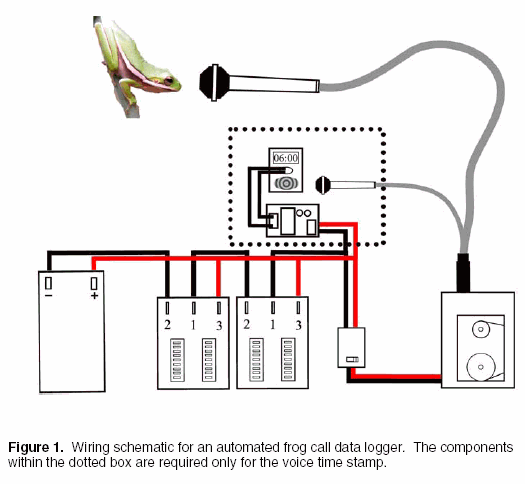
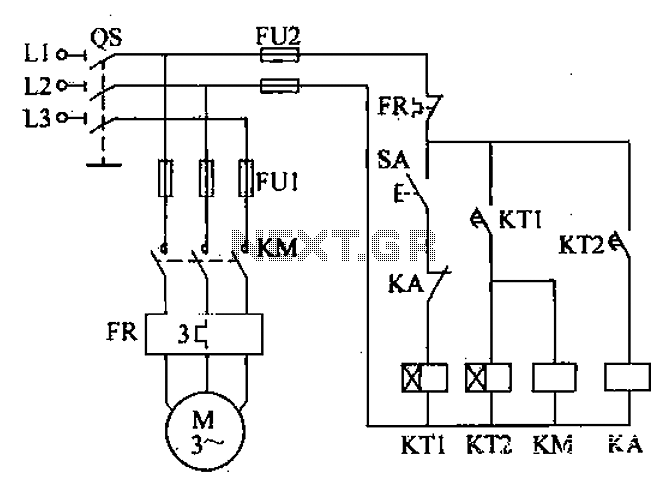
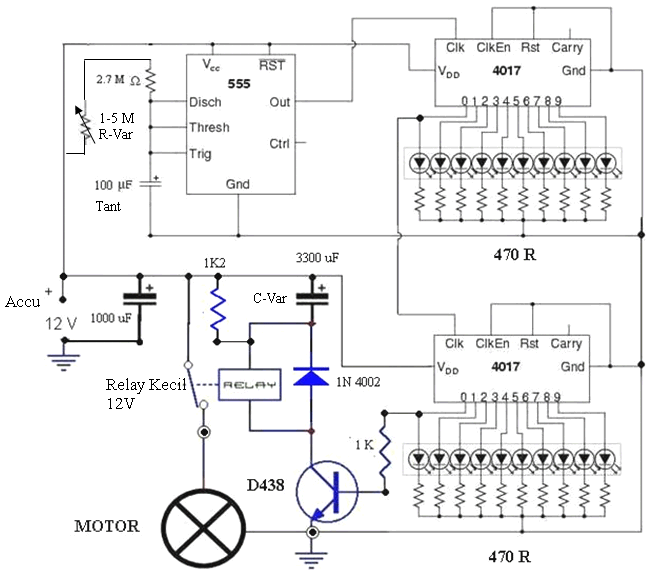
Motorola VWA63 Auto Radio
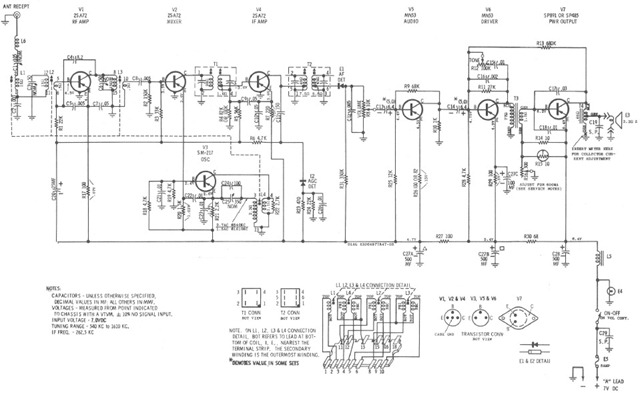
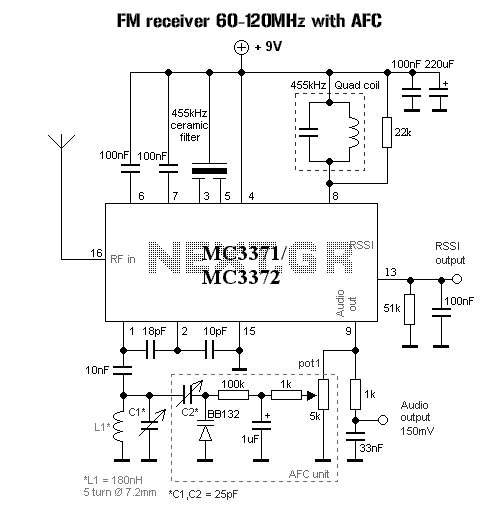
The Motorola VWA63 Auto Radio is an automotive all-transistor superheterodyne AM radio designed for standard broadcast reception. The accompanying schematic illustrates its configuration.
The Motorola VWA63 Auto Radio utilizes a superheterodyne architecture, which is a common design for AM radios that enhances the quality of signal reception and selectivity. The circuit typically consists of several key components: an antenna, a radio frequency (RF) amplifier, a mixer, an intermediate frequency (IF) amplifier, a demodulator, and an audio amplifier.
The antenna captures AM radio waves, which are then fed into the RF amplifier. This stage amplifies the weak signals received from the antenna. The amplified RF signal is then mixed with a locally generated frequency from a local oscillator within the mixer stage. This process converts the signal to an intermediate frequency, which is easier to process.
After mixing, the resulting signal is passed to the IF amplifier. This stage further amplifies the intermediate frequency signal while providing improved selectivity and sensitivity. The demodulator then extracts the audio information from the IF signal. This is typically achieved using envelope detection, which recovers the original audio waveform from the modulated carrier wave.
Finally, the audio amplifier amplifies the demodulated signal to a level suitable for driving the speakers in the vehicle. The schematic for the Motorola VWA63 Auto Radio would detail the specific connections and values of components, including resistors, capacitors, and transistors, that make up each of these stages, ensuring optimal performance for AM broadcast reception.Motorola VWA63 Auto Radio is an automotive type all-transistor superheterodyne AM radio for standard broadcast reception. The following schematic illustrates.. 🔗 External reference
The Motorola VWA63 Auto Radio utilizes a superheterodyne architecture, which is a common design for AM radios that enhances the quality of signal reception and selectivity. The circuit typically consists of several key components: an antenna, a radio frequency (RF) amplifier, a mixer, an intermediate frequency (IF) amplifier, a demodulator, and an audio amplifier.
The antenna captures AM radio waves, which are then fed into the RF amplifier. This stage amplifies the weak signals received from the antenna. The amplified RF signal is then mixed with a locally generated frequency from a local oscillator within the mixer stage. This process converts the signal to an intermediate frequency, which is easier to process.
After mixing, the resulting signal is passed to the IF amplifier. This stage further amplifies the intermediate frequency signal while providing improved selectivity and sensitivity. The demodulator then extracts the audio information from the IF signal. This is typically achieved using envelope detection, which recovers the original audio waveform from the modulated carrier wave.
Finally, the audio amplifier amplifies the demodulated signal to a level suitable for driving the speakers in the vehicle. The schematic for the Motorola VWA63 Auto Radio would detail the specific connections and values of components, including resistors, capacitors, and transistors, that make up each of these stages, ensuring optimal performance for AM broadcast reception.Motorola VWA63 Auto Radio is an automotive type all-transistor superheterodyne AM radio for standard broadcast reception. The following schematic illustrates.. 🔗 External reference