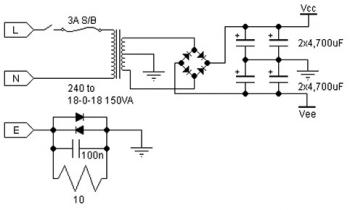
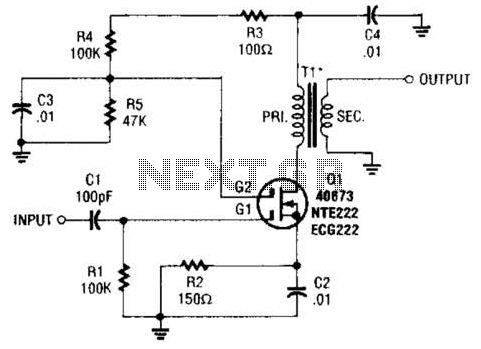
Simple Video Amplifier
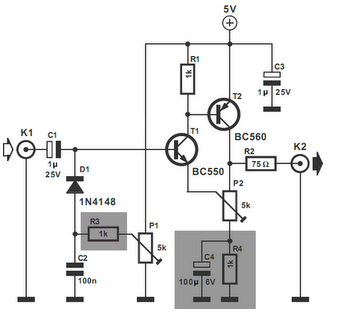
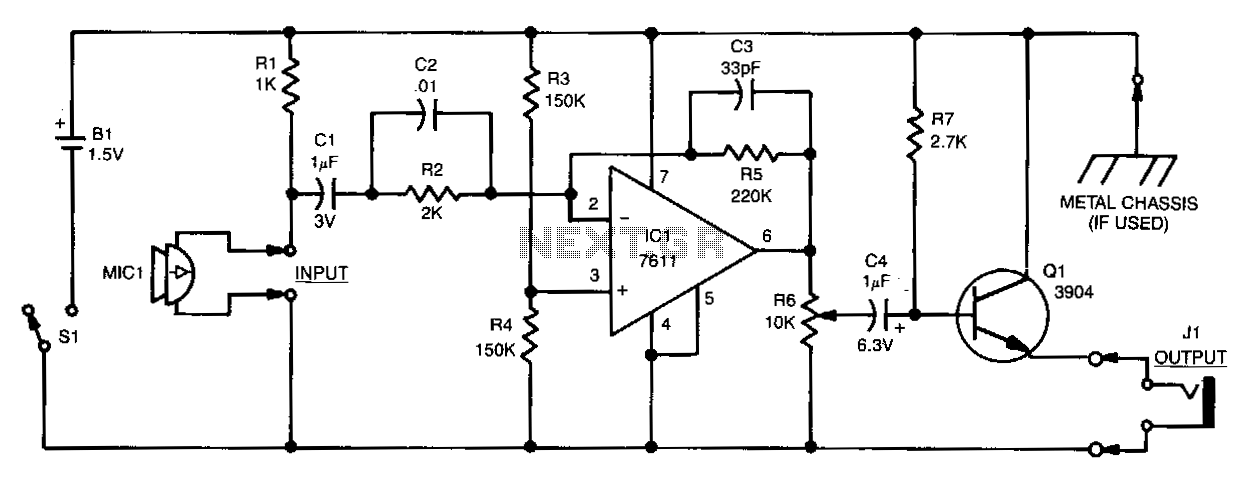
The video amplifier in the diagram represents a well-established design that is both simple and highly functional. However, it is important to note that the transistors can be easily damaged if the potentiometers (black level and signal amplitude) are set to their extreme positions. This issue can be mitigated by incorporating two resistors. In the original design, if R3 and R4 were directly connected and P1 was fully clockwise while P2 was fully counterclockwise, a large base current would flow through T1, potentially causing failure of this transistor. Additionally, with the wiper of P2 at ground level, the base current of T2 could reach dangerously high levels. The inclusion of resistors R3 and R4 provides adequate protection against these scenarios, as they limit the base currents to a maximum of 5 mA. The shunt capacitor C4 serves to prevent R4 from negatively impacting the amplification.
The video amplifier circuit is designed to enhance video signals while ensuring the integrity of the transistors involved. The circuit features two primary potentiometers, P1 and P2, which adjust the black level and signal amplitude, respectively. The potential risk arises when these potentiometers are set to their extremes, which can lead to excessive base currents flowing into the transistors T1 and T2.
To prevent transistor damage, resistors R3 and R4 are strategically placed in the circuit. These resistors act as current limiters, effectively capping the base currents to a safe level of no more than 5 mA. This precautionary measure is critical in maintaining the reliability and longevity of the transistors under varying operational conditions.
Additionally, the shunt capacitor C4 is included in the design to ensure that the resistor R4 does not adversely affect the overall amplification of the video signal. By providing a low-impedance path to ground for high-frequency signals, C4 helps maintain the desired frequency response and stability of the amplifier circuit.
Overall, the careful selection of components and their configuration in this video amplifier circuit not only enhances performance but also safeguards against potential damage, making it a robust solution for video amplification applications.The video amplifier in the diagram is a well-known design. Simple, yet very useful, were it not for the ease with which the transistors can be damaged if the potentiometers (black level and signal amplitude) are in their extreme position. Fortunately, this can be obviated by the addition of two resistors. If in the diagram R3 and R4 were direct co nnections, as in the original design, and P1 were fully clockwise and P2 fully anticlockwise, such a large base current would flow through T1 that this transistor would give up the ghost. Moreover, with the wiper of P2 at earth level, the base current of T2 would be dangerously high. Resistors R3 and R4 are sufficient protection against such mishaps, since they limit the base currents to a level of not more than 5 mA.
Shunt capacitor C4 prevents R4 having an adverse effect on the amplification. 🔗 External reference
The video amplifier circuit is designed to enhance video signals while ensuring the integrity of the transistors involved. The circuit features two primary potentiometers, P1 and P2, which adjust the black level and signal amplitude, respectively. The potential risk arises when these potentiometers are set to their extremes, which can lead to excessive base currents flowing into the transistors T1 and T2.
To prevent transistor damage, resistors R3 and R4 are strategically placed in the circuit. These resistors act as current limiters, effectively capping the base currents to a safe level of no more than 5 mA. This precautionary measure is critical in maintaining the reliability and longevity of the transistors under varying operational conditions.
Additionally, the shunt capacitor C4 is included in the design to ensure that the resistor R4 does not adversely affect the overall amplification of the video signal. By providing a low-impedance path to ground for high-frequency signals, C4 helps maintain the desired frequency response and stability of the amplifier circuit.
Overall, the careful selection of components and their configuration in this video amplifier circuit not only enhances performance but also safeguards against potential damage, making it a robust solution for video amplification applications.The video amplifier in the diagram is a well-known design. Simple, yet very useful, were it not for the ease with which the transistors can be damaged if the potentiometers (black level and signal amplitude) are in their extreme position. Fortunately, this can be obviated by the addition of two resistors. If in the diagram R3 and R4 were direct co nnections, as in the original design, and P1 were fully clockwise and P2 fully anticlockwise, such a large base current would flow through T1 that this transistor would give up the ghost. Moreover, with the wiper of P2 at earth level, the base current of T2 would be dangerously high. Resistors R3 and R4 are sufficient protection against such mishaps, since they limit the base currents to a level of not more than 5 mA.
Shunt capacitor C4 prevents R4 having an adverse effect on the amplification. 🔗 External reference