Negative Input Voltage Circuit using Voltage-to-Frequency Converter
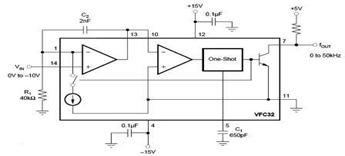
The circuit diagram of a voltage-to-frequency (V/F) converter is presented, designed to handle negative input voltage. It employs the VFC32 voltage-to-frequency converter, which is commonly utilized in various applications.
The V/F converter circuit is essential in converting an analog voltage signal into a corresponding frequency output. The VFC32 is a specialized integrated circuit that performs this conversion with high precision and efficiency. In this configuration, the circuit is designed to accept negative input voltages, which is critical for applications that require signal processing of negative ranges.
The core operation of the VFC32 involves generating a frequency output that is directly proportional to the input voltage. The circuit typically includes components such as resistors, capacitors, and operational amplifiers that establish the necessary gain and filtering characteristics. In the case of negative input voltage, the circuit may incorporate level-shifting techniques to ensure that the input signal is correctly processed without distortion.
Key features of the VFC32 include a wide operating range, low temperature drift, and the ability to interface with digital systems, making it suitable for applications in instrumentation, control systems, and data acquisition. The output frequency can be measured using frequency counters or microcontroller-based systems, allowing for easy integration into larger electronic systems.
In summary, the V/F converter utilizing the VFC32 is a versatile and reliable solution for converting negative voltage inputs into frequency outputs, providing crucial functionality in various electronic applications.Here is the circuit diagram of V/F Converter in negative input voltage. It uses the VFC32 voltage-to-frequency converter. This VFC32 used to be applied in. 🔗 External reference
The V/F converter circuit is essential in converting an analog voltage signal into a corresponding frequency output. The VFC32 is a specialized integrated circuit that performs this conversion with high precision and efficiency. In this configuration, the circuit is designed to accept negative input voltages, which is critical for applications that require signal processing of negative ranges.
The core operation of the VFC32 involves generating a frequency output that is directly proportional to the input voltage. The circuit typically includes components such as resistors, capacitors, and operational amplifiers that establish the necessary gain and filtering characteristics. In the case of negative input voltage, the circuit may incorporate level-shifting techniques to ensure that the input signal is correctly processed without distortion.
Key features of the VFC32 include a wide operating range, low temperature drift, and the ability to interface with digital systems, making it suitable for applications in instrumentation, control systems, and data acquisition. The output frequency can be measured using frequency counters or microcontroller-based systems, allowing for easy integration into larger electronic systems.
In summary, the V/F converter utilizing the VFC32 is a versatile and reliable solution for converting negative voltage inputs into frequency outputs, providing crucial functionality in various electronic applications.Here is the circuit diagram of V/F Converter in negative input voltage. It uses the VFC32 voltage-to-frequency converter. This VFC32 used to be applied in. 🔗 External reference