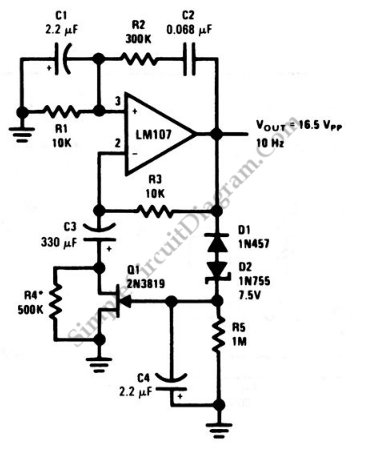
Self-powered Sine to Square wave Converters
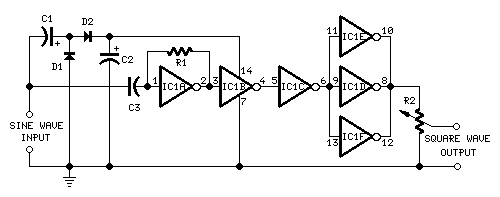
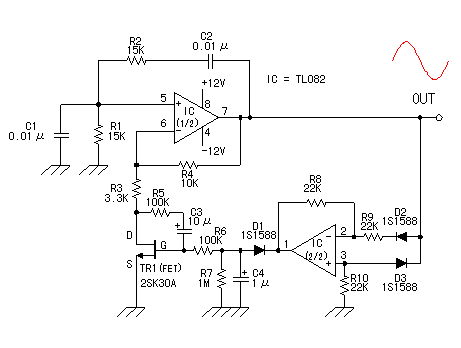
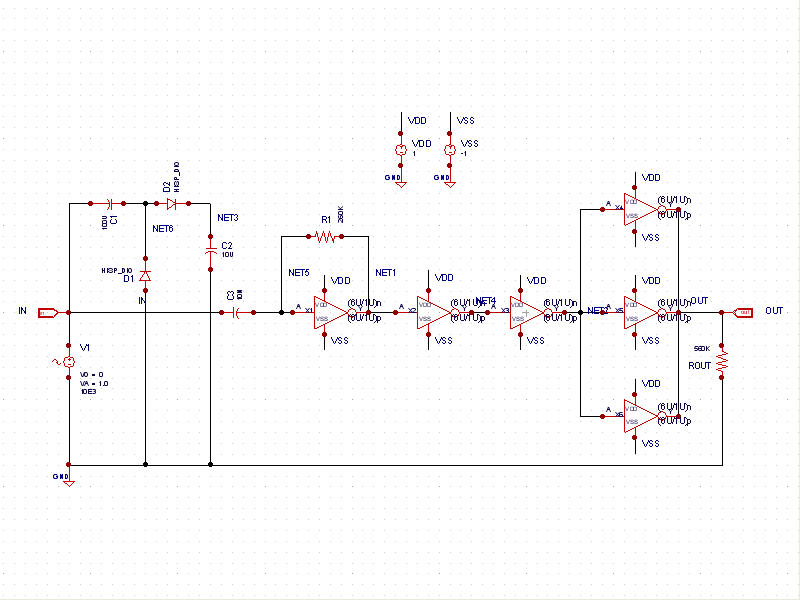
This circuit is designed to produce square waves by converting a sine wave obtained from an existing generator. A key feature is that it requires no external power source, allowing for simple connection between a sine wave generator and the device under test. The input sine wave is processed by a voltage doubler consisting of capacitors C1 and C2 and diodes D1 and D2, which powers the integrated circuit. IC1A amplifies the incoming sine wave, while additional inverters within IC1 convert the signal to a square wave, maintaining an equal mark/space ratio and providing good rise and fall times across a frequency range of 20Hz to 20kHz.
This circuit operates on the principle of signal conversion, leveraging a voltage doubler configuration to harness energy from the input sine wave. The capacitors C1 and C2, along with diodes D1 and D2, function as a rectifying and energy-storing mechanism, effectively doubling the voltage of the input signal. This increased voltage is crucial for powering the integrated circuit (IC) without the need for an external power supply, making the circuit highly efficient and portable.
The operational amplifier IC1A plays a vital role in amplifying the sine wave input, enhancing its amplitude to ensure that subsequent processing stages receive a robust signal. The inverters within the IC are configured to transform the amplified sine wave into a square wave. This transformation is characterized by maintaining a consistent mark/space ratio, which is essential for applications requiring precise timing and signal integrity.
The circuit is capable of operating effectively across a frequency range of 20Hz to 20kHz, making it suitable for various applications, including testing and signal generation in audio and communication systems. The design emphasizes fast rise and fall times, which are critical for minimizing distortion and ensuring the square wave output closely resembles an ideal square wave. This feature enhances the circuit's performance in real-world applications, where signal fidelity is paramount.
Overall, the described circuit represents a practical and efficient solution for converting sine waves to square waves, with applications spanning multiple fields in electronics and signal processing.This circuit is intended to provide good square waves converting a sine wave picked-up from an existing generator. Its major feature consists in the fact that no power-source is needed: thus it can be simply connected between a sine wave generator and the device under test.
The input sine wave feeds a voltage doubler formed by C1, C2, D1 & D2 that powers the IC. IC1A amplifies the input sine wave, other inverters included in IC1 squaring the signal and delivering an output square wave of equal mark/space ratio and good rise and fall times through the entire 20Hz-20KHz range. 🔗 External reference
This circuit operates on the principle of signal conversion, leveraging a voltage doubler configuration to harness energy from the input sine wave. The capacitors C1 and C2, along with diodes D1 and D2, function as a rectifying and energy-storing mechanism, effectively doubling the voltage of the input signal. This increased voltage is crucial for powering the integrated circuit (IC) without the need for an external power supply, making the circuit highly efficient and portable.
The operational amplifier IC1A plays a vital role in amplifying the sine wave input, enhancing its amplitude to ensure that subsequent processing stages receive a robust signal. The inverters within the IC are configured to transform the amplified sine wave into a square wave. This transformation is characterized by maintaining a consistent mark/space ratio, which is essential for applications requiring precise timing and signal integrity.
The circuit is capable of operating effectively across a frequency range of 20Hz to 20kHz, making it suitable for various applications, including testing and signal generation in audio and communication systems. The design emphasizes fast rise and fall times, which are critical for minimizing distortion and ensuring the square wave output closely resembles an ideal square wave. This feature enhances the circuit's performance in real-world applications, where signal fidelity is paramount.
Overall, the described circuit represents a practical and efficient solution for converting sine waves to square waves, with applications spanning multiple fields in electronics and signal processing.This circuit is intended to provide good square waves converting a sine wave picked-up from an existing generator. Its major feature consists in the fact that no power-source is needed: thus it can be simply connected between a sine wave generator and the device under test.
The input sine wave feeds a voltage doubler formed by C1, C2, D1 & D2 that powers the IC. IC1A amplifies the input sine wave, other inverters included in IC1 squaring the signal and delivering an output square wave of equal mark/space ratio and good rise and fall times through the entire 20Hz-20KHz range. 🔗 External reference