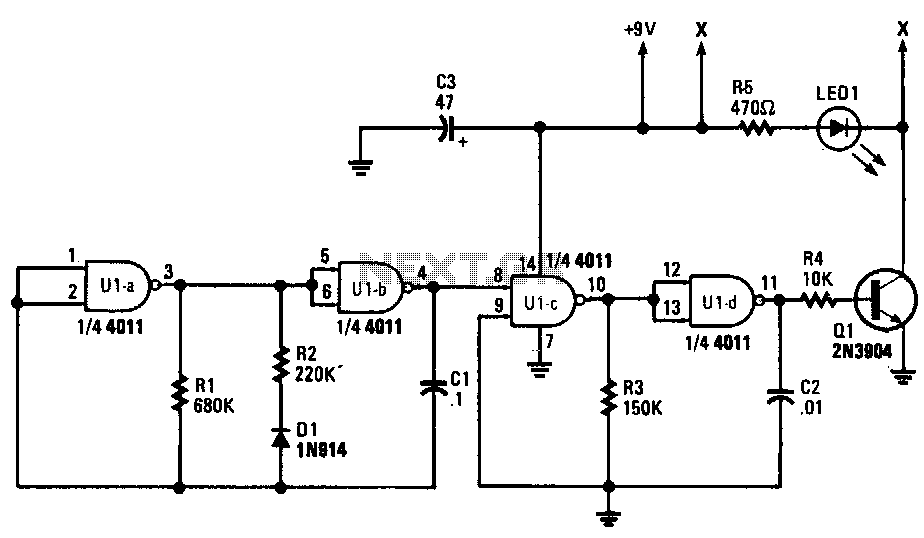
Ir-transmitter
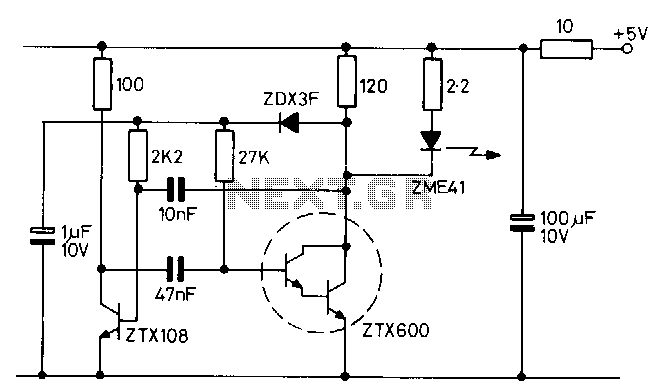
The transmitter consists of an oscillator that drives a high-output infrared (IR) emitting diode. The oscillator is a simple multivibrator circuit that provides an output with a mark-to-space ratio ranging from 15 to 1000 at a frequency of 1 kHz. This large mark-to-space ratio allows the IR diode to operate at a high peak current, supplied by the ZTX600 Darlington transistor, to maximize the transmitter's range. Additionally, a decoupling network is included in the power supply lead to isolate it from any logic circuitry that uses the same 5-V power supply source. The transmitter's supply current is approximately 65 mA.
The transmitter circuit is designed to generate a modulated infrared signal for applications such as remote controls or data transmission. The oscillator section employs a simple multivibrator configuration, which can be implemented using discrete components or integrated circuits. The output frequency of 1 kHz is suitable for many IR communication protocols, providing a balance between range and power consumption.
The mark-to-space ratio, which varies from 15 to 1000, is crucial for optimizing the performance of the IR diode. A higher mark-to-space ratio enables the diode to emit a stronger signal by allowing it to operate at a higher peak current. The ZTX600 Darlington transistor serves as an efficient driver for the IR diode, capable of handling the required current while minimizing power losses. This configuration enhances the transmitter's effective range, making it suitable for long-distance applications.
The inclusion of a decoupling network in the power supply line is essential for maintaining signal integrity. It prevents fluctuations in the power supply from affecting the oscillator's performance and ensures stable operation of any connected logic circuitry. The decoupling network typically consists of capacitors that filter out high-frequency noise, providing a clean and stable 5-V supply to the circuit. With a supply current of approximately 65 mA, the transmitter is designed for low to moderate power consumption, making it ideal for battery-operated devices. Overall, this transmitter design effectively combines efficient signal generation, robust output drive capability, and stable power supply management for reliable infrared communication.The transmitter consists of an oscillator which drives a high output IR emitting diode. The oscillator is a sJire start multivibrator circuit that provides an output of 15 to 1000 mark to space ratio at a frequency of 1 kHz. This large mark to space ratio allows the IR diode to be operated at a high peak current, provided by the ZTX600 Darlington transistor, to maximize the transmitter range.
A decoupling network is included in the power supply lead to isolate it from any logic circuitry using the same 5-V power supply source. The transmitter supply current is approximately 65 mA.
The transmitter circuit is designed to generate a modulated infrared signal for applications such as remote controls or data transmission. The oscillator section employs a simple multivibrator configuration, which can be implemented using discrete components or integrated circuits. The output frequency of 1 kHz is suitable for many IR communication protocols, providing a balance between range and power consumption.
The mark-to-space ratio, which varies from 15 to 1000, is crucial for optimizing the performance of the IR diode. A higher mark-to-space ratio enables the diode to emit a stronger signal by allowing it to operate at a higher peak current. The ZTX600 Darlington transistor serves as an efficient driver for the IR diode, capable of handling the required current while minimizing power losses. This configuration enhances the transmitter's effective range, making it suitable for long-distance applications.
The inclusion of a decoupling network in the power supply line is essential for maintaining signal integrity. It prevents fluctuations in the power supply from affecting the oscillator's performance and ensures stable operation of any connected logic circuitry. The decoupling network typically consists of capacitors that filter out high-frequency noise, providing a clean and stable 5-V supply to the circuit. With a supply current of approximately 65 mA, the transmitter is designed for low to moderate power consumption, making it ideal for battery-operated devices. Overall, this transmitter design effectively combines efficient signal generation, robust output drive capability, and stable power supply management for reliable infrared communication.The transmitter consists of an oscillator which drives a high output IR emitting diode. The oscillator is a sJire start multivibrator circuit that provides an output of 15 to 1000 mark to space ratio at a frequency of 1 kHz. This large mark to space ratio allows the IR diode to be operated at a high peak current, provided by the ZTX600 Darlington transistor, to maximize the transmitter range.
A decoupling network is included in the power supply lead to isolate it from any logic circuitry using the same 5-V power supply source. The transmitter supply current is approximately 65 mA.