Remote Controlled Fan Regulator EEE Project Report
This report presents a comprehensive overview of a mini project titled "Remote Controlled Fan Regulator," developed in accordance with the curriculum requirements for the sixth semester of the Bachelor of Technology degree in Electrical and Electronics Engineering. The report is structured into 15 chapters and details the methodology for regulating fan speed using a remote control. The project employs a Triac to vary the firing angle, thereby adjusting the fan's operational speed. Additionally, the report includes a block diagram that outlines the different sections of the remote-controlled fan regulator, as well as a circuit diagram, working principles, and a component list. This project report serves as a valuable resource for study and reference.
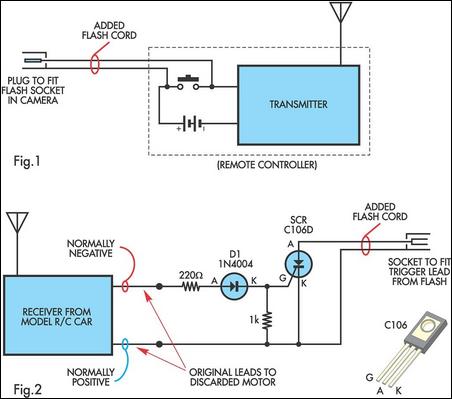
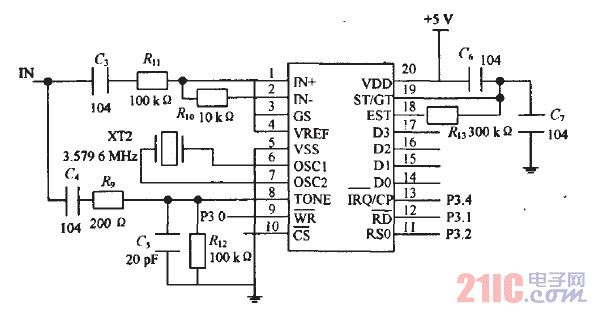
The remote-controlled fan regulator project integrates several key electronic components and principles to achieve effective fan speed control. At the heart of the system is a Triac, which acts as a semiconductor device capable of controlling power flow to the fan motor. The firing angle of the Triac is modulated through a microcontroller, which receives input signals from a remote control.
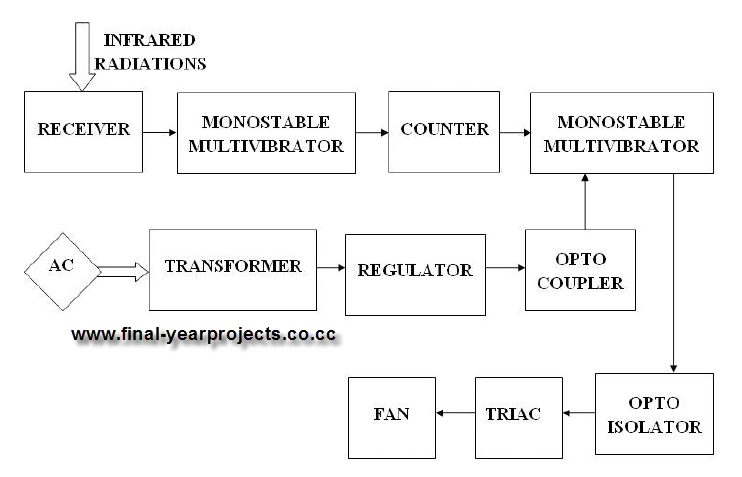
The block diagram of the system typically includes the following sections: a remote control unit, a receiver module, a microcontroller unit, a Triac driver circuit, and the fan motor. The remote control unit transmits commands that are received by the receiver module, which decodes the signals and sends the corresponding commands to the microcontroller. The microcontroller processes these commands and determines the appropriate firing angle for the Triac, effectively controlling the voltage applied to the fan motor.
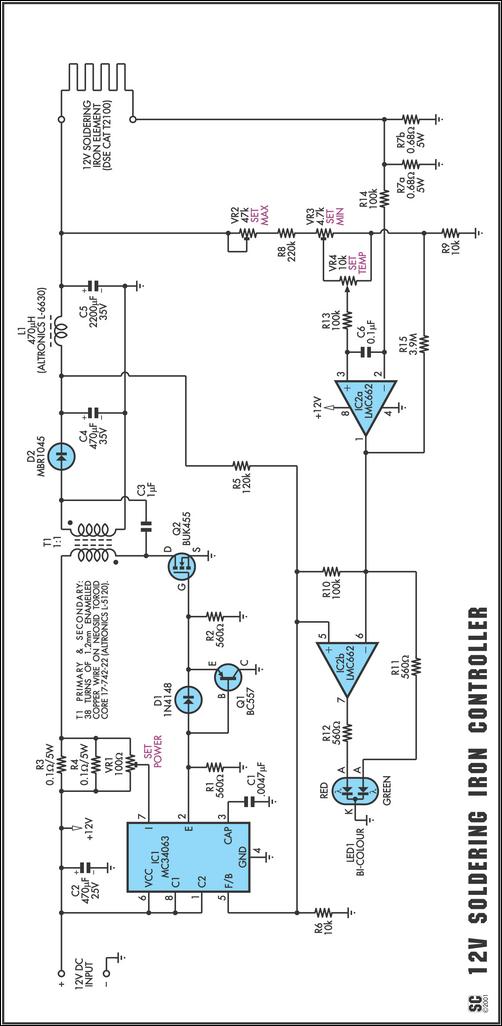
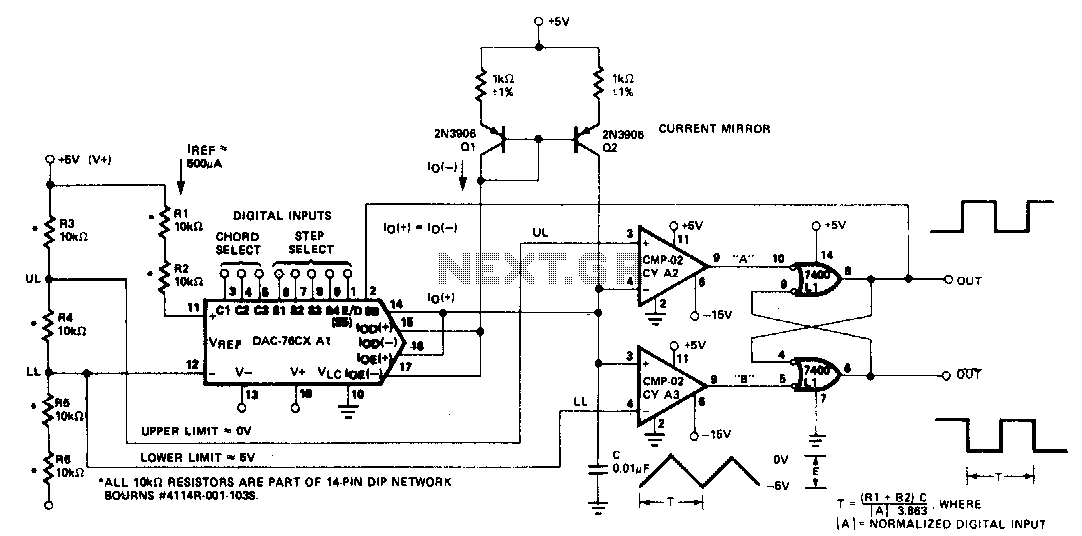
The circuit diagram outlines the connections between the components, highlighting the power supply, the Triac with its gate control, and the fan motor. Protection elements such as fuses or circuit breakers may also be included to ensure safety during operation. The working principle revolves around phase control, where the Triac is triggered at specific intervals within each AC cycle, allowing for the adjustment of power delivered to the fan.
The component list for the project typically includes a microcontroller (such as an Arduino or PIC), a Triac (like the BT136), a receiver module (such as an IR receiver), resistors, capacitors, and a fan motor. Each component plays a critical role in ensuring the system operates efficiently and safely.
This project not only demonstrates the application of electronic principles but also provides a practical solution for controlling fan speed remotely, enhancing user convenience and energy efficiency.This is a good Electrical & Electronics mini project report on "Remote Controlled Fan Regulator" and submitted in accordance with the curriculum requirements for sixth semester of the degree course in Bachelor of Technology in the branch of Electrical and Electronics Engineering. This final year EEE report is divided into 15 chapters. By doing thi s project we can regulate the speed of the fan by using a remote. Here the variation in the firing angle of Triac is used for regulating the speed. You can also Subscribe to FINAL YEAR PROJECT`S by Email for more such Projects and Seminar. The above image shows the block diagram of remote controlled fan regulator which is divided into different section. This report also contains the circuit diagram, Working principle, Component list of remote controlled fan regulator.
Use this project report for your study and reference work. 🔗 External reference
The remote-controlled fan regulator project integrates several key electronic components and principles to achieve effective fan speed control. At the heart of the system is a Triac, which acts as a semiconductor device capable of controlling power flow to the fan motor. The firing angle of the Triac is modulated through a microcontroller, which receives input signals from a remote control.
The block diagram of the system typically includes the following sections: a remote control unit, a receiver module, a microcontroller unit, a Triac driver circuit, and the fan motor. The remote control unit transmits commands that are received by the receiver module, which decodes the signals and sends the corresponding commands to the microcontroller. The microcontroller processes these commands and determines the appropriate firing angle for the Triac, effectively controlling the voltage applied to the fan motor.
The circuit diagram outlines the connections between the components, highlighting the power supply, the Triac with its gate control, and the fan motor. Protection elements such as fuses or circuit breakers may also be included to ensure safety during operation. The working principle revolves around phase control, where the Triac is triggered at specific intervals within each AC cycle, allowing for the adjustment of power delivered to the fan.
The component list for the project typically includes a microcontroller (such as an Arduino or PIC), a Triac (like the BT136), a receiver module (such as an IR receiver), resistors, capacitors, and a fan motor. Each component plays a critical role in ensuring the system operates efficiently and safely.
This project not only demonstrates the application of electronic principles but also provides a practical solution for controlling fan speed remotely, enhancing user convenience and energy efficiency.This is a good Electrical & Electronics mini project report on "Remote Controlled Fan Regulator" and submitted in accordance with the curriculum requirements for sixth semester of the degree course in Bachelor of Technology in the branch of Electrical and Electronics Engineering. This final year EEE report is divided into 15 chapters. By doing thi s project we can regulate the speed of the fan by using a remote. Here the variation in the firing angle of Triac is used for regulating the speed. You can also Subscribe to FINAL YEAR PROJECT`S by Email for more such Projects and Seminar. The above image shows the block diagram of remote controlled fan regulator which is divided into different section. This report also contains the circuit diagram, Working principle, Component list of remote controlled fan regulator.
Use this project report for your study and reference work. 🔗 External reference