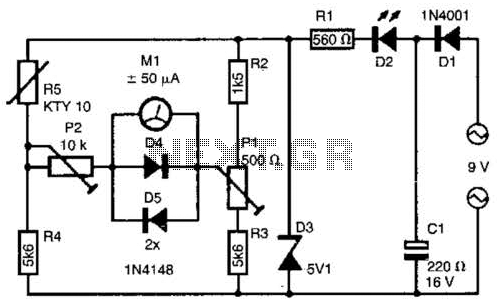
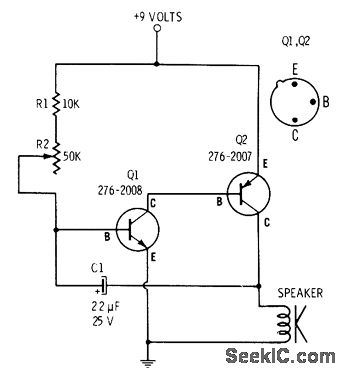
Schematic diagram for the One Transistor FM Radio with Improved Audio Gain
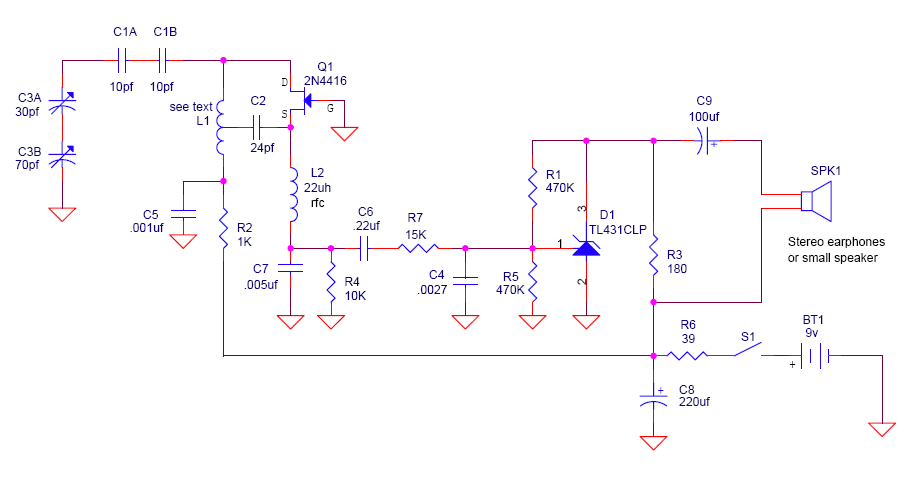
Connect the two sections of the variable capacitor (C3) in series to linearize the tuning somewhat. Use the connections on either end of C3 and do not use the middle lead. The gain is sufficient to drive an earphone. If located too far from radio stations, reception may be problematic. There is no provision for an external antenna, which would require an additional transistor. For increased audio gain or if a TL431CLP chip is unavailable, an alternative audio amplifier can be used in the circuit where pins 1 and 2 of D1 typically connect. Options include the LM386 or TDA7052 audio amplifiers. The Quasar DIY project kit #3027 includes a complete TDA7052 audio amplifier kit that functions effectively in this application.
To implement the described circuit modifications, the variable capacitor (C3) must be configured in a series arrangement to enhance tuning linearity. This configuration utilizes the outer terminals of C3, effectively bypassing the central lead to provide a more stable tuning range. The gain achieved through this setup is adequate for driving standard earphones; however, users situated at a considerable distance from broadcasting stations may experience challenges in audio clarity and volume.
The absence of an external antenna option presents limitations in reception capabilities. An external antenna would necessitate the integration of an additional transistor to amplify the incoming signal. For users seeking to improve audio performance, especially in cases where the TL431CLP chip is not accessible, alternative audio amplification solutions are recommended. The LM386 and TDA7052 amplifiers are both viable substitutes that can be integrated into the design.
In the case of the TDA7052, the Quasar DIY project kit #3027 serves as a comprehensive solution, offering all necessary components for assembly. This kit is particularly suitable for users who require a straightforward application of the TDA7052 amplifier, ensuring compatibility and ease of use within the existing circuit framework. The integration of these components will enhance audio output, making the overall system more effective for various listening environments.Connect the two sections of the variable capacitor (C3) in series to linearize the tuning somewhat. That is, use the connections on either end of C3 and don`t use the middle lead. The gain is just enough to drive an earphone. If you live too far away from radio stations, you might have trouble hearing one. There is no option here for an external a ntenna (that would require and extra transistor). If you want a little more audio gain, or you cannot locate a TL431CLP chip, you can use some other audio amplifier in the circuit where pins 1 and 2 of D1 normally connect. You can use an LM386 or a TDA7052 audio amplifier. Quasar DIY project kit #3027 is a complete TDA7052 audio amplifier kit and it works fine in this application.
🔗 External reference
To implement the described circuit modifications, the variable capacitor (C3) must be configured in a series arrangement to enhance tuning linearity. This configuration utilizes the outer terminals of C3, effectively bypassing the central lead to provide a more stable tuning range. The gain achieved through this setup is adequate for driving standard earphones; however, users situated at a considerable distance from broadcasting stations may experience challenges in audio clarity and volume.
The absence of an external antenna option presents limitations in reception capabilities. An external antenna would necessitate the integration of an additional transistor to amplify the incoming signal. For users seeking to improve audio performance, especially in cases where the TL431CLP chip is not accessible, alternative audio amplification solutions are recommended. The LM386 and TDA7052 amplifiers are both viable substitutes that can be integrated into the design.
In the case of the TDA7052, the Quasar DIY project kit #3027 serves as a comprehensive solution, offering all necessary components for assembly. This kit is particularly suitable for users who require a straightforward application of the TDA7052 amplifier, ensuring compatibility and ease of use within the existing circuit framework. The integration of these components will enhance audio output, making the overall system more effective for various listening environments.Connect the two sections of the variable capacitor (C3) in series to linearize the tuning somewhat. That is, use the connections on either end of C3 and don`t use the middle lead. The gain is just enough to drive an earphone. If you live too far away from radio stations, you might have trouble hearing one. There is no option here for an external a ntenna (that would require and extra transistor). If you want a little more audio gain, or you cannot locate a TL431CLP chip, you can use some other audio amplifier in the circuit where pins 1 and 2 of D1 normally connect. You can use an LM386 or a TDA7052 audio amplifier. Quasar DIY project kit #3027 is a complete TDA7052 audio amplifier kit and it works fine in this application.
🔗 External reference