Simple Voltmeter
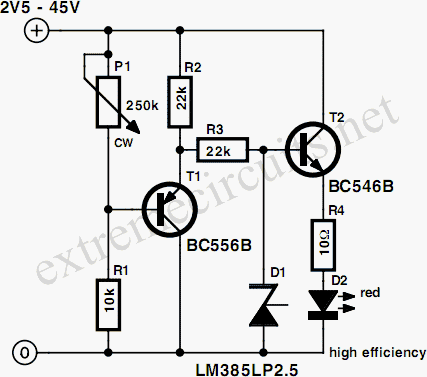
This circuit provides a straightforward method for measuring the voltage of a low-impedance voltage source. It operates as follows: P1, a 1-W potentiometer, acts as a voltage divider in conjunction with resistor R1. The voltage at their junction is buffered by transistor T1 and subsequently sent to reference diode D1 through resistor R3. Diode D1 restricts the voltage following the resistor to 2.5 V. Additionally, an indicator stage composed of transistor T2, resistor R4, and LED D2 is connected in parallel with D1. The LED will not be fully illuminated as long as the voltage is not limited by D1. This constitutes the fundamental operating principle of the measurement circuit.
The circuit is designed to measure low-impedance voltage sources effectively, utilizing a combination of passive and active components to achieve accurate readings. The potentiometer P1 allows for adjustable scaling of the input voltage, while resistor R1 is selected based on the expected voltage range to ensure that the voltage divider provides a suitable output for further processing. The buffering stage using transistor T1 is critical; it isolates the voltage divider from the subsequent circuit elements, preventing loading effects that could distort the measurement.
Reference diode D1 serves a dual purpose: it not only clamps the output voltage to a maximum of 2.5 V, protecting downstream components from overvoltage conditions, but it also provides a stable reference point for the circuit's operation. Resistor R3 is strategically placed to limit the current flowing into D1, ensuring that it operates within its specified limits.
The indicator stage, which includes transistor T2 and LED D2, functions as a visual feedback mechanism. When the input voltage exceeds the clamping threshold set by D1, the LED will gradually illuminate, providing a clear indication of the voltage level. Resistor R4 is used to control the current through the LED, ensuring it operates efficiently without exceeding its ratings.
Overall, this circuit provides a reliable and user-friendly solution for voltage measurement in low-impedance applications, combining precision and visual feedback in a compact design. The selection of components and their arrangement is crucial for achieving the desired performance, making this circuit suitable for various electronic measurement tasks.This circuit provides a simple means to determine the voltage of a low-impedance voltage source. It works as follows. P1, which is a 1-W potentiometer, forms a voltage divider in combination with R1. The voltage at their junction is buffered by T1, and then passed to reference diode D1 via R3. D1 limits the voltage following the resistor to 2. 5 V. An indicator stage consisting of T2, R4 and LED D2 is connected in parallel with D1. As long as the voltage is not limited by D1, the LED will not be fully illuminated. This is the basic operating principle of this measurement circuit. 🔗 External reference
The circuit is designed to measure low-impedance voltage sources effectively, utilizing a combination of passive and active components to achieve accurate readings. The potentiometer P1 allows for adjustable scaling of the input voltage, while resistor R1 is selected based on the expected voltage range to ensure that the voltage divider provides a suitable output for further processing. The buffering stage using transistor T1 is critical; it isolates the voltage divider from the subsequent circuit elements, preventing loading effects that could distort the measurement.
Reference diode D1 serves a dual purpose: it not only clamps the output voltage to a maximum of 2.5 V, protecting downstream components from overvoltage conditions, but it also provides a stable reference point for the circuit's operation. Resistor R3 is strategically placed to limit the current flowing into D1, ensuring that it operates within its specified limits.
The indicator stage, which includes transistor T2 and LED D2, functions as a visual feedback mechanism. When the input voltage exceeds the clamping threshold set by D1, the LED will gradually illuminate, providing a clear indication of the voltage level. Resistor R4 is used to control the current through the LED, ensuring it operates efficiently without exceeding its ratings.
Overall, this circuit provides a reliable and user-friendly solution for voltage measurement in low-impedance applications, combining precision and visual feedback in a compact design. The selection of components and their arrangement is crucial for achieving the desired performance, making this circuit suitable for various electronic measurement tasks.This circuit provides a simple means to determine the voltage of a low-impedance voltage source. It works as follows. P1, which is a 1-W potentiometer, forms a voltage divider in combination with R1. The voltage at their junction is buffered by T1, and then passed to reference diode D1 via R3. D1 limits the voltage following the resistor to 2. 5 V. An indicator stage consisting of T2, R4 and LED D2 is connected in parallel with D1. As long as the voltage is not limited by D1, the LED will not be fully illuminated. This is the basic operating principle of this measurement circuit. 🔗 External reference