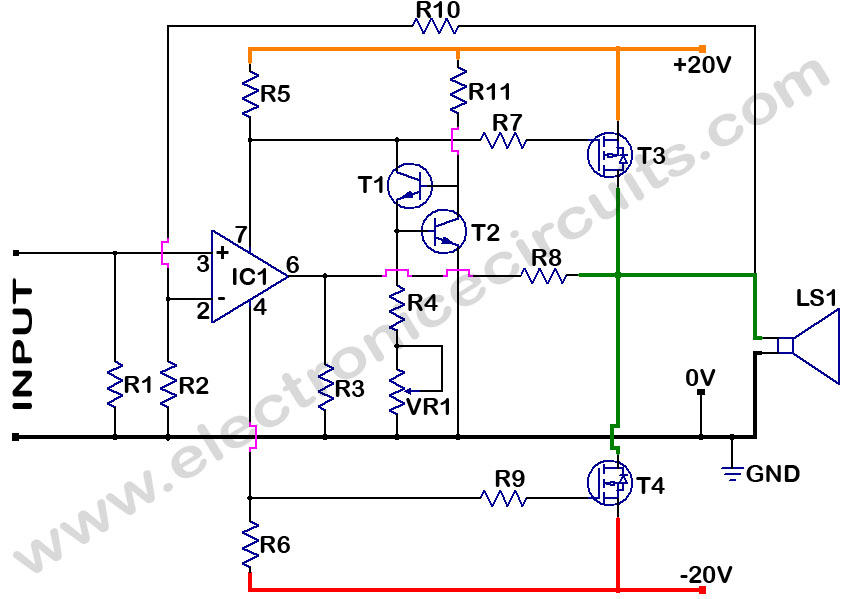
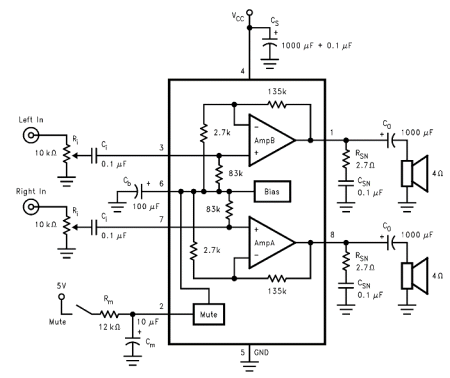
Switch For Switch-Free Power Supplies

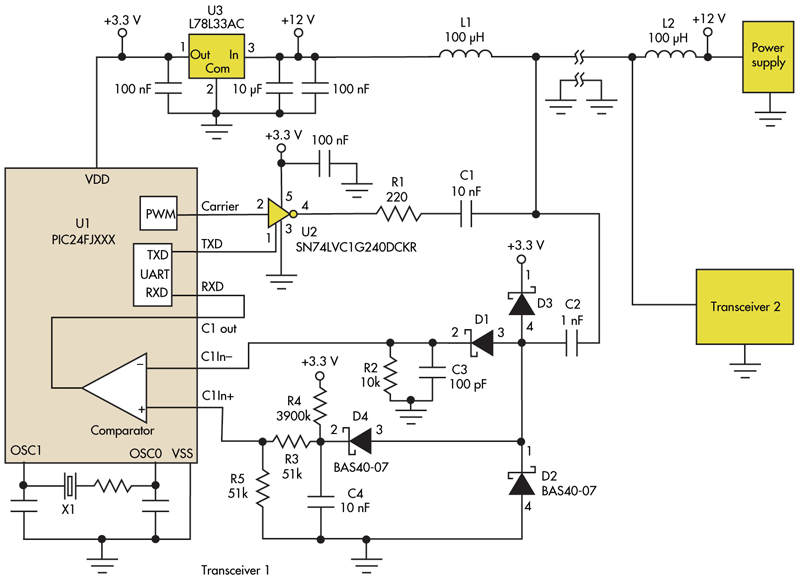
Portable radios, CD players, and cassette recorders that can also be operated from mains power often do not have a mains power switch, but instead are switched on and off using a different mechanism.
Portable audio devices such as radios, CD players, and cassette recorders designed for dual power operation—both battery and mains—often omit a dedicated mains power switch. This design choice is primarily due to the convenience factor, allowing users to seamlessly transition between power sources without the need for manual switching. Instead, these devices typically incorporate a power management system that automatically detects the power source.
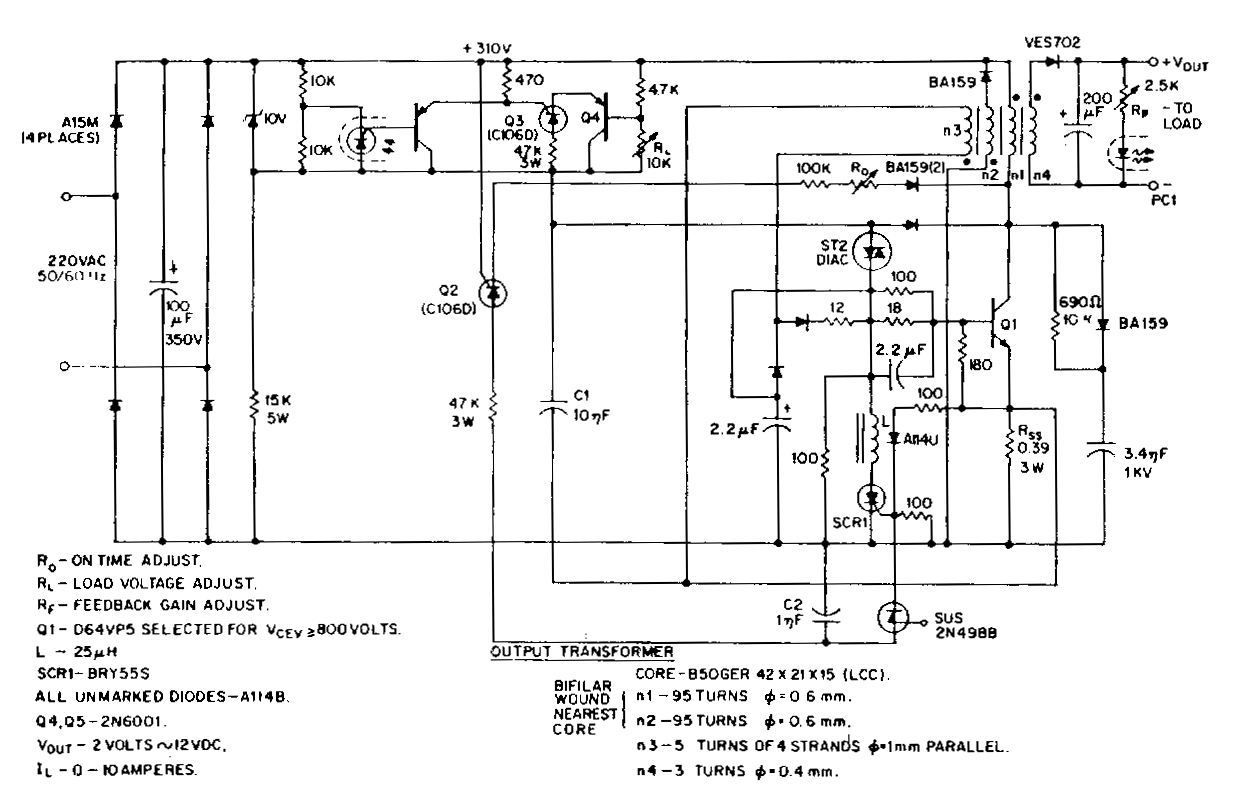
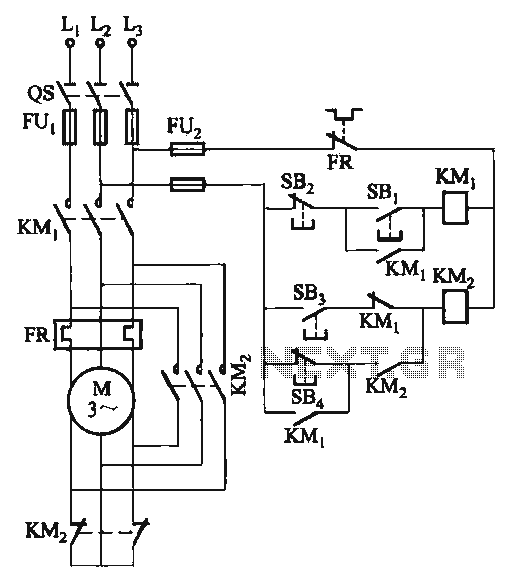
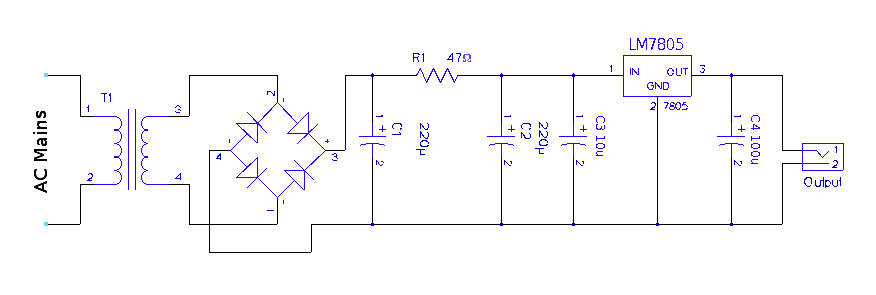
In these devices, the power supply circuit includes a rectifier and a voltage regulator that convert the mains AC voltage to the appropriate DC voltage required by the internal circuitry. When the device is connected to mains power, the power management circuitry automatically engages, providing power to the device and charging any internal batteries if applicable. Conversely, when the mains power is disconnected, the device switches to battery operation, ensuring uninterrupted function.
The absence of a traditional mains power switch can lead to a more compact design, reducing the overall size and complexity of the device. However, it is essential to implement adequate safety measures to prevent electrical hazards, such as incorporating fuses and surge protection elements. Additionally, the design must ensure that the transition between power sources is smooth, preventing any audio disruption or damage to the internal components.
Overall, the integration of a power management system in portable audio devices enhances user convenience while maintaining functionality and safety.Portable radios, CD-players and cassette recorders that can also be operated from mains power often do not have a mains power switch, but instead are swit.. 🔗 External reference
Portable audio devices such as radios, CD players, and cassette recorders designed for dual power operation—both battery and mains—often omit a dedicated mains power switch. This design choice is primarily due to the convenience factor, allowing users to seamlessly transition between power sources without the need for manual switching. Instead, these devices typically incorporate a power management system that automatically detects the power source.
In these devices, the power supply circuit includes a rectifier and a voltage regulator that convert the mains AC voltage to the appropriate DC voltage required by the internal circuitry. When the device is connected to mains power, the power management circuitry automatically engages, providing power to the device and charging any internal batteries if applicable. Conversely, when the mains power is disconnected, the device switches to battery operation, ensuring uninterrupted function.
The absence of a traditional mains power switch can lead to a more compact design, reducing the overall size and complexity of the device. However, it is essential to implement adequate safety measures to prevent electrical hazards, such as incorporating fuses and surge protection elements. Additionally, the design must ensure that the transition between power sources is smooth, preventing any audio disruption or damage to the internal components.
Overall, the integration of a power management system in portable audio devices enhances user convenience while maintaining functionality and safety.Portable radios, CD-players and cassette recorders that can also be operated from mains power often do not have a mains power switch, but instead are swit.. 🔗 External reference