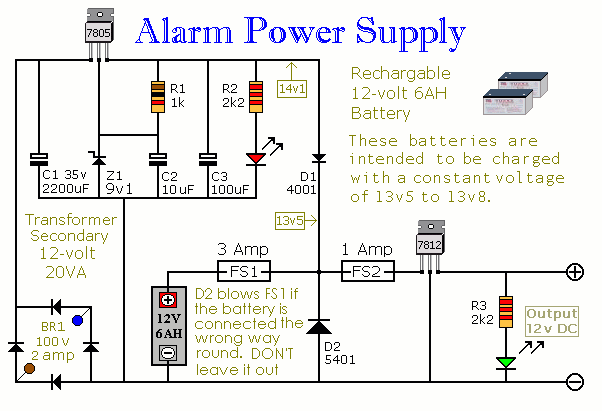
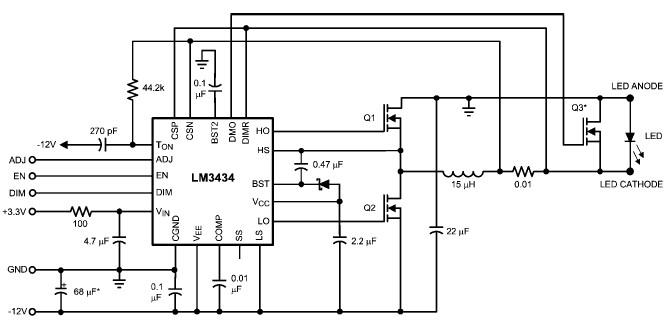
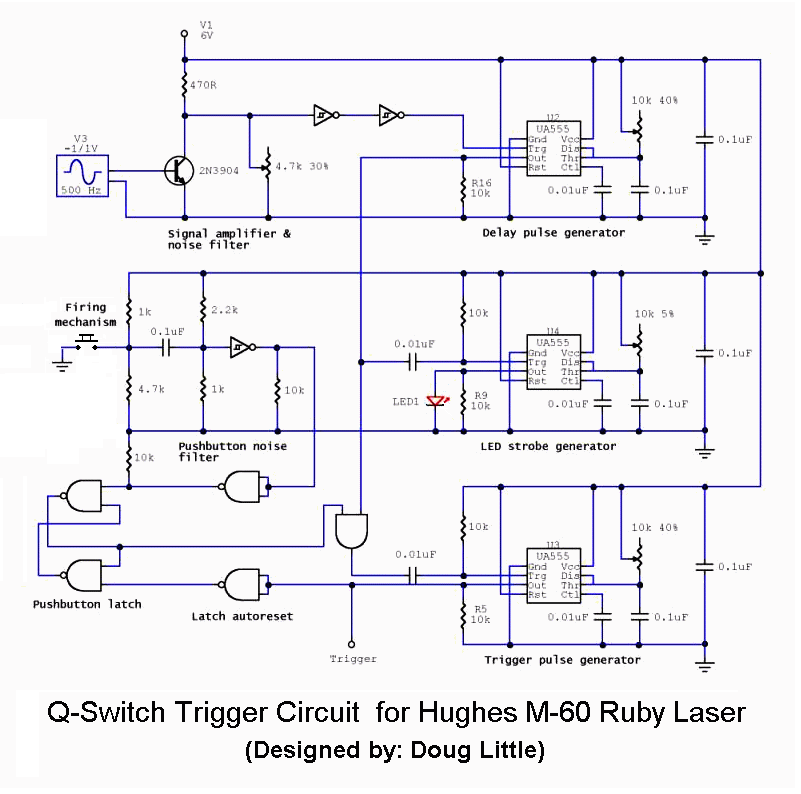
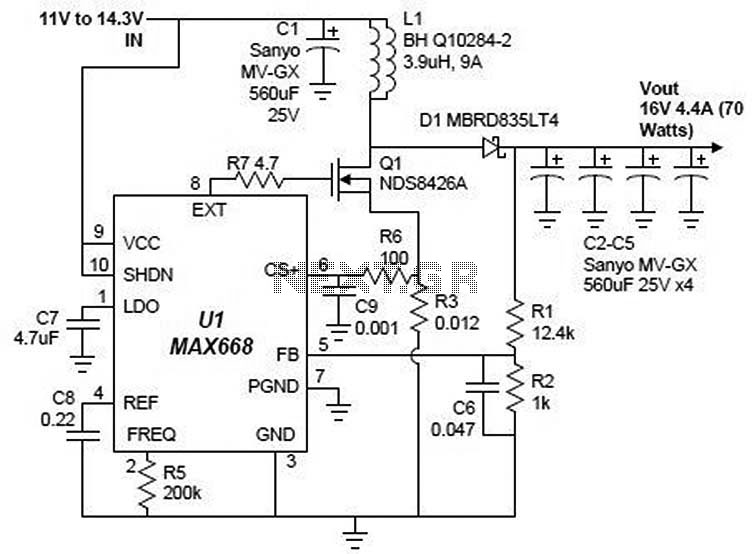
Power FET Lamp Flasher
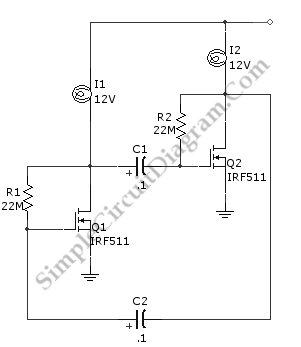
As an alternative to a bipolar transistor, a lamp flasher can be constructed using two power FETs. Similar to other flasher circuits, this circuit alternately switches the...
The proposed lamp flasher circuit utilizes two power Field-Effect Transistors (FETs) to control the alternation of a lamp's illumination. This design offers several advantages over traditional bipolar transistor circuits, including higher efficiency and faster switching times.
In this configuration, the two power FETs are arranged in a complementary manner, allowing one FET to conduct while the other is off, and vice versa. This creates a pulsing effect that can be adjusted for various flashing rates by incorporating a timing circuit, typically based on a resistor-capacitor (RC) network or a microcontroller.
The circuit begins with a control signal that triggers the first FET, allowing current to flow through the lamp, which illuminates. Once the control signal is removed, the first FET turns off, and the second FET is activated, completing the circuit and allowing the lamp to flash alternately. This switching can be controlled through various means, such as a timer IC, a 555 timer, or a microcontroller, which can provide precise timing adjustments.
The use of power FETs in this application enhances the thermal performance of the circuit, as they typically have lower on-resistance compared to bipolar transistors, resulting in reduced power loss and heat generation during operation. Additionally, the FETs can be driven directly by low-voltage logic signals, simplifying the control circuitry.
To ensure reliable operation, it is essential to include protection components such as diodes to prevent back EMF from inductive loads, which can damage the FETs. Proper heat sinking may also be required to dissipate heat generated during operation, particularly at higher current levels.
Overall, this lamp flasher circuit design with power FETs presents an efficient and reliable alternative to traditional bipolar transistor-based designs, suitable for various applications in lighting control systems.As an alternative to bipolar transistor, a lamp flasher can be built by using two power FETs. Like other flasher circuit, this circuit alternately switch the.. 🔗 External reference
The proposed lamp flasher circuit utilizes two power Field-Effect Transistors (FETs) to control the alternation of a lamp's illumination. This design offers several advantages over traditional bipolar transistor circuits, including higher efficiency and faster switching times.
In this configuration, the two power FETs are arranged in a complementary manner, allowing one FET to conduct while the other is off, and vice versa. This creates a pulsing effect that can be adjusted for various flashing rates by incorporating a timing circuit, typically based on a resistor-capacitor (RC) network or a microcontroller.
The circuit begins with a control signal that triggers the first FET, allowing current to flow through the lamp, which illuminates. Once the control signal is removed, the first FET turns off, and the second FET is activated, completing the circuit and allowing the lamp to flash alternately. This switching can be controlled through various means, such as a timer IC, a 555 timer, or a microcontroller, which can provide precise timing adjustments.
The use of power FETs in this application enhances the thermal performance of the circuit, as they typically have lower on-resistance compared to bipolar transistors, resulting in reduced power loss and heat generation during operation. Additionally, the FETs can be driven directly by low-voltage logic signals, simplifying the control circuitry.
To ensure reliable operation, it is essential to include protection components such as diodes to prevent back EMF from inductive loads, which can damage the FETs. Proper heat sinking may also be required to dissipate heat generated during operation, particularly at higher current levels.
Overall, this lamp flasher circuit design with power FETs presents an efficient and reliable alternative to traditional bipolar transistor-based designs, suitable for various applications in lighting control systems.As an alternative to bipolar transistor, a lamp flasher can be built by using two power FETs. Like other flasher circuit, this circuit alternately switch the.. 🔗 External reference