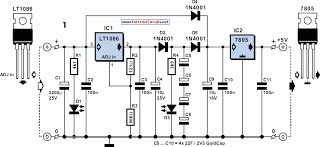
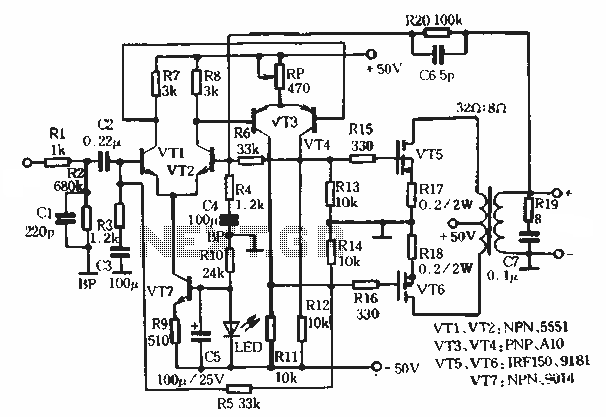
One power supply circuit soft start
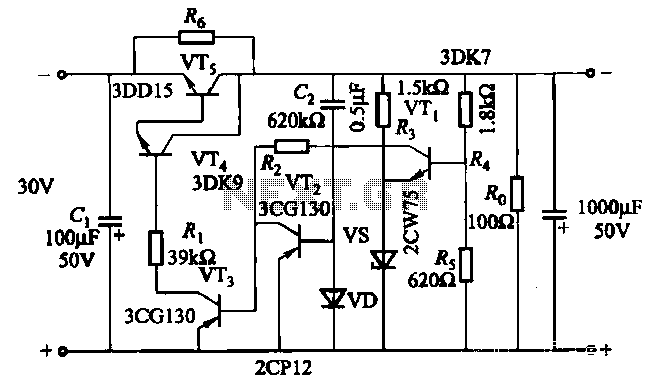
The soft start circuit refers to a power circuit where the output voltage gradually increases to a specified value, thereby protecting the load circuit from unwanted voltage surges. It can output a voltage of 24V and a current of 2A. The soft-start circuit is composed of capacitor Cz, transistors VT2, and diode VD. By adjusting R6 and C2, the time duration for the soft start can be modified as needed.
The soft start circuit is designed to limit the inrush current during the initial power-up phase of a load, which can be crucial for sensitive electronic components that may be damaged by sudden voltage spikes. The gradual ramp-up of the output voltage reduces stress on both the power supply and the connected load.
In the circuit, the capacitor Cz plays a vital role in controlling the charging time, which in turn influences the rate at which the output voltage rises. The transistors, specifically VT2, are used to regulate the flow of current based on the voltage across Cz. The diode VD ensures that the current only flows in one direction, preventing potential damage to the circuit during the discharge phase of Cz.
Resistor R6 can be used to fine-tune the discharge rate of the capacitor, while capacitor C2 can be adjusted to modify the time constant of the circuit, allowing for flexibility in the soft start duration. By selecting appropriate values for R6 and C2, the designer can achieve the desired soft start characteristics, ensuring that the load is powered up smoothly and without abrupt changes in voltage.
Overall, this soft start circuit is essential for applications where load protection is critical, providing a reliable method to manage power delivery during startup.The so-called soft start, refers to a circuit power, the output voltage through a startup process to a slower rate of increase to a given value, in order to protect not want to have surges of the load circuit. It can output voltage 24V, current 2A. Soft-start circuit by the capacitor cz, transistors VT2 and diode VD composition. Adjust R6 and C2, available when needed playing time levy.
The soft start circuit is designed to limit the inrush current during the initial power-up phase of a load, which can be crucial for sensitive electronic components that may be damaged by sudden voltage spikes. The gradual ramp-up of the output voltage reduces stress on both the power supply and the connected load.
In the circuit, the capacitor Cz plays a vital role in controlling the charging time, which in turn influences the rate at which the output voltage rises. The transistors, specifically VT2, are used to regulate the flow of current based on the voltage across Cz. The diode VD ensures that the current only flows in one direction, preventing potential damage to the circuit during the discharge phase of Cz.
Resistor R6 can be used to fine-tune the discharge rate of the capacitor, while capacitor C2 can be adjusted to modify the time constant of the circuit, allowing for flexibility in the soft start duration. By selecting appropriate values for R6 and C2, the designer can achieve the desired soft start characteristics, ensuring that the load is powered up smoothly and without abrupt changes in voltage.
Overall, this soft start circuit is essential for applications where load protection is critical, providing a reliable method to manage power delivery during startup.The so-called soft start, refers to a circuit power, the output voltage through a startup process to a slower rate of increase to a given value, in order to protect not want to have surges of the load circuit. It can output voltage 24V, current 2A. Soft-start circuit by the capacitor cz, transistors VT2 and diode VD composition. Adjust R6 and C2, available when needed playing time levy.