Small FM Radio Circuit
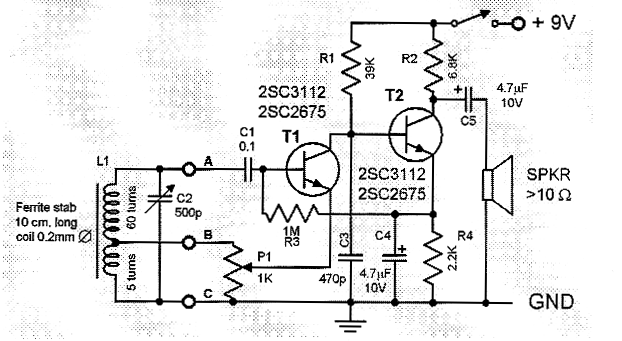
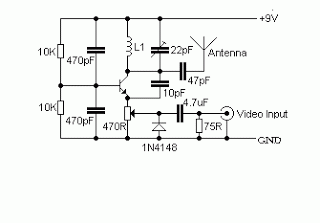
This is a compact and straightforward FM radio receiver capable of tuning into local FM stations. Its minimalistic design renders it suitable for various applications.
The FM radio receiver circuit typically consists of several key components that work together to demodulate the frequency-modulated signals transmitted by local radio stations. The main components of this circuit include an antenna, a radio frequency (RF) amplifier, a mixer, a local oscillator, an intermediate frequency (IF) amplifier, a demodulator, and an audio amplifier.
The antenna captures the radio signals, which are then amplified by the RF amplifier to improve the signal strength. The amplified signal is fed into the mixer, where it is combined with a signal from the local oscillator. This mixing process produces an intermediate frequency that is easier to process than the original RF signal.
The IF amplifier further boosts the intermediate frequency signal, which is then passed to the demodulator. The demodulator extracts the audio information from the modulated carrier wave, converting it into an audio signal that can be amplified by the audio amplifier. Finally, the audio output can be connected to a speaker or headphones for listening.
The simplicity of this FM radio receiver design makes it accessible for hobbyists and beginners in electronics, while still providing reliable performance for receiving FM broadcasts. The compact size allows for easy integration into various devices or projects, making it a versatile choice for anyone interested in building their own radio receiver.Perhaps this is one of the simplest and smallest FM radio receiver that can receive the FM stations available locally. Its simple design makes it ideal for.. 🔗 External reference
The FM radio receiver circuit typically consists of several key components that work together to demodulate the frequency-modulated signals transmitted by local radio stations. The main components of this circuit include an antenna, a radio frequency (RF) amplifier, a mixer, a local oscillator, an intermediate frequency (IF) amplifier, a demodulator, and an audio amplifier.
The antenna captures the radio signals, which are then amplified by the RF amplifier to improve the signal strength. The amplified signal is fed into the mixer, where it is combined with a signal from the local oscillator. This mixing process produces an intermediate frequency that is easier to process than the original RF signal.
The IF amplifier further boosts the intermediate frequency signal, which is then passed to the demodulator. The demodulator extracts the audio information from the modulated carrier wave, converting it into an audio signal that can be amplified by the audio amplifier. Finally, the audio output can be connected to a speaker or headphones for listening.
The simplicity of this FM radio receiver design makes it accessible for hobbyists and beginners in electronics, while still providing reliable performance for receiving FM broadcasts. The compact size allows for easy integration into various devices or projects, making it a versatile choice for anyone interested in building their own radio receiver.Perhaps this is one of the simplest and smallest FM radio receiver that can receive the FM stations available locally. Its simple design makes it ideal for.. 🔗 External reference