received infrared signals are then converted back into audio signals for playback through a speaker or other audio output device.
Overall, this basic Infra Red link circuit demonstrates a straightforward method for wireless audio communication, showcasing the principles of modulation and demodulation of audio signals using infrared technology.A basic Imfra Red Link for audio communication for distances upto 3 metres. Transistors can be replaced with 2N3904 and 2N2222. In his circuit Milan has created a basic Infra Red transmitter and receiver. The transmitter comprises a single amplifying stage driving two series connected IR LEDS. The input source is connected to J1. Please note that the device will pass a small DC current through it and also directly bias the transistor. A suitable device is therefore a high output crystal microphone. These can produce high output voltages up to 1 🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes infrared (IR) technology to facilitate audio communication over short distances, specifically up to 3 meters. The core components include a transmitter and a receiver, with the transmitter being responsible for converting audio signals into infrared light signals for transmission.
The transmitter section is built around a single amplifying stage, which is crucial for boosting the audio signal before it is emitted as infrared light. The use of two series-connected IR LEDs allows for enhanced light output, improving the transmission range and reliability of the signal. These LEDs operate in the infrared spectrum, making them invisible to the naked eye while effectively transmitting audio information.
The input source, connected at J1, typically involves a high-output crystal microphone. This type of microphone is advantageous because it can generate sufficient output voltage—up to 1 volt—necessary for driving the amplifier stage. When the microphone picks up sound, it converts the acoustic energy into electrical signals, which are then amplified by the transistor.
Transistors, specifically the 2N3904 or 2N2222, can be utilized in this circuit configuration. These transistors serve as the amplifying element, where they are biased with a small DC current from the circuit. This biasing is essential for ensuring that the transistor operates correctly in the active region, allowing it to amplify the audio signals effectively.
The receiver section of the circuit, while not detailed in the original description, typically includes a photodiode or phototransistor that detects the infrared light emitted by the transmitter. The received infrared signals are then converted back into audio signals for playback through a speaker or other audio output device.
Overall, this basic Infra Red link circuit demonstrates a straightforward method for wireless audio communication, showcasing the principles of modulation and demodulation of audio signals using infrared technology.A basic Imfra Red Link for audio communication for distances upto 3 metres. Transistors can be replaced with 2N3904 and 2N2222. In his circuit Milan has created a basic Infra Red transmitter and receiver. The transmitter comprises a single amplifying stage driving two series connected IR LEDS. The input source is connected to J1. Please note that the device will pass a small DC current through it and also directly bias the transistor. A suitable device is therefore a high output crystal microphone. These can produce high output voltages up to 1 🔗 External reference