
Series-telephone-connection
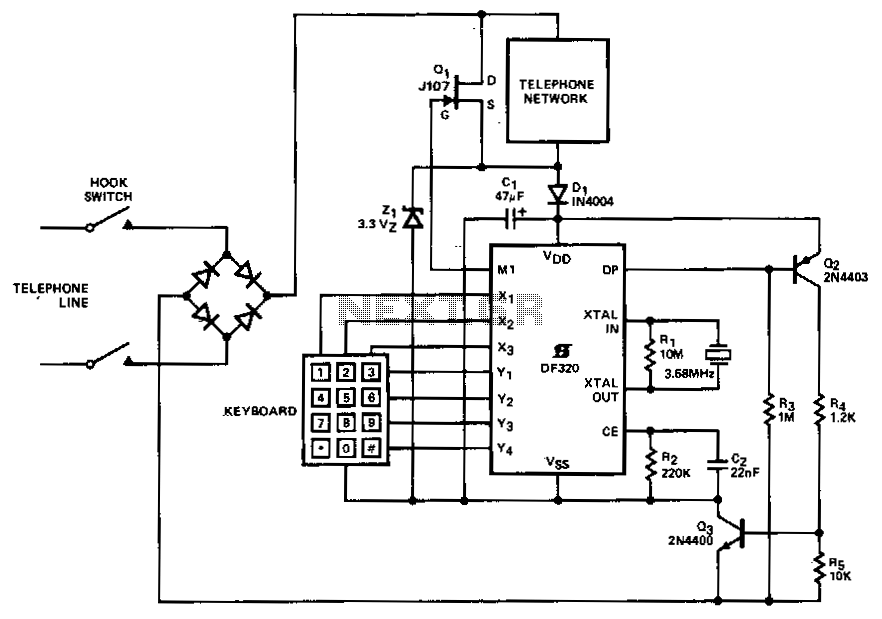
A straightforward method of connecting in series within a telephone set is suitable for PABX or short line applications. When the telephone handset is lifted, capacitor C1 is charged through diode D1 to (Vz1 - 0.7) V, initiating a DF320 power-on reset. Once the first digit is keyed in, the output of M1 transitions to logic high, which mutes the telephone network by activating the low-resistance JFET Q1, thereby maximizing the line-loop current for dialing impulses. Dialing impulses are generated through the DP switching mechanism Q2, leading to the deactivation of Q3. The rapid discharge of C1 through Z1 is prevented during a line break by the blocking diode D1. After dialing is complete, the circuit reverts to a static standby state, and Q1 is turned off. The circuit reset, triggered by a line interruption via the cradle switch, is designed for the parallel connection mode.
The described circuit functions as an efficient interface for telephone systems, particularly in PABX or short line scenarios. It effectively manages the charging of capacitor C1 upon lifting the handset, allowing for a reliable power-on reset via the DF320 component. The transition of M1 to a logic high state upon detecting the first digit signifies the initiation of the dialing process, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the telephone network during this operation.
The low-resistance JFET Q1 plays a vital role in muting the network, ensuring that the line-loop current is optimized for impulse signaling. This is essential for accurate and efficient dialing, as it allows the system to handle the necessary current levels without distortion. The use of DP switching through Q2 facilitates the generation of dialing impulses, while the deactivation of Q3 ensures that the circuit remains stable during this process.
The protective function of diode D1 is significant, as it prevents the rapid discharge of capacitor C1 during any line interruptions. This feature enhances the reliability of the circuit, ensuring that it can withstand transient conditions without losing its operational state. Following the completion of dialing, the circuit's return to a static standby condition is a critical aspect of its design, allowing for energy efficiency and readiness for subsequent calls.
The reset mechanism, activated by the cradle switch during a line interruption, is tailored for parallel connection modes. This design consideration ensures that the circuit can adapt to various operational requirements, making it versatile for different telephone applications. Overall, this circuit design exemplifies a well-thought-out approach to managing telephone signaling and network integrity, ensuring reliable performance in PABX and short line environments.Here is a simple method of series connection into the telephone set suitable for PABX or short line applications. When the telephone handset is lifted, Cl is charged via D1 to (Vz1 -0.7) V and DF320 power on reset occurs.
When the first keyed digit is recognized, Ml goes to logic 1, muting the telephone network by switching on the low on resistance JFET Ql, and maximizing the line-loop current for impulsing. Impulsing occurs through DP switching Q2, and hence Q3 turns off. Rapid discharge of Cl through Zl is prevented during line break by blocking diode Dl. When dialing is complete, the circuit returns to the static standby condition, and Ql is switched off. The circuit reset, during a line interruption by the cradle switch, is for the parallel connection mode.
🔗 External reference
The described circuit functions as an efficient interface for telephone systems, particularly in PABX or short line scenarios. It effectively manages the charging of capacitor C1 upon lifting the handset, allowing for a reliable power-on reset via the DF320 component. The transition of M1 to a logic high state upon detecting the first digit signifies the initiation of the dialing process, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the telephone network during this operation.
The low-resistance JFET Q1 plays a vital role in muting the network, ensuring that the line-loop current is optimized for impulse signaling. This is essential for accurate and efficient dialing, as it allows the system to handle the necessary current levels without distortion. The use of DP switching through Q2 facilitates the generation of dialing impulses, while the deactivation of Q3 ensures that the circuit remains stable during this process.
The protective function of diode D1 is significant, as it prevents the rapid discharge of capacitor C1 during any line interruptions. This feature enhances the reliability of the circuit, ensuring that it can withstand transient conditions without losing its operational state. Following the completion of dialing, the circuit's return to a static standby condition is a critical aspect of its design, allowing for energy efficiency and readiness for subsequent calls.
The reset mechanism, activated by the cradle switch during a line interruption, is tailored for parallel connection modes. This design consideration ensures that the circuit can adapt to various operational requirements, making it versatile for different telephone applications. Overall, this circuit design exemplifies a well-thought-out approach to managing telephone signaling and network integrity, ensuring reliable performance in PABX and short line environments.Here is a simple method of series connection into the telephone set suitable for PABX or short line applications. When the telephone handset is lifted, Cl is charged via D1 to (Vz1 -0.7) V and DF320 power on reset occurs.
When the first keyed digit is recognized, Ml goes to logic 1, muting the telephone network by switching on the low on resistance JFET Ql, and maximizing the line-loop current for impulsing. Impulsing occurs through DP switching Q2, and hence Q3 turns off. Rapid discharge of Cl through Zl is prevented during line break by blocking diode Dl. When dialing is complete, the circuit returns to the static standby condition, and Ql is switched off. The circuit reset, during a line interruption by the cradle switch, is for the parallel connection mode.
🔗 External reference