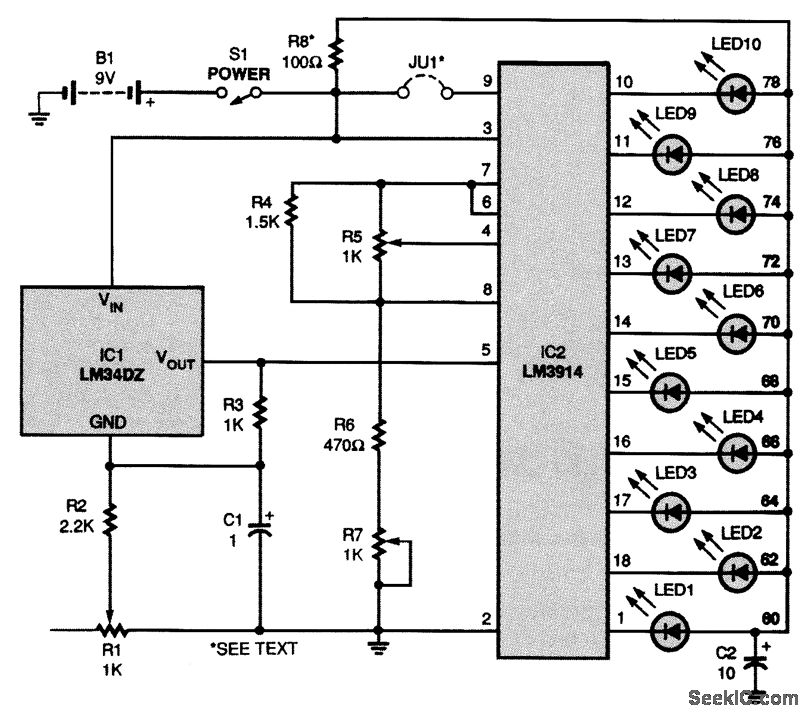
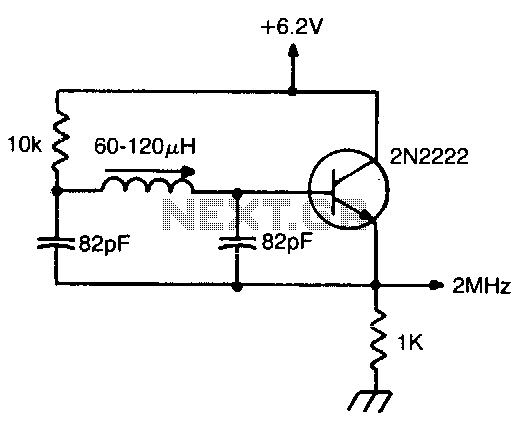
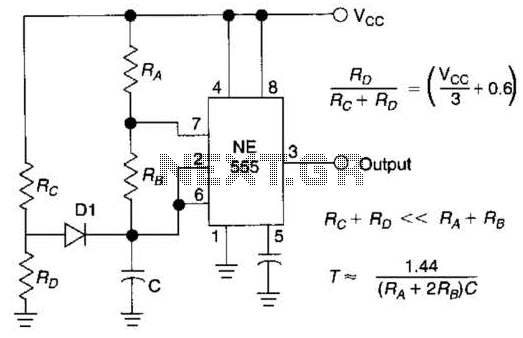
Simple UHF oscillator
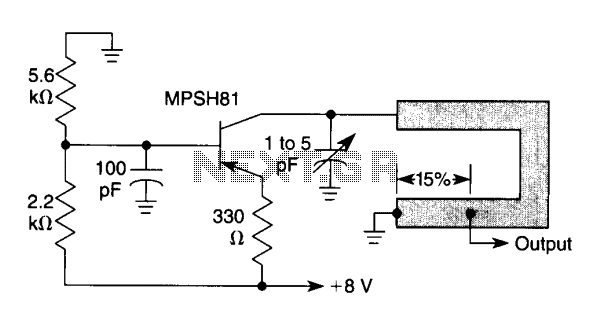
This oscillator is typical for operation between 350 to 500 MHz. The microstrip inductor is implemented as a printed circuit board (PCB) trace. The output power ranges from 55 to 100 mW into a 50-ohm load, with frequency stability typically at 0.1% over a temperature range of -20°C to 50°C. The tap is generally positioned 15% from the lower end of the inductor.
The oscillator described operates within the frequency range of 350 to 500 MHz, making it suitable for various RF applications. The use of a microstrip inductor as a PCB trace allows for compact integration within the circuit layout, which is essential for minimizing parasitic capacitance and maintaining signal integrity at high frequencies. The output power specification of 55 to 100 mW indicates that this oscillator can drive a variety of RF loads effectively, ensuring compatibility with standard 50-ohm systems commonly used in RF communications.
Frequency stability is a critical parameter for oscillators, especially in communication systems where signal integrity must be maintained. The stated stability of 0.1% over a temperature range of -20°C to 50°C suggests that the oscillator is designed to perform reliably in varying environmental conditions, which is important for outdoor or industrial applications.
The tap point, typically located 15% from the bottom end of the inductor, is crucial for achieving the desired feedback and tuning characteristics of the oscillator. This tap allows for the extraction of a portion of the signal, which is fed back into the circuit to sustain oscillation. The placement of the tap affects the overall performance, including the amplitude and stability of the output signal.
In summary, the oscillator's design leverages a microstrip inductor and is optimized for RF applications, providing stable frequency output with suitable power levels for integration into various systems. Proper attention to the tap placement and PCB layout will enhance the performance and reliability of the oscillator in practical applications.This oscillator is typical for 350 to 500 operation. The microstrip inductor is a PC board trace. The output power is 55 to 100 mW into 50, with the frequency stability typically 0.1% over to 50°C. The tap is typically 15% from the bottom end.
The oscillator described operates within the frequency range of 350 to 500 MHz, making it suitable for various RF applications. The use of a microstrip inductor as a PCB trace allows for compact integration within the circuit layout, which is essential for minimizing parasitic capacitance and maintaining signal integrity at high frequencies. The output power specification of 55 to 100 mW indicates that this oscillator can drive a variety of RF loads effectively, ensuring compatibility with standard 50-ohm systems commonly used in RF communications.
Frequency stability is a critical parameter for oscillators, especially in communication systems where signal integrity must be maintained. The stated stability of 0.1% over a temperature range of -20°C to 50°C suggests that the oscillator is designed to perform reliably in varying environmental conditions, which is important for outdoor or industrial applications.
The tap point, typically located 15% from the bottom end of the inductor, is crucial for achieving the desired feedback and tuning characteristics of the oscillator. This tap allows for the extraction of a portion of the signal, which is fed back into the circuit to sustain oscillation. The placement of the tap affects the overall performance, including the amplitude and stability of the output signal.
In summary, the oscillator's design leverages a microstrip inductor and is optimized for RF applications, providing stable frequency output with suitable power levels for integration into various systems. Proper attention to the tap placement and PCB layout will enhance the performance and reliability of the oscillator in practical applications.This oscillator is typical for 350 to 500 operation. The microstrip inductor is a PC board trace. The output power is 55 to 100 mW into 50, with the frequency stability typically 0.1% over to 50°C. The tap is typically 15% from the bottom end.