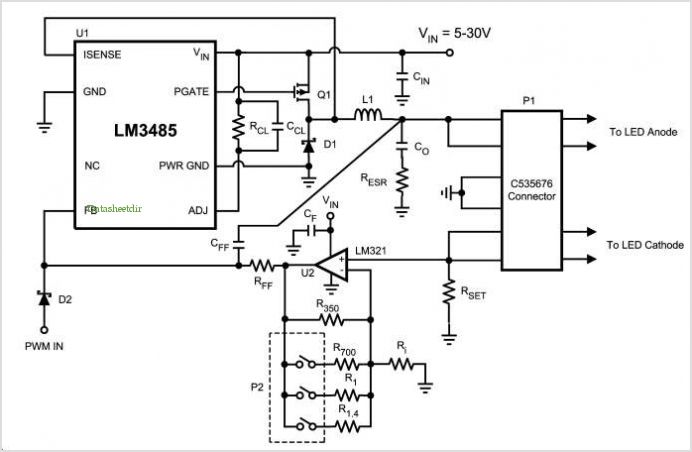
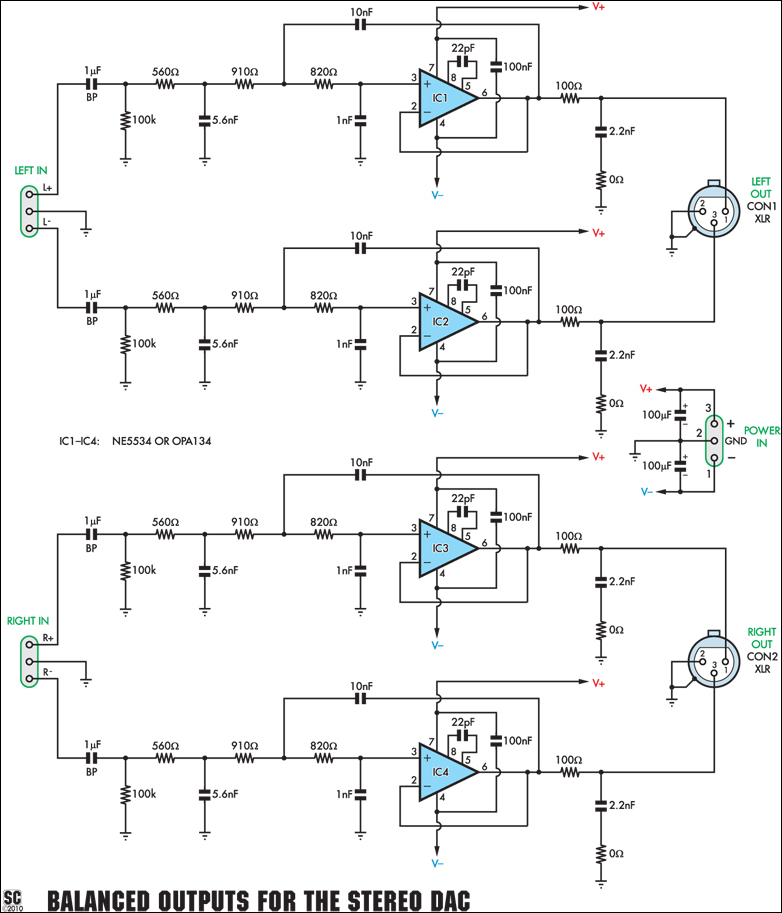
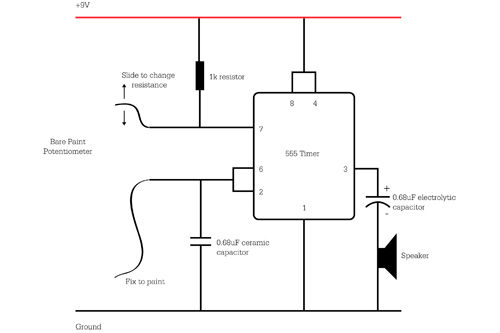
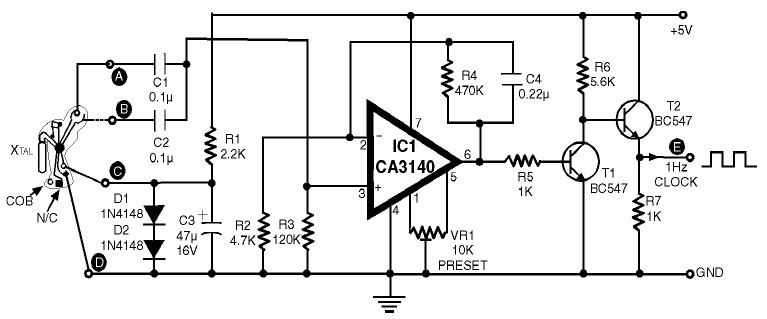
NMEA to RS232 Interface Board
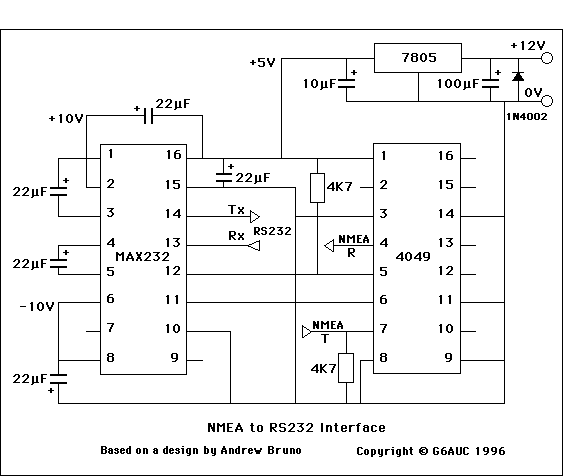
This design is based on the work of Andrew Bruno, referred to as "bruno-if." The contribution involved providing Postscript files for a Printed Circuit Board. The circuit is relatively old, dating back to the NMEA-0180 and NMEA-0182 standards. It is designed to be non-inverting and its primary function is to convert NMEA voltage levels to comply with RS232 standards. Many early GPS units did not fully comply with RS232 specifications, particularly in not generating negative voltage levels. The output voltages were at TTL levels, which allowed direct connection to many RS232 computer interfaces, but not to those requiring negative voltage levels. NMEA-0183 suggests that a talker output should utilize EIA-422 differential outputs and that the input circuit should incorporate an opto-isolator with appropriate protection circuitry. Therefore, this circuit is not recommended for use with NMEA-0183 compliant equipment.
ICs:
- MAX232CPE RS232/TTL Interface
- CD4049UBE Hex Inverting Buffer
- L7805C 5 Volt Regulator
Capacitors:
- C1, C2, C3, C4, C5: 22 microfarad (electrolytic - 16 volt working)
- C6: 10 microfarad (electrolytic - 16 volt working)
- C7: 100 microfarad (electrolytic - 16 volt working for 12 volts in, electrolytic - 50 volt working for 40 volts in)
Resistors:
- R1, R2: 4.7K ohm (4700 ohm)
Diode:
- D1: 1N4002 Power Diode
Two Postscript files are included, which can be printed directly or utilized as EPS files without further scaling.
The circuit design, based on Andrew Bruno's original concept, serves as a voltage level shifter for integrating early GPS units with RS232 interfaces. It addresses the limitation of early GPS devices that output TTL levels without negative voltage, making them unsuitable for direct connection to certain RS232 interfaces. The MAX232CPE integrated circuit is pivotal in this design, as it facilitates the conversion of TTL levels to RS232 levels, ensuring compatibility with a broader range of devices.
The inclusion of the CD4049UBE hex inverting buffer serves to stabilize the signal and improve the integrity of the communication between the GPS unit and the RS232 interface. The L7805C voltage regulator is responsible for providing a stable 5V power supply to the circuit, ensuring consistent operation.
The capacitor selection is critical for filtering and stabilizing voltage levels throughout the circuit. The electrolytic capacitors (C1-C5) provide decoupling, while C6 and C7 are specifically chosen to handle voltage fluctuations from the power supply, with C7 rated for higher voltage operation to accommodate varying input conditions.
The resistors R1 and R2 are utilized for biasing and limiting current within the circuit, ensuring that the components operate within their specified parameters. The 1N4002 diode serves as a protection mechanism against reverse polarity, safeguarding the circuit from potential damage.
Overall, this circuit design is a historical reference point for interfacing early GPS technology with RS232 communication standards, though it is advised against using it with newer NMEA-0183 compliant systems due to differences in output requirements. The provided Postscript files facilitate the reproduction of the PCB layout, ensuring accurate implementation of the design.This design is based on that of Andrew Bruno. His design appeared under the name of "bruno-if". My contribution was to provide Postscript files for a Printed Circuit Board. This circuit is quite old and goes back to the days of NMEA-0180 and 0182. Note that it is non-inverting. Its purpose was to shift the NEMA voltage levels to be RS232 compliant . Many early GPS units were not fully RS232 compliant, in the sense that they did not produce a negative voltage level. The voltages were at TTL levels, but in the same sense as RS232: Although not fully compliant, this meant that a GPS unit could be directly connected to many computer RS232 interfaces, but not to those that required the negative voltage.
NMEA-0183 recommends that a talker output should have EIA-422 differential outputs and that the input circuit should use an opto-isolator with suitable protection circuitry. I cannot, therefore, recommend the use of this circuit with NMEA-0183 compliant equipment. ICs: MAX232CPE RS232/TTL Interface CD4049UBE Hex Inverting Buffer L7805C 5 Volt regulator Capacitors: C1, C2, C3, C4, C5 22 microfarad (electrolytic - 16 volt working) C6 10 microfarad (electrolytic - 16 volt working) C7 100 microfarad (electrolytic - 16 volt working for 12 volts in) (electrolytic - 50 volt working for 40 volts in) Resistors: R1, R2 4K7 ohm (4700 ohm) Diode: D1 1N4002 Power Diode Two Postscript files are provided.
They can be printed directly or used as EPS files. When used as EPS files, they should not be subject to any further scaling. 🔗 External reference
ICs:
- MAX232CPE RS232/TTL Interface
- CD4049UBE Hex Inverting Buffer
- L7805C 5 Volt Regulator
Capacitors:
- C1, C2, C3, C4, C5: 22 microfarad (electrolytic - 16 volt working)
- C6: 10 microfarad (electrolytic - 16 volt working)
- C7: 100 microfarad (electrolytic - 16 volt working for 12 volts in, electrolytic - 50 volt working for 40 volts in)
Resistors:
- R1, R2: 4.7K ohm (4700 ohm)
Diode:
- D1: 1N4002 Power Diode
Two Postscript files are included, which can be printed directly or utilized as EPS files without further scaling.
The circuit design, based on Andrew Bruno's original concept, serves as a voltage level shifter for integrating early GPS units with RS232 interfaces. It addresses the limitation of early GPS devices that output TTL levels without negative voltage, making them unsuitable for direct connection to certain RS232 interfaces. The MAX232CPE integrated circuit is pivotal in this design, as it facilitates the conversion of TTL levels to RS232 levels, ensuring compatibility with a broader range of devices.
The inclusion of the CD4049UBE hex inverting buffer serves to stabilize the signal and improve the integrity of the communication between the GPS unit and the RS232 interface. The L7805C voltage regulator is responsible for providing a stable 5V power supply to the circuit, ensuring consistent operation.
The capacitor selection is critical for filtering and stabilizing voltage levels throughout the circuit. The electrolytic capacitors (C1-C5) provide decoupling, while C6 and C7 are specifically chosen to handle voltage fluctuations from the power supply, with C7 rated for higher voltage operation to accommodate varying input conditions.
The resistors R1 and R2 are utilized for biasing and limiting current within the circuit, ensuring that the components operate within their specified parameters. The 1N4002 diode serves as a protection mechanism against reverse polarity, safeguarding the circuit from potential damage.
Overall, this circuit design is a historical reference point for interfacing early GPS technology with RS232 communication standards, though it is advised against using it with newer NMEA-0183 compliant systems due to differences in output requirements. The provided Postscript files facilitate the reproduction of the PCB layout, ensuring accurate implementation of the design.This design is based on that of Andrew Bruno. His design appeared under the name of "bruno-if". My contribution was to provide Postscript files for a Printed Circuit Board. This circuit is quite old and goes back to the days of NMEA-0180 and 0182. Note that it is non-inverting. Its purpose was to shift the NEMA voltage levels to be RS232 compliant . Many early GPS units were not fully RS232 compliant, in the sense that they did not produce a negative voltage level. The voltages were at TTL levels, but in the same sense as RS232: Although not fully compliant, this meant that a GPS unit could be directly connected to many computer RS232 interfaces, but not to those that required the negative voltage.
NMEA-0183 recommends that a talker output should have EIA-422 differential outputs and that the input circuit should use an opto-isolator with suitable protection circuitry. I cannot, therefore, recommend the use of this circuit with NMEA-0183 compliant equipment. ICs: MAX232CPE RS232/TTL Interface CD4049UBE Hex Inverting Buffer L7805C 5 Volt regulator Capacitors: C1, C2, C3, C4, C5 22 microfarad (electrolytic - 16 volt working) C6 10 microfarad (electrolytic - 16 volt working) C7 100 microfarad (electrolytic - 16 volt working for 12 volts in) (electrolytic - 50 volt working for 40 volts in) Resistors: R1, R2 4K7 ohm (4700 ohm) Diode: D1 1N4002 Power Diode Two Postscript files are provided.
They can be printed directly or used as EPS files. When used as EPS files, they should not be subject to any further scaling. 🔗 External reference