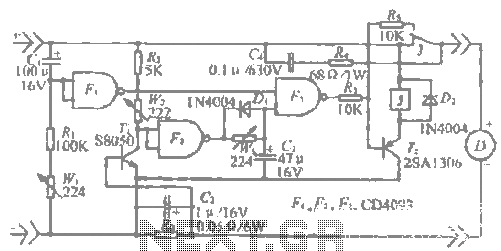
low power voltage doubler booster

All miniature electronic devices operate on batteries. Some require voltages higher than the standard battery voltages for efficient operation. When a battery of the specific voltage is unavailable, it becomes necessary to connect additional cells in series to increase the DC voltage. Consequently, the essence of miniaturization is compromised. A straightforward solution to this issue is to utilize a voltage doubler, provided that the device in question can function at a low current.
A voltage doubler is a circuit that converts a lower input voltage to a higher output voltage, effectively doubling the input voltage. This is achieved through the use of capacitors and diodes, which work together to store and transfer energy. In a typical voltage doubler configuration, the circuit is composed of two diodes and two capacitors. The first diode allows current to flow into the first capacitor during the positive half-cycle of the input AC signal, charging it to the peak voltage of the input. During the negative half-cycle, the second diode becomes forward-biased, allowing the charge from the first capacitor to be combined with the input voltage, thereby doubling the output voltage across the second capacitor.
The design of a voltage doubler circuit must consider several factors, including the load current, the frequency of the input signal, and the characteristics of the components used. The capacitors should be rated for a voltage higher than the expected output to ensure reliability, and the diodes must have a low forward voltage drop to maximize efficiency. Additionally, the output ripple voltage should be minimized to provide a stable DC output, which may require the use of filtering techniques.
When implementing a voltage doubler in miniature electronic devices, it is crucial to ensure that the circuit does not exceed the power ratings of the components, as overheating can lead to failure. Furthermore, the overall size of the voltage doubler circuit should be considered to maintain the miniaturization objective of the device. By effectively integrating a voltage doubler, designers can enhance the performance of battery-operated miniature devices without compromising their size or functionality.All miniature electronic devices operate off batteries. Some of them need higher than the standard battery voltages to operate efficiently. If the battery of that specific voltage is unavailable, we are forced to connect additional cells in series to step up the DC voltage. Thus, the true meaning of miniaturisation is lost. A simple way to overcome this problem is to employ a voltage doubler, if the device under consideration can operate at a small current..
🔗 External reference
A voltage doubler is a circuit that converts a lower input voltage to a higher output voltage, effectively doubling the input voltage. This is achieved through the use of capacitors and diodes, which work together to store and transfer energy. In a typical voltage doubler configuration, the circuit is composed of two diodes and two capacitors. The first diode allows current to flow into the first capacitor during the positive half-cycle of the input AC signal, charging it to the peak voltage of the input. During the negative half-cycle, the second diode becomes forward-biased, allowing the charge from the first capacitor to be combined with the input voltage, thereby doubling the output voltage across the second capacitor.
The design of a voltage doubler circuit must consider several factors, including the load current, the frequency of the input signal, and the characteristics of the components used. The capacitors should be rated for a voltage higher than the expected output to ensure reliability, and the diodes must have a low forward voltage drop to maximize efficiency. Additionally, the output ripple voltage should be minimized to provide a stable DC output, which may require the use of filtering techniques.
When implementing a voltage doubler in miniature electronic devices, it is crucial to ensure that the circuit does not exceed the power ratings of the components, as overheating can lead to failure. Furthermore, the overall size of the voltage doubler circuit should be considered to maintain the miniaturization objective of the device. By effectively integrating a voltage doubler, designers can enhance the performance of battery-operated miniature devices without compromising their size or functionality.All miniature electronic devices operate off batteries. Some of them need higher than the standard battery voltages to operate efficiently. If the battery of that specific voltage is unavailable, we are forced to connect additional cells in series to step up the DC voltage. Thus, the true meaning of miniaturisation is lost. A simple way to overcome this problem is to employ a voltage doubler, if the device under consideration can operate at a small current..
🔗 External reference