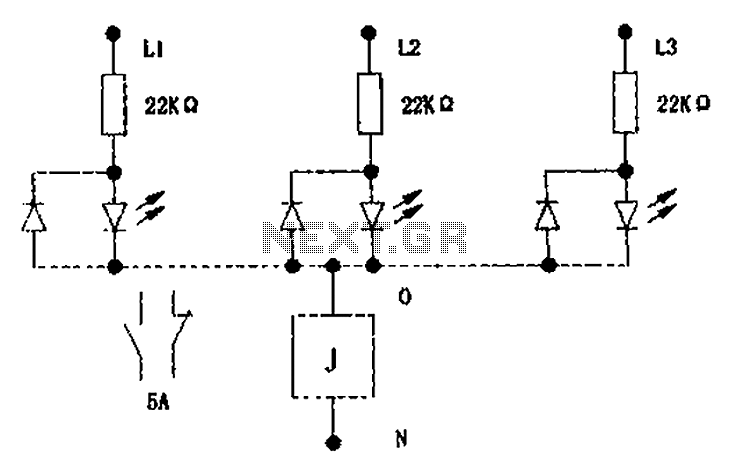
LED or bulb flickers
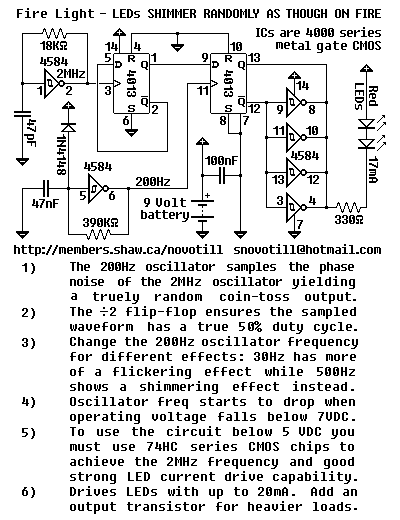
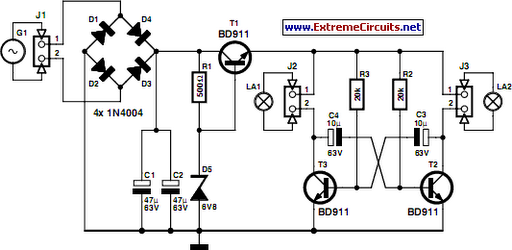
This may well be the world's only discreet logic circuit to generate truly random output. It makes an excellent candle flicker light for your Halloween pumpkin and looks much more authentic than a shimmer light wherever a good simulated flame effect is required. It flickers even more authentically than a candle in a light breeze. More: Here is a 120VAC hot chassis version of the above circuit. This is the one I use to run my pumpkin every Halloween. Note that the AC line provides the low frequency oscillator waveform.
The described circuit is a discrete logic-based design intended to simulate the flickering of a candle flame, providing a more realistic effect than standard lighting options. The circuit operates on a 120VAC power supply, which is commonly used in household applications. The use of a hot chassis design indicates that the circuit may have exposed live components, necessitating careful handling and appropriate insulation measures to ensure user safety.
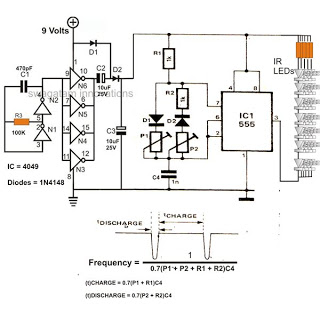
The core functionality of this circuit relies on a low-frequency oscillator, which is derived from the AC line voltage. The oscillator generates a waveform that modulates the brightness of the output light, creating a flickering effect that mimics the irregular flicker of a real candle flame. This is achieved through a combination of discrete components such as resistors, capacitors, and possibly transistors or diodes that shape the oscillator's output.
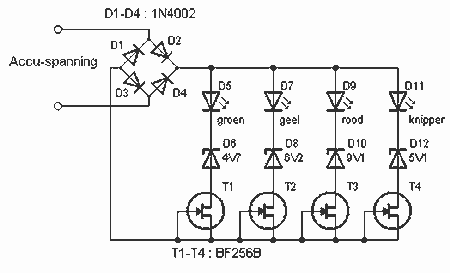
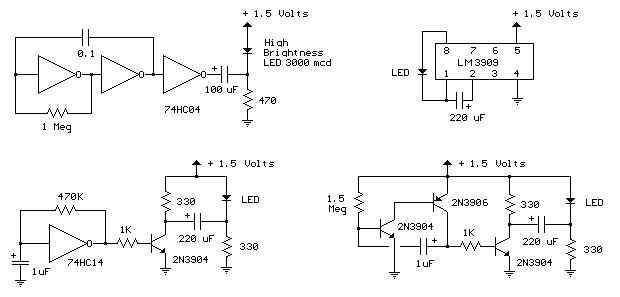
To enhance the authenticity of the flickering effect, the circuit may include additional features such as variable resistor components to adjust the flicker frequency and amplitude, allowing for customization based on the desired effect. The integration of a light-emitting diode (LED) or incandescent bulb serves as the visual output, with the circuit design ensuring that the light source responds dynamically to the oscillating signal.
Safety considerations are paramount in this design, particularly due to the use of 120VAC. Proper fusing and isolation techniques should be implemented to protect both the circuit and the user. Additionally, the circuit should be housed in a non-conductive enclosure to prevent accidental contact with live parts.
Overall, this circuit represents a creative application of discrete logic components to achieve a specific aesthetic effect, enhancing the ambiance for events such as Halloween by providing a visually appealing and safe alternative to traditional candle use.This may well be the world`s only discreet logic circuit to generate truely random output. It makes an excellent candle flicker light for your haloween pumpkin, and looks much more authentic than a shimmer light wherever a good a simulated flame effect is required. It flickers even more authentically than a candle in a light breeze. Here is a 120VAC hot chassis version of the above circuit. This is the one I use to run my pumpkin every haloween. Note that the AC line provides the low frequency oscillator waveform. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit is a discrete logic-based design intended to simulate the flickering of a candle flame, providing a more realistic effect than standard lighting options. The circuit operates on a 120VAC power supply, which is commonly used in household applications. The use of a hot chassis design indicates that the circuit may have exposed live components, necessitating careful handling and appropriate insulation measures to ensure user safety.
The core functionality of this circuit relies on a low-frequency oscillator, which is derived from the AC line voltage. The oscillator generates a waveform that modulates the brightness of the output light, creating a flickering effect that mimics the irregular flicker of a real candle flame. This is achieved through a combination of discrete components such as resistors, capacitors, and possibly transistors or diodes that shape the oscillator's output.
To enhance the authenticity of the flickering effect, the circuit may include additional features such as variable resistor components to adjust the flicker frequency and amplitude, allowing for customization based on the desired effect. The integration of a light-emitting diode (LED) or incandescent bulb serves as the visual output, with the circuit design ensuring that the light source responds dynamically to the oscillating signal.
Safety considerations are paramount in this design, particularly due to the use of 120VAC. Proper fusing and isolation techniques should be implemented to protect both the circuit and the user. Additionally, the circuit should be housed in a non-conductive enclosure to prevent accidental contact with live parts.
Overall, this circuit represents a creative application of discrete logic components to achieve a specific aesthetic effect, enhancing the ambiance for events such as Halloween by providing a visually appealing and safe alternative to traditional candle use.This may well be the world`s only discreet logic circuit to generate truely random output. It makes an excellent candle flicker light for your haloween pumpkin, and looks much more authentic than a shimmer light wherever a good a simulated flame effect is required. It flickers even more authentically than a candle in a light breeze. Here is a 120VAC hot chassis version of the above circuit. This is the one I use to run my pumpkin every haloween. Note that the AC line provides the low frequency oscillator waveform. 🔗 External reference