
Low-cost-half-duplex-information-transmission-link
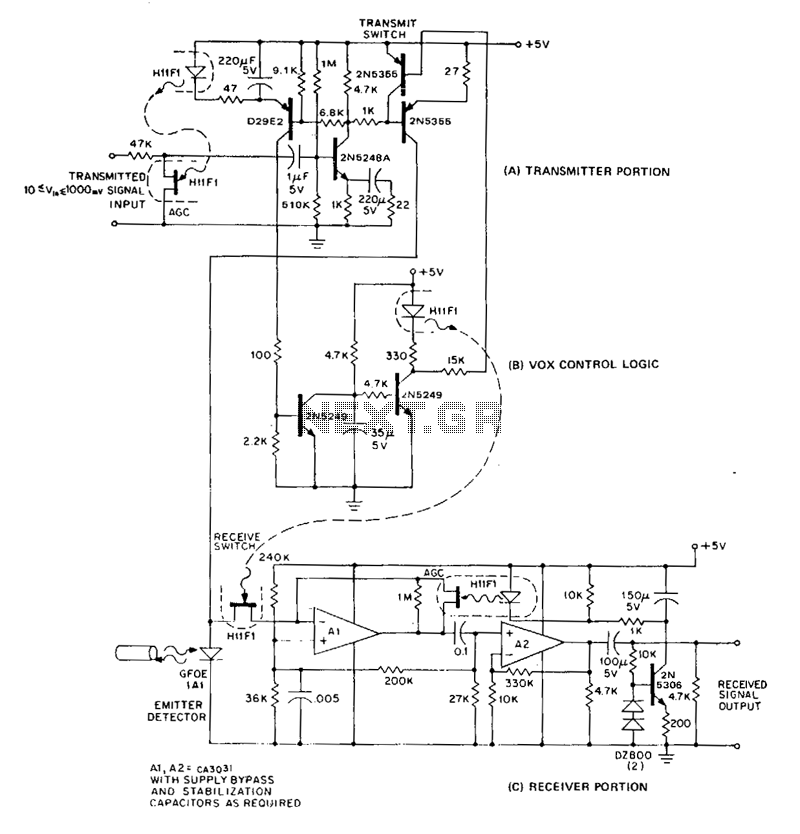
In a half-duplex system, information can flow in both directions, but only one direction at any given time. The conventional method of building a half-duplex link requires a separate emitter and detector, connected with directional couplers, at each end of the fiber. The GFOE1A series of infrared emitting diodes are highly efficient, long-lived emitters, which are also sensitive to the 940 nm infrared they produce. Biased as a photodiode, they exhibit a sensitivity of about 30 nA per pW irradiation at 940 nm. In a suitable bias and switching logic network, they form the basis for a half-duplex information link. A half-duplex link illustrating the emitter-detector operation of the GFOE1A1 is shown. This schematic represents a full, general-purpose system, including: approximately 50 dB compliance range with 1 V rms output, passive receive, voice-activated switching logic, 100 Hz to 50 kHz frequency response, and inexpensive components and hardware. The system is simple, inexpensive, and can be upgraded to provide more capability through the use of higher gain bandwidth amplifier stages. Conversely, performance and cost can be lowered simply by removing undesired features.
The half-duplex communication system is designed to facilitate bidirectional information transfer, albeit with the limitation that only one direction can transmit at any given time. This configuration typically employs a dedicated emitter and detector at opposite ends of the optical fiber, connected via directional couplers to manage the signal flow effectively.
The GFOE1A series of infrared emitting diodes serves as the primary emitter in this system. These diodes are characterized by their high efficiency and longevity, making them suitable for continuous operation. They emit infrared light at a wavelength of 940 nm, which is crucial for the photodetection process. When configured as a photodiode, the GFOE1A diodes demonstrate a sensitivity of approximately 30 nA per pW of irradiation at the same wavelength, enabling effective detection of the emitted infrared signals.
To establish a functional half-duplex link, the GFOE1A diodes are integrated into a biasing and switching logic network. This network is essential for managing the operational states of the emitter and detector, ensuring that they alternate between transmitting and receiving modes without interference. The resulting schematic encompasses a versatile system capable of supporting a compliance range of approximately 50 dB, with an output voltage of 1 V rms.
The passive receiving mechanism and the voice-activated switching logic contribute to the system's user-friendly operation, allowing for seamless transitions between transmission and reception. The frequency response of the system is designed to cover a range from 100 Hz to 50 kHz, making it suitable for various audio and data communication applications.
This half-duplex system is not only cost-effective but also modular, allowing for enhancements through the integration of higher gain bandwidth amplifier stages. Such upgrades can significantly improve performance, catering to applications requiring greater sensitivity or data throughput. Conversely, the system's design permits the removal of non-essential features to reduce costs and simplify the setup, making it adaptable to a wide range of operational requirements.In a half-duplex system, information can flow in both directions, but only one direction at any given time. The conventional method of building a half-duplex link requires a separate emitter and detector, connected with directional couplers, at each end of the fiber.
The GFOE1A series of infrared emitting diodes are highly efficient, long-lived emitters, which are also sensitive to the 940 nm infrared they produce. Biased as a photodiode, they exhibit a sensitivity of about 30 nAper p.W irradiation at 940 nm. In a suitable ·bias and switching logic network, they form the basis for a half-duplex information link. A half-duplex link, illustrating the emitter-detector operation of the GFOE1A1, is shown. This schematic represents a full, general purpose system, including: approximately 50-dB compliance range with 1-V rms output, passive receive, voice-activated switching logic, 100Hz to 50 kHz frequency response, and inexpensive components and hardware.
The system is simple, inexpensive, and can be upgraded to provide more capability through use of higher gain bandwidth amplifier stages. Conversely, performance and cost can be lowered simply by removing undesired features.
The half-duplex communication system is designed to facilitate bidirectional information transfer, albeit with the limitation that only one direction can transmit at any given time. This configuration typically employs a dedicated emitter and detector at opposite ends of the optical fiber, connected via directional couplers to manage the signal flow effectively.
The GFOE1A series of infrared emitting diodes serves as the primary emitter in this system. These diodes are characterized by their high efficiency and longevity, making them suitable for continuous operation. They emit infrared light at a wavelength of 940 nm, which is crucial for the photodetection process. When configured as a photodiode, the GFOE1A diodes demonstrate a sensitivity of approximately 30 nA per pW of irradiation at the same wavelength, enabling effective detection of the emitted infrared signals.
To establish a functional half-duplex link, the GFOE1A diodes are integrated into a biasing and switching logic network. This network is essential for managing the operational states of the emitter and detector, ensuring that they alternate between transmitting and receiving modes without interference. The resulting schematic encompasses a versatile system capable of supporting a compliance range of approximately 50 dB, with an output voltage of 1 V rms.
The passive receiving mechanism and the voice-activated switching logic contribute to the system's user-friendly operation, allowing for seamless transitions between transmission and reception. The frequency response of the system is designed to cover a range from 100 Hz to 50 kHz, making it suitable for various audio and data communication applications.
This half-duplex system is not only cost-effective but also modular, allowing for enhancements through the integration of higher gain bandwidth amplifier stages. Such upgrades can significantly improve performance, catering to applications requiring greater sensitivity or data throughput. Conversely, the system's design permits the removal of non-essential features to reduce costs and simplify the setup, making it adaptable to a wide range of operational requirements.In a half-duplex system, information can flow in both directions, but only one direction at any given time. The conventional method of building a half-duplex link requires a separate emitter and detector, connected with directional couplers, at each end of the fiber.
The GFOE1A series of infrared emitting diodes are highly efficient, long-lived emitters, which are also sensitive to the 940 nm infrared they produce. Biased as a photodiode, they exhibit a sensitivity of about 30 nAper p.W irradiation at 940 nm. In a suitable ·bias and switching logic network, they form the basis for a half-duplex information link. A half-duplex link, illustrating the emitter-detector operation of the GFOE1A1, is shown. This schematic represents a full, general purpose system, including: approximately 50-dB compliance range with 1-V rms output, passive receive, voice-activated switching logic, 100Hz to 50 kHz frequency response, and inexpensive components and hardware.
The system is simple, inexpensive, and can be upgraded to provide more capability through use of higher gain bandwidth amplifier stages. Conversely, performance and cost can be lowered simply by removing undesired features.