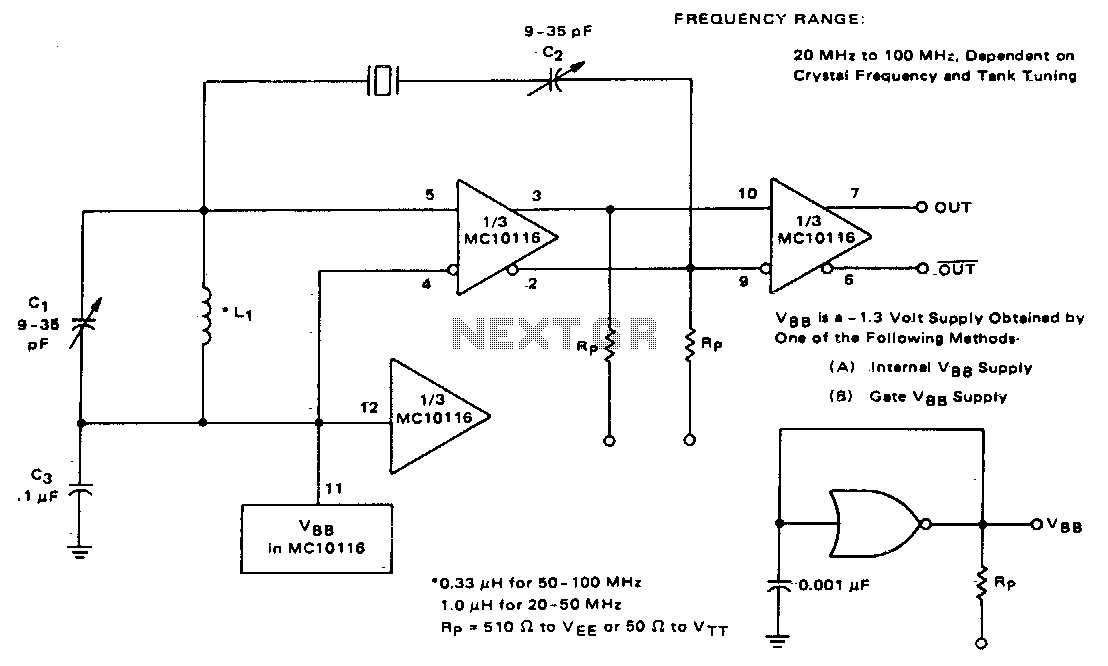
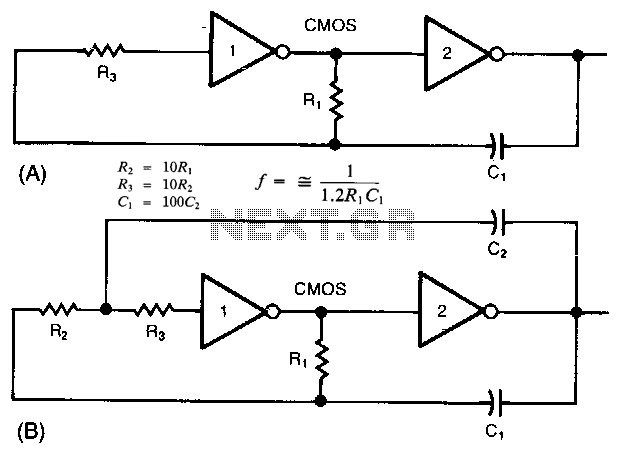
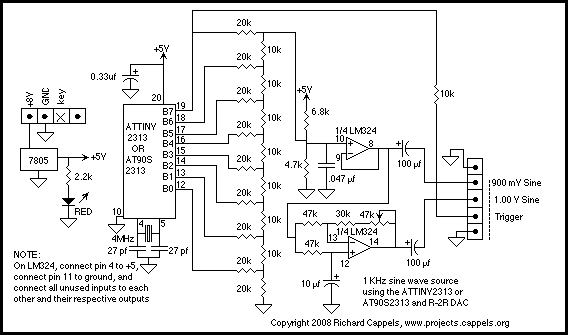
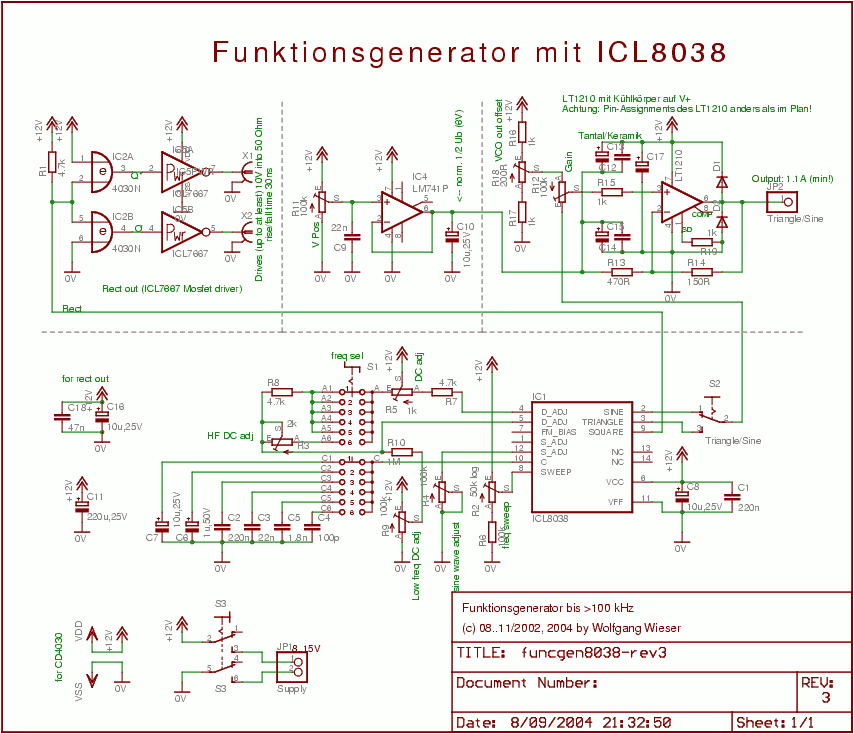
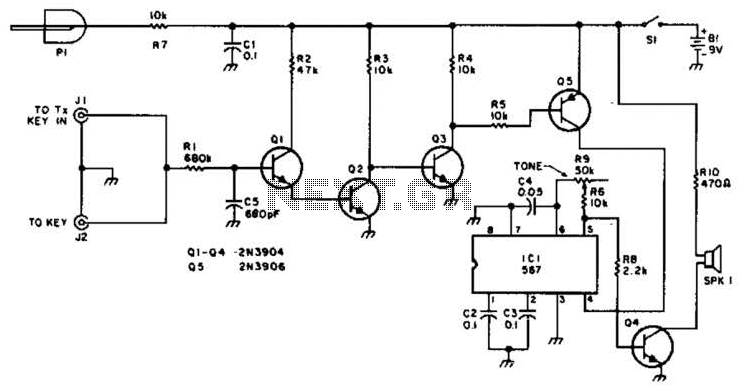
phase shift oscillator

Phase-shift oscillator. An oscillator in which a network has a phase shift of 180 degrees.
A phase-shift oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates a sinusoidal output signal. It typically consists of an amplifier and a phase-shifting network that provides the necessary phase shift of 180 degrees, which is essential for the feedback loop to sustain oscillation. The phase-shifting network is usually composed of resistors and capacitors arranged in such a way that it introduces a total phase shift of 180 degrees at the desired frequency of oscillation.
The most common configuration includes three RC (resistor-capacitor) stages, each contributing a phase shift of 60 degrees, resulting in a total phase shift of 180 degrees when combined with the 180-degree phase shift from the inverting amplifier. This configuration allows for a stable oscillation frequency that can be determined by the values of the resistors and capacitors used in the phase-shifting network.
The output frequency of a phase-shift oscillator can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2\pi R C \sqrt{6}} \]
where \( R \) is the resistance of the resistors in the network and \( C \) is the capacitance of the capacitors. The design of the oscillator must ensure that the gain of the amplifier is sufficient to compensate for the losses in the phase-shifting network, typically requiring a gain greater than three.
Phase-shift oscillators are widely used in various applications such as audio signal generation, tone generation, function generators, and as clock sources in digital circuits. Their simple design and ease of implementation make them a popular choice for low-frequency oscillation requirements.phase-shift oscillator. An oscillator in which a network having a phase shift o.. 🔗 External reference
A phase-shift oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates a sinusoidal output signal. It typically consists of an amplifier and a phase-shifting network that provides the necessary phase shift of 180 degrees, which is essential for the feedback loop to sustain oscillation. The phase-shifting network is usually composed of resistors and capacitors arranged in such a way that it introduces a total phase shift of 180 degrees at the desired frequency of oscillation.
The most common configuration includes three RC (resistor-capacitor) stages, each contributing a phase shift of 60 degrees, resulting in a total phase shift of 180 degrees when combined with the 180-degree phase shift from the inverting amplifier. This configuration allows for a stable oscillation frequency that can be determined by the values of the resistors and capacitors used in the phase-shifting network.
The output frequency of a phase-shift oscillator can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2\pi R C \sqrt{6}} \]
where \( R \) is the resistance of the resistors in the network and \( C \) is the capacitance of the capacitors. The design of the oscillator must ensure that the gain of the amplifier is sufficient to compensate for the losses in the phase-shifting network, typically requiring a gain greater than three.
Phase-shift oscillators are widely used in various applications such as audio signal generation, tone generation, function generators, and as clock sources in digital circuits. Their simple design and ease of implementation make them a popular choice for low-frequency oscillation requirements.phase-shift oscillator. An oscillator in which a network having a phase shift o.. 🔗 External reference